
STS-66 was a Space Shuttle program mission that was flown by the Space Shuttle Atlantis. STS-66 launched on 3 November 1994 at 11:59:43.060 am EDT from Launch Pad 39-B at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. Atlantis landed at Edwards Air Force Base on 14 November 1994 at 10:33:45 am EST.
SCISAT-1 is a Canadian satellite designed to make observations of the Earth's atmosphere. Its main instruments are an optical Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, the ACE-FTS Instrument, and an ultraviolet spectrophotometer, MAESTRO. These devices record spectra of the Sun, as sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere, making analyses of the chemical elements of the atmosphere possible.

The Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment (SORCE) was a NASA-sponsored satellite mission that measured incoming X-ray, ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared, and total solar radiation. These measurements specifically addressed long-term climate change, natural variability, atmospheric ozone, and UV-B radiation, enhancing climate prediction. These measurements are critical to studies of the Sun, its effect on the Earth's system, and its influence on humankind. SORCE was launched on 25 January 2003 on a Pegasus XL launch vehicle to provide NASA's Earth Science Enterprise (ESE) with precise measurements of solar radiation.

NOAA-19, known as NOAA-N' before launch, is the last of the American National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) series of weather satellites. NOAA-19 was launched on 6 February 2009. NOAA-19 is in an afternoon Sun-synchronous orbit and is intended to replace NOAA-18 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.

Over the last two centuries many environmental chemical observations have been made from a variety of ground-based, airborne, and orbital platforms and deposited in databases. Many of these databases are publicly available. All of the instruments mentioned in this article give online public access to their data. These observations are critical in developing our understanding of the Earth's atmosphere and issues such as climate change, ozone depletion and air quality. Some of the external links provide repositories of many of these datasets in one place. For example, the Cambridge Atmospheric Chemical Database, is a large database in a uniform ASCII format. Each observation is augmented with the meteorological conditions such as the temperature, potential temperature, geopotential height, and equivalent PV latitude.

NOAA-17, also known as NOAA-M before launch, was an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-17 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-L series and a new launch vehicle.

NOAA-16, also known as NOAA-L before launch, was an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-16 continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft that began with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983; but it had additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-K series and a new launch vehicle. It was launched on 21 September 2000 and, following an unknown anomaly, it was decommissioned on 9 June 2014. In November of 2015 it broke up in orbit, creating more than 200 pieces of debris.

NOAA-18, also known as NOAA-N before launch, is an operational, polar orbiting, weather satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite Service (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-18 also continued the series of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983 but with additional new and improved instrumentation over the NOAA A-M series and a new launch vehicle. NOAA-18 is in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and replaced NOAA-17 as the prime afternoon spacecraft.

The Solar Mesosphere Explorer was a NASA spacecraft to investigate the processes that create and destroy ozone in Earth's upper of the atmosphere of Earth. The mesosphere is a layer of the atmosphere extending from the top of the stratosphere to an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi). The spacecraft carried five instruments to measure ozone, water vapor, and incoming solar radiation.
NOAA-13, also known as NOAA-I before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the operational, polar orbiting, meteorological satellite series operated by the National Environmental Satellite System (NESS) of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). NOAA-I continued the series (fifth) of Advanced TIROS-N (ATN) spacecraft begun with the launch of NOAA-8 (NOAA-E) in 1983. NOAA-I was in an afternoon equator-crossing orbit and was intended to replace the NOAA-11 (NOAA-H) as the prime afternoon (14:00) spacecraft.
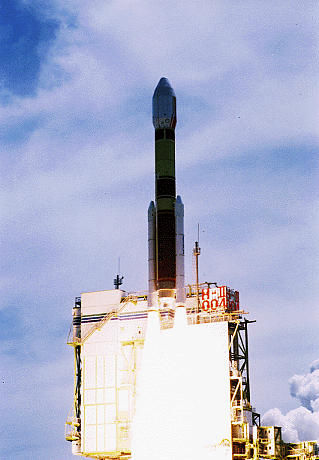
ADEOS I was an Earth observation satellite launched by NASDA in 1996. The mission's Japanese name, Midori means "green". The mission ended in July 1997 after the satellite sustained structural damage to the solar panel. Its successor, ADEOS II, was launched in 2002. Like the first mission, it ended after less than a year, also following solar panel malfunctions.

The Joint Polar Satellite System (JPSS) is the latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites. JPSS will provide the global environmental data used in numerical weather prediction models for forecasts, and scientific data used for climate monitoring. JPSS will aid in fulfilling the mission of the U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), an agency of the Department of Commerce. Data and imagery obtained from the JPSS will increase timeliness and accuracy of public warnings and forecasts of climate and weather events, thus reducing the potential loss of human life and property and advancing the national economy. The JPSS is developed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), who is responsible for operation of JPSS. Three to five satellites are planned for the JPSS constellation of satellites. JPSS satellites will be flown, and the scientific data from JPSS will be processed, by the JPSS – Common Ground System (JPSS-CGS).

Nimbus 7 was a meteorological satellite. It was the seventh and last in a series of the Nimbus program.

NOAA-21, designated JPSS-2 prior to launch, is the second of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)'s latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-21 was launched on 10 November 2022 and join NOAA-20 and Suomi NPP in the same orbit. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it will cross the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day.

NOAA-20, designated JPSS-1 prior to launch, is the first of the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's latest generation of U.S. polar-orbiting, non-geosynchronous, environmental satellites called the Joint Polar Satellite System. NOAA-20 was launched on 18 November 2017 and joined the Suomi National Polar-orbiting Partnership satellite in the same orbit. NOAA-20 operates about 50 minutes ahead of Suomi NPP, allowing important overlap in observational coverage. Circling the Earth from pole-to-pole, it crosses the equator about 14 times daily, providing full global coverage twice a day. This gives meteorologists information on "atmospheric temperature and moisture, clouds, sea-surface temperature, ocean color, sea ice cover, volcanic ash, and fire detection" so as to enhance weather forecasting including hurricane tracking, post-hurricane recovery by detailing storm damage and mapping of power outages.

Nimbus 4 was a meteorological satellite. It was the fourth in a series of the Nimbus program.
Explorer 55, also called as AE-E, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to series Atmosphere Explorer, being launched on 20 November 1975 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) board a Thor-Delta 2910 launch vehicle.

NOAA-9, known as NOAA-F before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the second of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-10, known as NOAA-G before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Environmental Satellite Data and Information Service (NESDIS). It was the third of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.
NOAA-11, known as NOAA-H before launch, was an American weather satellite operated by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) for use in the National Operational Environmental Satellite System (NOESS) and for support of the Global Atmospheric Research Program (GARP) during 1978–1984. It was the fourth of the Advanced TIROS-N series of satellites. The satellite design provided an economical and stable Sun-synchronous platform for advanced operational instruments to measure the atmosphere of Earth, its surface and cloud cover, and the near-space environment.













