
The ionosphere is the ionized part of the upper atmosphere of Earth, from about 48 km (30 mi) to 965 km (600 mi) above sea level, a region that includes the thermosphere and parts of the mesosphere and exosphere. The ionosphere is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important role in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere. It has practical importance because, among other functions, it influences radio propagation to distant places on Earth. It also affects GPS signals that travel through this layer.

Ulysses was a robotic space probe whose primary mission was to orbit the Sun and study it at all latitudes. It was launched in 1990 and made three "fast latitude scans" of the Sun in 1994/1995, 2000/2001, and 2007/2008. In addition, the probe studied several comets. Ulysses was a joint venture of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the United States' National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), under leadership of ESA with participation from Canada's National Research Council. The last day for mission operations on Ulysses was 30 June 2009.

The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center.

Mars 96 was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a 320 km (200 mi) long portion of the Pacific Ocean, Chile, and Bolivia. The Mars 96 spacecraft was based on the Phobos probes launched to Mars in 1988. They were of a new design at the time and both ultimately failed. For the Mars 96 mission the designers believed they had corrected the flaws of the Phobos probes, but the value of their improvements was never demonstrated due to the destruction of the probe during the launch phase.

Explorer 35,, was a spin-stabilized spacecraft built by NASA as part of the Explorer program. Designed for the study of the interplanetary plasma, magnetic field, energetic particles, and solar X-rays, from lunar orbit.

Explorer 32, also known as Atmosphere Explorer-B (AE-B), was a NASA satellite launched by the United States to study the Earth's upper atmosphere. It was launched from Cape Canaveral on a Delta C1 launch vehicle, on 25 May 1966. It was the second of five "Atmosphere Explorer", the first being Explorer 17. Though it was placed in a higher-than-expected orbit by a malfunctioning second stage on its launch vehicle, Explorer 32 returned data for ten months before failing due to a sudden depressurization. The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 22 February 1985.

The Global Geospace Science (GGS) Wind satellite is a NASA science spacecraft designed to study radio waves and plasma that occur in the solar wind and in the Earth's magnetosphere. It was launched on 1 November 1994, at 09:31:00 UTC, from launch pad LC-17B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) in Merritt Island, Florida, aboard a McDonnell Douglas Delta II 7925-10 rocket. Wind was designed and manufactured by Martin Marietta Astro Space Division in East Windsor Township, New Jersey. The satellite is a spin-stabilized cylindrical satellite with a diameter of 2.4 m and a height of 1.8 m.

Explorer 8 was a NASA research satellite launched on 3 November 1960. It was intended to study the temporal and spatial distribution of the electron density, the electron temperature, the ion concentration, the ion mass, the micrometeorite distribution, and the micrometeorite mass in the ionosphere at altitudes between 400 km (250 mi) and 1,600 km (990 mi) and their variation from full sunlit conditions to full shadow, or nighttime, conditions.

Explorer 33, also known as IMP-D and AIMP-1, is a spacecraft in the Explorer program launched by NASA on 1 July 1966 on a mission of scientific exploration. It was the fourth satellite launched as part of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, and the first of two "Anchored IMP" spacecraft to study the environment around Earth at lunar distances, aiding the Apollo program. It marked a departure in design from its predecessors, IMP-A through IMP-C. Explorer 35 was the companion spacecraft to Explorer 33 in the Anchored IMP program, but Explorer 34 (IMP-F) was the next spacecraft to fly, launching about two months before AIMP-E, both in 1967.
The Stretched Rohini Satellite Series (SROSS) are a series of satellites developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation as follow ons to the Rohini Satellites for conducting astrophysics, Earth Remote Sensing, and upper atmospheric monitoring experiments as well as for new and novel application-oriented missions. These satellites were the payload of the developmental flights of the Augmented Satellite Launch Vehicle.

C/NOFS, or Communications/Navigation Outage Forecasting System was a USAF satellite developed by the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) Space Vehicles Directorate to investigate and forecast scintillations in the Earth's ionosphere. It was launched by an Orbital Sciences Corporation Pegasus-XL launch vehicle at 17:02:48 UTC on 16 April 2008 and decayed on 28 November 2015.

Explorer 54, also called as AE-D, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to series Atmosphere Explorer, being launched on 6 October 1975 from Vandenberg Air Force Base board a Thor-Delta 2910 launch vehicle.

The ISEE-1 was an Explorer-class mother spacecraft, International Sun-Earth Explorer-1, was part of the mother/daughter/heliocentric mission. ISEE-1 was a 340.2 kg (750 lb) space probe used to study magnetic fields near the Earth. ISEE-1 was a spin-stabilized spacecraft and based on the design of the prior IMP series of spacecraft. ISEE-1 and ISEE-2 were launched on 22 October 1977, and they re-entered on 26 September 1987.
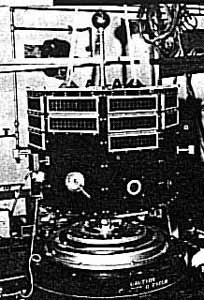
Explorer 31, also called DME-A, was a NASA satellite launched as part of the Explorer program. Explorer 31 was launched on 29 November 1965 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, California, with a Thor-Agena launch vehicle. Explorer 31 was released along with the Canadian satellite Alouette 2.
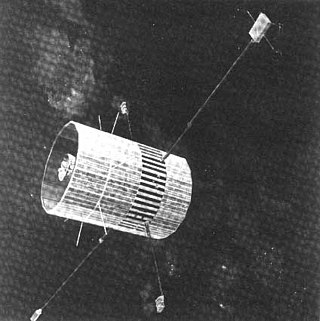
Explorer 47, was a NASA satellite launched as part of Explorer program. Explorer 47 was launched on 23 September 1972 from Cape Canaveral, Florida, with a Thor-Delta 1604. Explorer 47 was the ninth overall launch of the Interplanetary Monitoring Platform series, but received the launch designation "IMP-7" because two previous "Anchored IMP" flights had used "AIMP" instead.

Explorer 51, also called as AE-C, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to series Atmosphere Explorer, being launched on 16 December 1973, at 06:18:00 UTC, from Vandenberg board a Delta 1900 launch vehicle.
Explorer 55, also called as AE-E, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to series Atmosphere Explorer, being launched on 20 November 1975 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) board a Thor-Delta 2910 launch vehicle.

Dynamics Explorer 1 was a NASA high-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981, and terminated on 28 February 1991. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.

Dynamics Explorer 2 was a NASA low-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.
















