
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA1 gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. BRCA1 is a human tumor suppressor gene and is responsible for repairing DNA.
Malignant transformation is the process by which cells acquire the properties of cancer. This may occur as a primary process in normal tissue, or secondarily as malignant degeneration of a previously existing benign tumor.

ATM serine/threonine kinase or Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated, symbol ATM, is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is recruited and activated by DNA double-strand breaks, oxidative stress, topoisomerase cleavage complexes, splicing intermediates, R-loops and in some cases by single-strand DNA breaks. It phosphorylates several key proteins that initiate activation of the DNA damage checkpoint, leading to cell cycle arrest, DNA repair or apoptosis. Several of these targets, including p53, CHK2, BRCA1, NBS1 and H2AX are tumor suppressors.
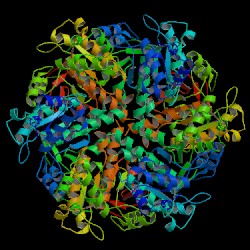
DNA repair protein RAD51 homolog 1 is a protein encoded by the gene RAD51. The enzyme encoded by this gene is a member of the RAD51 protein family which assists in repair of DNA double strand breaks. RAD51 family members are homologous to the bacterial RecA, Archaeal RadA and yeast Rad51. The protein is highly conserved in most eukaryotes, from yeast to humans.
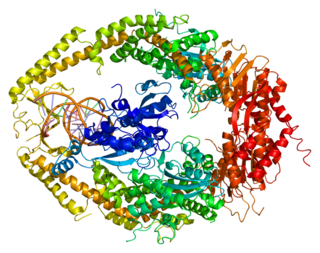
DNA mismatch repair protein Msh2 also known as MutS homolog 2 or MSH2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MSH2 gene, which is located on chromosome 2. MSH2 is a tumor suppressor gene and more specifically a caretaker gene that codes for a DNA mismatch repair (MMR) protein, MSH2, which forms a heterodimer with MSH6 to make the human MutSα mismatch repair complex. It also dimerizes with MSH3 to form the MutSβ DNA repair complex. MSH2 is involved in many different forms of DNA repair, including transcription-coupled repair, homologous recombination, and base excision repair.
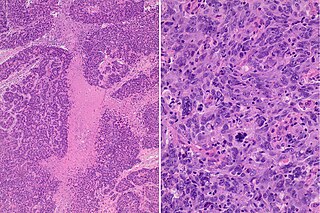
The basal-like carcinoma is a recently proposed subtype of breast cancer defined by its gene expression and protein expression profile.

Secreted frizzled-related protein 1, also known as SFRP1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the SFRP1 gene.

Dickkopf-related protein 3 is a protein in the Dickkopf family that in humans is encoded by the DKK3 gene.

ID4 is a protein coding gene. In humans, it encodes for the protein known as DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-4. This protein is known to be involved in the regulation of many cellular processes during both prenatal development and tumorigenesis. This is inclusive of embryonic cellular growth, senescence, cellular differentiation, apoptosis, and as an oncogene in angiogenesis.

Cystatin-M is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CST6 gene.

LIM domain transcription factor LMO4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMO4 gene.

OTU domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the OTUD4 gene.

Ectoderm-neural cortex protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ENC1 gene.

BRCA1 associated protein-1 is a deubiquitinating enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BAP1 gene. BAP1 encodes an 80.4 kDa nuclear-localizing protein with a ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase (UCH) domain that gives BAP1 its deubiquitinase activity. Recent studies have shown that BAP1 and its fruit fly homolog, Calypso, are members of the polycomb-group proteins (PcG) of highly conserved transcriptional repressors required for long-term silencing of genes that regulate cell fate determination, stem cell pluripotency, and other developmental processes.

Secretoglobin family 3A member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCGB3A2 gene.

Retinoic acid receptor responder protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RARRES1 gene.

Transcription factor AP-2 gamma also known as AP2-gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TFAP2C gene. AP2-gamma is a member of the activating protein 2 family of transcription factors.

Cancer epigenetics is the study of epigenetic modifications to the DNA of cancer cells that do not involve a change in the nucleotide sequence, but instead involve a change in the way the genetic code is expressed. Epigenetic mechanisms are necessary to maintain normal sequences of tissue specific gene expression and are crucial for normal development. They may be just as important, if not even more important, than genetic mutations in a cell's transformation to cancer. The disturbance of epigenetic processes in cancers, can lead to a loss of expression of genes that occurs about 10 times more frequently by transcription silencing than by mutations. As Vogelstein et al. points out, in a colorectal cancer there are usually about 3 to 6 driver mutations and 33 to 66 hitchhiker or passenger mutations. However, in colon tumors compared to adjacent normal-appearing colonic mucosa, there are about 600 to 800 heavily methylated CpG islands in the promoters of genes in the tumors while these CpG islands are not methylated in the adjacent mucosa. Manipulation of epigenetic alterations holds great promise for cancer prevention, detection, and therapy. In different types of cancer, a variety of epigenetic mechanisms can be perturbed, such as the silencing of tumor suppressor genes and activation of oncogenes by altered CpG island methylation patterns, histone modifications, and dysregulation of DNA binding proteins. There are several medications which have epigenetic impact, that are now used in a number of these diseases.

GTP-binding protein Di-Ras3 (DIRAS3) also known as aplysia ras homology member I (ARHI) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIRAS3 gene.

Deleted in lung and esophageal cancer 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLEC1 gene.


















