
Mariner 4 was the fourth in a series of spacecraft intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode. It was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations of Mars and to transmit these observations to Earth. Launched on November 28, 1964, Mariner 4 performed the first successful flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first close-up pictures of the Martian surface. It captured the first images of another planet ever returned from deep space; their depiction of a cratered, dead planet largely changed the scientific community's view of life on Mars. Other mission objectives were to perform field and particle measurements in interplanetary space in the vicinity of Mars and to provide experience in and knowledge of the engineering capabilities for interplanetary flights of long duration. Initially expected to remain in space for eight months, Mariner 4's mission lasted about three years in solar orbit. On December 21, 1967, communications with Mariner 4 were terminated.

A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of detecting a physical phenomenon.

Explorer 35,, was a spin-stabilized spacecraft built by NASA as part of the Explorer program. It was designed for the study of the interplanetary plasma, magnetic field, energetic particles, and solar X-rays, from lunar orbit.

Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There are a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically use a p–n junction that converts photons into charge. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy.
A load cell converts a force such as tension, compression, pressure, or torque into a signal that can be measured and standardized. It is a force transducer. As the force applied to the load cell increases, the signal changes proportionally. The most common types of load cells are pneumatic, hydraulic, and strain gauge types for industrial applications. Typical non-electronic bathroom scales are a widespread example of a mechanical displacement indicator where the applied weight (force) is indicated by measuring the deflection of springs supporting the load platform, technically a "load cell".

Maximum power point tracking (MPPT), or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar systems but can also be used with wind turbines, optical power transmission and thermophotovoltaics.

An active-pixel sensor (APS) is an image sensor, which was invented by Peter J.W. Noble in 1968, where each pixel sensor unit cell has a photodetector and one or more active transistors. In a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) active-pixel sensor, MOS field-effect transistors (MOSFETs) are used as amplifiers. There are different types of APS, including the early NMOS APS and the now much more common complementary MOS (CMOS) APS, also known as the CMOS sensor. CMOS sensors are used in digital camera technologies such as cell phone cameras, web cameras, most modern digital pocket cameras, most digital single-lens reflex cameras (DSLRs), mirrorless interchangeable-lens cameras (MILCs), and lensless imaging for cells.
A positioning system is a system for determining the position of an object in space. Positioning system technologies exist ranging from interplanetary coverage with meter accuracy to workspace and laboratory coverage with sub-millimeter accuracy. A major subclass is made of geopositioning systems, used for determining an object's position with respect to Earth, i.e., its geographical position; one of the most well-known and commonly used geopositioning systems is the Global Positioning System (GPS) and similar global navigation satellite systems (GNSS).
Astrionics is the science and technology of the development and application of electronic systems, subsystems, and components used in spacecraft. The electronic systems on-board a spacecraft are embedded systems and include attitude determination and control, communications, command and telemetry, and computer systems. Sensors refers to the electronic components on board a spacecraft.

Landsat 8 is an American Earth observation satellite launched on 11 February 2013. It is the eighth satellite in the Landsat program; the seventh to reach orbit successfully. Originally called the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM), it is a collaboration between NASA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS). NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provided development, mission systems engineering, and acquisition of the launch vehicle while the USGS provided for development of the ground systems and will conduct on-going mission operations. It comprises the camera of the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS), which can be used to study Earth surface temperature and is used to study global warming.

Magsat was a NASA / USGS spacecraft, launched on 30 October 1979. The mission was to map the Earth's magnetic field, the satellite had two magnetometers. The scalar and vector magnetometers gave Magsat a capability beyond that of any previous spacecraft. Extended by a telescoping boom, the magnetometers were distanced from the magnetic field created by the satellite and its electronics. The satellite carried two magnetometers, a three-axis fluxgate magnetometer for determining the strength and direction of magnetic fields, and an ion-vapor/vector magnetometer for determining the magnetic field caused by the vector magnetometer itself. Magsat is considered to be one of the more important Science/Earth-orbiting satellites launched; the data it accumulated is still being used, particularly in linking new satellite data to past observations.

Explorer 54, also known as AE-D, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to the Atmosphere Explorer series launched on 6 October 1975 from Vandenberg Air Force Base aboard a Thor-Delta 2910 launch vehicle.

An inertial navigation system is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors (magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous.

Explorer 14, also called EPE-B or Energetic Particles Explorer-B, was a NASA spacecraft instrumented to measure cosmic-ray particles, trapped particles, solar wind protons, and magnetospheric and interplanetary magnetic fields. It was the second of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 2 October 1962, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle.

An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body's specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs.

Explorer 10 was a NASA satellite that investigated Earth's magnetic field and nearby plasma. Launched on 25 March 1961, it was an early mission in the Explorer program and was the first satellite to measure the "shock wave" generated by a solar flare.

Explorer 12, also called EPE-A or Energetic Particles Explorer-A and as S3), was a NASA satellite built to measure the solar wind, cosmic rays, and the Earth's magnetic field. It was the first of the S-3 series of spacecraft, which also included Explorer 12, 14, 15, and 26. It was launched on 16 August 1961, aboard a Thor-Delta launch vehicle. It ceased transmitting on 6 December 1961 due to power failure.

Explorer 51, also known as AE-C, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to the Atmosphere Explorer series launched on 16 December 1973, at 06:18:00 UTC, from Vandenberg aboard a Delta 1900 launch vehicle.
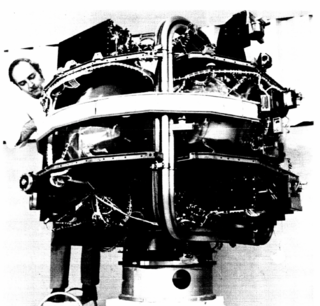
Explorer 55, also known as AE-E, was a NASA scientific satellite belonging to the Atmosphere Explorer series launched on 20 November 1975 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station (CCAFS) aboard a Thor-Delta 2910 launch vehicle.

Dynamics Explorer 2 was a NASA low-altitude mission, launched on 3 August 1981. It consisted of two satellites, DE-1 and DE-2, whose purpose was to investigate the interactions between plasmas in the magnetosphere and those in the ionosphere. The two satellites were launched together into polar coplanar orbits, which allowed them to simultaneously observe the upper and lower parts of the atmosphere.

















