
Operation Argus was a series of United States low-yield, high-altitude nuclear weapons tests and missile tests secretly conducted from 27 August to 9 September 1958 over the South Atlantic Ocean. The tests were performed by the Defense Nuclear Agency.

Alouette 1 is a deactivated Canadian satellite that studied the ionosphere. Launched in 1962, it was Canada's first satellite, and the first satellite constructed by a country other than the Soviet Union or the United States. Canada was the fourth country to operate a satellite, as the British Ariel 1, constructed in the United States by NASA, preceded Alouette 1 by five months. The name "Alouette" came from the French for "skylark" and the French-Canadian folk song of the same name.
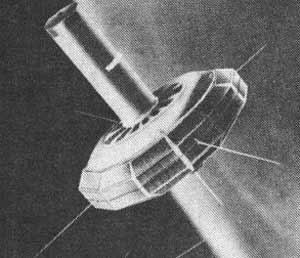
The Transit Research and Attitude Control (TRAAC) satellite was launched by the U. S. Navy from Cape Canaveral along with Transit 4B on November 15, 1961.

Starfish Prime was a high-altitude nuclear test conducted by the United States, a joint effort of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) and the Defense Atomic Support Agency. It was launched from Johnston Atoll on July 9, 1962, and was the largest nuclear test conducted in outer space, and one of five conducted by the US in space.

Operation Fishbowl was a series of high-altitude nuclear tests in 1962 that were carried out by the United States as a part of the larger Operation Dominic nuclear test program. Flight-test vehicles were designed and manufactured by Avco Corporation.

High-altitude nuclear explosions are the result of nuclear weapons testing within the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere and in outer space. Several such tests were performed at high altitudes by the United States and the Soviet Union between 1958 and 1962.

The Pegasus Project was a NASA initiative to study the frequency of micrometeoroid impacts on spacecraft by means of a constellation of three satellites launched in 1965. All three Pegasus satellites were launched by Saturn I rockets, and remained connected with their upper stages.

Project West Ford was a test carried out by Massachusetts Institute of Technology's Lincoln Laboratory on behalf of the United States military in 1961 and 1963 to create an artificial ionosphere above the Earth. This was done to solve a major weakness that had been identified in military communications.

SOLRAD was an American series of satellites sponsored by the US Navy in a program to continuously monitor the Sun. SOLRAD was the Naval Research Laboratory's first post-Vanguard satellite.

The year 1954 saw the conception of Project Orbiter, the first practicable satellite launching project, utilizing the Redstone, a newly developed Short Range Ballistic Missile.

Orbiting Vehicle or OV, originally designated SATAR, comprised five disparate series of standardized American satellites operated by the US Air Force, launched between 1965 and 1971. Forty seven satellites were built, of which forty three were launched and thirty seven reached orbit. With the exception of the OV3 series and OV4-3, they were launched as secondary payloads, using excess space on other missions. This resulted in extremely low launch costs and short proposal-to-orbit times. Typically, OV satellites carried scientific and/or technological experiments, 184 being successfully orbited through the lifespan of the program.
Kosmos 5, also known as 2MS #2 and occasionally in the West as Sputnik 15 was a scientific research and technology demonstration satellite launched by the Soviet Union in 1962. It was the fifth satellite to be designated under the Kosmos system, and the third spacecraft to be launched as part of the MS programme, after Kosmos 2 and Kosmos 3. Its primary missions were to develop systems for future satellites, and to record data about artificial radiation around the Earth.

Ariel 1, was the first British-American satellite, and the first satellite in the Ariel programme. Its launch in 1962 made the United Kingdom the third country to operate a satellite, after the Soviet Union and the United States. It was constructed in the UK and the United States by NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and SERC, under an agreement reached as the result of political discussions in 1959 and 1960. The US Starfish Prime exoatmospheric nuclear test affected Ariel 1's operational capability.

Alexander Henry Flax was the Chief Scientist of the U.S. Air Force (USAF) from 1959 to 1961, Assistant Secretary of the Air Force for Research and Development from 1963 to 1969, and the third Director of the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) from 1965 to 1969. He was the director at a time when the second generation of imaging systems became operational and began to play a major role in United States intelligence during the Cold War. He oversaw major growth in NRO funding and personnel, the development of signals intelligence collectors from space, and the development of electro-optical imaging for US reconnaissance satellites.

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) was created in 1958 from the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), and other related organizations, as the result of the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1950s.

Elektron ('electron'), in American sources sometimes called Electron, was the first Soviet multiple satellite program, comprising two identical pairs of particle physics satellites launched by the Soviet Union in 1964. The four spacecraft simultaneously monitored the lower and upper Van Allen radiation belts and returned a considerable volume of data regarding radiation in space and atmospheric conditions to an altitude of more than 58,000 kilometres (36,000 mi) above the Earth. Two of the four launched satellites are still in orbit as of 2020, the other two having reentered.

Orbiting Vehicle 2-1, the first satellite of the second series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program, was an American life science research satellite. Its purpose was to determine the extent of the threat posed to astronauts by the Van Allen radiation belts. Launched 15 October 1965, the mission resulted in failure when the upper stage of OV2-1's Titan IIIC booster broke up.

FR-1 was the second French satellite. Planned as the first French satellite, it was launched on 6 December 1965—ten days after the actual first French satellite, Astérix—by an American Scout X-4 rocket from the Western Range at Vandenberg Air Force Base. The scientific satellite studied the composition and structure of the ionosphere, plasmasphere, and magnetosphere by measuring the propagation of very low frequency (VLF) waves and the electron density of plasma in those portions of the Earth's atmosphere. FR-1's VLF receiver operated until 26 August 1968. FR-1 remains in orbit as of 2023.

The Environmental Research Satellite program was a series of small satellites initially operated by the United States Air Force Office of Aerospace Research. Designed to be launched "piggyback" to other satellites during launch, detaching once in orbit, they were the smallest satellites launched to date—what would today be classified as microsatellites. 33 ERS satellites in six different series were launched between 1962 and 1971, conducting scientific research and serving as test beds to investigate the reliability of new spacecraft components.

















