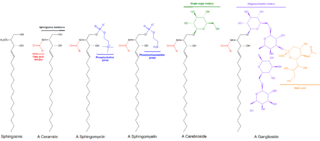
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine. They were discovered in brain extracts in the 1870s and were named after the mythological sphinx because of their enigmatic nature. These compounds play important roles in signal transduction and cell recognition. Sphingolipidoses, or disorders of sphingolipid metabolism, have particular impact on neural tissue. A sphingolipid with an R group consisting of a hydrogen atom only is a ceramide. Other common R groups include phosphocholine, yielding a sphingomyelin, and various sugar monomers or dimers, yielding cerebrosides and globosides, respectively. Cerebrosides and globosides are collectively known as glycosphingolipids.

Sphingomyelin is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath that surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphocholine and ceramide, or a phosphoethanolamine head group; therefore, sphingomyelins can also be classified as sphingophospholipids. In humans, SPH represents ~85% of all sphingolipids, and typically make up 10–20 mol % of plasma membrane lipids.

Ceramides are a family of waxy lipid molecules. A ceramide is composed of sphingosine and a fatty acid. Ceramides are found in high concentrations within the cell membrane of eukaryotic cells, since they are component lipids that make up sphingomyelin, one of the major lipids in the lipid bilayer. Contrary to previous assumptions that ceramides and other sphingolipids found in cell membrane were purely supporting structural elements, ceramide can participate in a variety of cellular signaling: examples include regulating differentiation, proliferation, and programmed cell death (PCD) of cells.

Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase is a hydrolase enzyme that is involved in sphingolipid metabolism reactions. SMase is a member of the DNase I superfamily of enzymes and is responsible for breaking sphingomyelin (SM) down into phosphocholine and ceramide. The activation of SMase has been suggested as a major route for the production of ceramide in response to cellular stresses.
Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase D (EC 3.1.4.41, sphingomyelinase D) is an enzyme of the sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase family with systematic name sphingomyelin ceramide-phosphohydrolase. These enzymes catalyse the hydrolysis of sphingomyelin, resulting in the formation of ceramide 1-phosphate and choline:

C-X-C motif chemokine 11 (CXCL11) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CXCL11 gene.

Sphingosine kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SPHK1 gene.

Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase K is a transglutaminase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TGM1 gene.

Ras-related protein Rap-1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAP1A gene.

Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 1 (SMPD1), also known as acid sphingomyelinase (ASM), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMPD1 gene.

The ASAH1 gene encodes in humans the acid ceramidase enzyme.

Toll interacting protein, also known as TOLLIP, is an inhibitory adaptor protein that in humans is encoded by the TOLLIP gene.
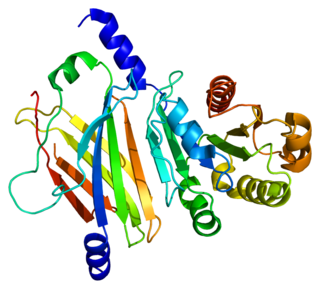
Retinal rod rhodopsin-sensitive cGMP 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase subunit delta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDE6D gene. PDE6D was originally identified as a fourth subunit of rod cell-specific cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE). The precise function of PDE delta subunit in the rod specific GMP-PDE complex is unclear. In addition, PDE delta subunit is not confined to photoreceptor cells but is widely distributed in different tissues. PDE delta subunit is thought to be a specific soluble transport factor for certain prenylated proteins and Arl2-GTP a regulator of PDE-mediated transport.

Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMPD4 gene.

Ectonucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase family member 7 also known as alkaline sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase (Alk-SMase) or intestinal alkaline sphingomyelinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ENPP7 gene.

Nucleobindin-2 is a protein that when found in humans is encoded by the NUCB2 gene.

Sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SMPD3 gene.

cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1, alpha isozyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKG1 gene.
Neutral ceramidase C also known as N-acylsphingosine amidohydrolase 2C or non-lysosomal ceramidase C or ASAH2C is a ceramidase enzyme which in humans is encoded by the ASAH2C gene.
Acid sphingomyelinase is one of the enzymes that make up the sphingomyelinase (SMase) family, responsible for catalyzing the breakdown of sphingomyelin to ceramide and phosphorylcholine. They are organized into alkaline, neutral, and acidic SMase depending on the pH in which their enzymatic activity is optimal. Acid Sphingomyelinases (aSMases) enzymatic activity can be influenced by drugs, lipids, cations, pH, redox and other proteins in the environment. Specifically aSMases have been shown to have increased enzymatic activity in lysobisphosphatidic acid (LBPA) or phosphatidylinositol (PI) enriched environments, and inhibited activity when phosphorylated derivatives of PI are present.


















