Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRRM1 gene. [3] [4]
Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRRM1 gene. [3] [4]

Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions.
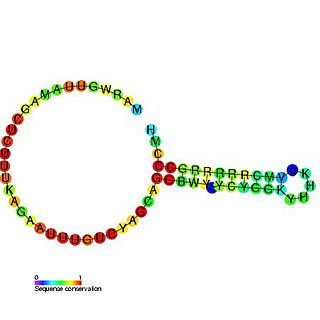
The U7 small nuclear RNA is an RNA molecule and a component of the small nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex. The U7 snRNA is required for histone pre-mRNA processing.

snRNP70 also known as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRNP70 gene. snRNP70 is a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein that associates with U1 spliceosomal RNA, forming the U1snRNP a core component of the spliceosome. The U1-70K protein and other components of the spliceosome complex form detergent-insoluble aggregates in both sporadic and familial human cases of Alzheimer's disease. U1-70K co-localizes with Tau in neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease.

RNA-binding protein 8A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBM8A gene.
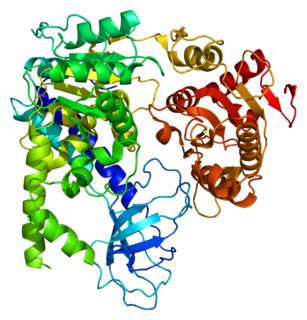
Regulator of nonsense transcripts 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF1 gene.

The human DEKgene encodes the DEK protein.
Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX5 also known as DEAD box protein 5 or RNA helicase p68 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DDX5 gene.

Transformer-2 protein homolog beta, also known as TRA2B previously known as splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 10 (SFRS10), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRA2B gene.

Pinin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PNN gene.

RNA-binding protein with serine-rich domain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNPS1 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF2 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3B gene.
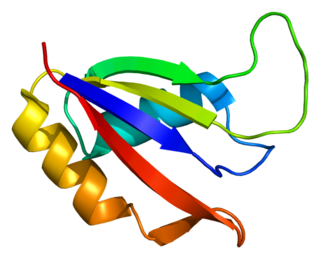
Aly/REF export factor, also known as THO complex subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALYREF gene.
Protein mago nashi homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MAGOH gene.

Splicing factor, arginine/serine-rich 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SFRS4 gene.

Serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRRM2 gene.

U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein A' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNRPA1 gene.

Cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CPSF1 gene.

Regulator of nonsense transcripts 3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UPF3A gene.
An exon junction complex (EJC) is a protein complex which forms on a pre-messenger RNA strand at the junction of two exons which have been joined together during RNA splicing. The EJC has major influences on translation, surveillance and localization of the spliced mRNA. It is first deposited onto mRNA during splicing and is then transported into the cytoplasm. There it plays a major role in post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. It is believed that exon junction complexes provide a position-specific memory of the splicing event. The EJC consists of a stable heterotetramer core, which serves as a binding platform for other factors necessary for the mRNA pathway. The core of the EJC contains the protein eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III bound to an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) analog, as well as the additional proteins Magoh and Y14. The binding of these proteins to nuclear speckled domains has been measured recently and it may be regulated by PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. In order for the binding of the complex to the mRNA to occur, the eIF4AIII factor is inhibited, stopping the hydrolysis of ATP. This recognizes EJC as an ATP dependent complex. EJC also interacts with a large number of additional proteins; most notably SR proteins. These interactions are suggested to be important for mRNA compaction. The role of EJC in mRNA export is controversial.