Tyazhely Sputnik, also known by its development name as Venera 1VA No. 1, and in the West as Sputnik 7, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was intended to be the first spacecraft to explore Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit. In order to avoid acknowledging the failure, the Soviet government instead announced that the entire spacecraft, including the upper stage, was a test of a "Heavy Satellite" which would serve as a launch platform for future missions. This resulted in the upper stage being considered a separate spacecraft, from which the probe was "launched", on several subsequent missions.
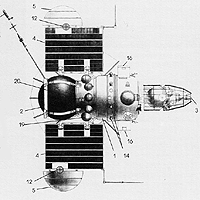
Venera 2MV-1 No.1, also known as Sputnik 19 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme.
Venera 2MV-1 No.2, also known as Sputnik 20 in the Western world, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second of two Venera 2MV-1 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit. The previous mission, Venera 2MV-1 No.1, was launched several days earlier.

Mars 2MV-4 No.1 also known as Sputnik 22 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Mars programme, and was intended to make a flyby of Mars, and transmit images of the planet back to Earth. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it was destroyed in low Earth orbit. It was the first of two Mars 2MV-4 spacecraft to be launched, the other being the Mars 1 spacecraft which was launched eight days later.
Luna E-6 No.2, also identified as No.1, and sometimes known in the West as Sputnik 25, was a Soviet spacecraft which launched in 1963, but was placed into a useless orbit due to a problem with the upper stage of the rocket that launched it. It was a 1,500-kilogram (3,300 lb) Luna Ye-6 spacecraft, the first of twelve to be launched. It was intended to be the first spacecraft to perform a soft landing on the Moon, a goal which would eventually be accomplished by the final Ye-6 spacecraft, Luna 9.
Venera 2MV-2 No.1, also known as Sputnik 21 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to make a flyby of Venus. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the atmosphere a few days later. It was the second Venera 2MV-2 spacecraft, both of which failed to leave Earth orbit.
Kosmos 36, also known as DS-P1-Yu #1 was a satellite which was used for use in calibrating the Dnestr space surveillance and as a radar calibration target, for tests of anti-ballistic missiles. It was launched by the Soviet Union in 1964 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau.
Kosmos 76, also known as DS-P1-Yu No.3 was a Soviet satellite which was used as a radar calibration target for tests of anti-ballistic missiles. It was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and launched in 1965 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme.
Kosmos 295, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.29, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1969 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 311, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.27, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1969 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 334, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.31, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1970 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 455, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.54, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1971 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 501, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.50, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1972 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 250-kilogram (550 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 562, known before launch as DS-P1-Yu No.66, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1973 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 400-kilogram (880 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used as a radar calibration target for anti-ballistic missile tests.
Kosmos 108, also known as DS-U1-G No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1966 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 355 kilograms (783 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Office and was used to study the effects of solar activity on the upper atmosphere.
Kosmos 335, also known as DS-U1-R No.1, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1970 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 295-kilogram (650 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to study spectral ranges in the Earth's atmosphere.
Kosmos 95, also known as DS-U2-V No.2, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1965 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. The spacecraft weighed 325 kilograms (717 lb), and was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Office, and was used to conduct classified technology development experiments for the Soviet armed forces.
Kosmos 259, also known as DS-U2-I No.3, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1968 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 325-kilogram (717 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to study the effects on radio waves of passing through the ionosphere.
Kosmos 225, also known as DS-U1-Ya No.2, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1968 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 400 kilograms (880 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to investigate cosmic rays and flows of charged particles in the Earth's magnetosphere.
Kosmos 348, also known as DS-U2-GK No.2, was a Soviet satellite which was launched in 1970 as part of the Dnepropetrovsk Sputnik programme. It was a 357-kilogram (787 lb) spacecraft, which was built by the Yuzhnoye Design Bureau, and was used to study the density of air in the upper atmosphere, and investigate aurorae.




