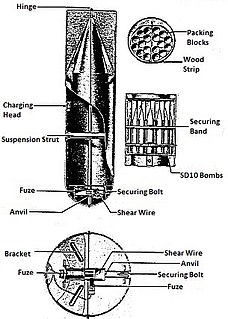
| SBe 250 | |
|---|---|
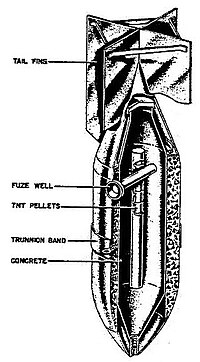 | |
| Type | Fragmentation bomb |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Luftwaffe |
| Wars | World War II |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 250 kg (550 lb) |
| Length | 1.63 m (5 ft 4 in) |
| Diameter | 14 in (36 cm) |
| Warhead | Ammonal |
| Warhead weight | 46 kg (101 lb) |
Detonation mechanism | TNT [1] |
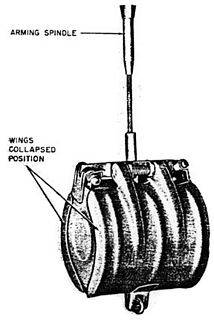
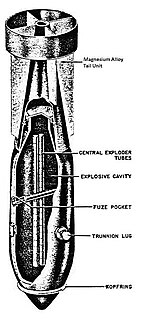
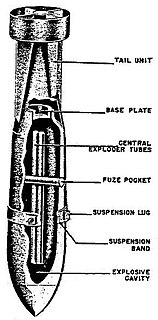
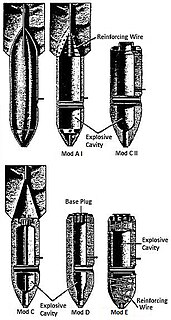
The SBe 250 (Splitter Beton) or concrete fragmentation in English was a fragmentation bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.

The Luftwaffe was the aerial warfare branch of the combined German Wehrmacht military forces during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the Luftstreitkräfte of the Army and the Marine-Fliegerabteilung of the Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 as a result of the terms of the Treaty of Versailles which stated that Germany was forbidden to have any air force.

World War II, also known as the Second World War, was a global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The vast majority of the world's countries—including all the great powers—eventually formed two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis. A state of total war emerged, directly involving more than 100 million people from over 30 countries. The major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. World War II was the deadliest conflict in human history, marked by 50 to 85 million fatalities, most of whom were civilians in the Soviet Union and China. It included massacres, the genocide of the Holocaust, strategic bombing, premeditated death from starvation and disease, and the only use of nuclear weapons in war.