
Australopithecus is a genus of early hominins that existed in Africa during the Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. The genera Homo, Paranthropus, and Kenyanthropus evolved from some Australopithecus species. Australopithecus is a member of the subtribe Australopithecina, which sometimes also includes Ardipithecus, though the term "australopithecine" is sometimes used to refer only to members of Australopithecus. Species include A. garhi, A. africanus, A. sediba, A. afarensis, A. anamensis, A. bahrelghazali and A. deyiremeda. Debate exists as to whether some Australopithecus species should be reclassified into new genera, or if Paranthropus and Kenyanthropus are synonymous with Australopithecus, in part because of the taxonomic inconsistency.

Australopithecus afarensis is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived from about 3.9–2.9 million years ago (mya) in the Pliocene of East Africa. The first fossils were discovered in the 1930s, but major fossil finds would not take place until the 1970s. From 1972 to 1977, the International Afar Research Expedition—led by anthropologists Maurice Taieb, Donald Johanson and Yves Coppens—unearthed several hundreds of hominin specimens in Hadar, Ethiopia, the most significant being the exceedingly well-preserved skeleton AL 288-1 ("Lucy") and the site AL 333. Beginning in 1974, Mary Leakey led an expedition into Laetoli, Tanzania, and notably recovered fossil trackways. In 1978, the species was first described, but this was followed by arguments for splitting the wealth of specimens into different species given the wide range of variation which had been attributed to sexual dimorphism. A. afarensis probably descended from A. anamensis and is hypothesised to have given rise to Homo, though the latter is debated.

The Cradle of Humankind is a paleoanthropological site and is located about 50 km (31 mi) northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa, in the Gauteng province. Declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1999, the site is home to the largest concentration of human ancestral remains anywhere in the world. The site currently occupies 47,000 hectares (180 sq mi) and contains a complex system of limestone caves. The registered name of the site in the list of World Heritage Sites is Fossil Hominid Sites of South Africa.

Sterkfontein is a set of limestone caves of special interest in paleoanthropology located in Gauteng province, about 40 kilometres (25 mi) northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa in the Muldersdrift area close to the town of Krugersdorp. The archaeological sites of Swartkrans and Kromdraai are in the same area. Sterkfontein is a South African National Heritage Site and was also declared a World Heritage Site in 2000. The area in which it is situated is known as the Cradle of Humankind. The Sterkfontein Caves are also home to numerous wild African species including Belonogaster petiolata, a wasp species of which there is a large nesting presence.

Mrs. Ples is the popular nickname for the most complete skull of an Australopithecus africanus ever found in South Africa. Many Australopithecus fossils have been found near Sterkfontein, about 40 kilometres (25 mi) northwest of Johannesburg, in a region of Gauteng now designated as the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site. Mrs. Ples was discovered by Robert Broom and John T. Robinson on April 18, 1947. Because of Broom's use of dynamite and pickaxe while excavating, Mrs. Ples's skull was blown into pieces and some fragments are missing. Nonetheless, Mrs./Mr. Ples is one of the most "perfect" pre-human skulls ever found. The skull is currently held at the Ditsong National Museum of Natural History in Pretoria.

Australopithecus africanus is an extinct species of australopithecine which lived between about 3.3 and 2.1 million years ago in the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene of South Africa. The species has been recovered from Taung, Sterkfontein, Makapansgat, and Gladysvale. The first specimen, the Taung child, was described by anatomist Raymond Dart in 1924, and was the first early hominin found. However, its closer relations to humans than to other apes would not become widely accepted until the middle of the century because most had believed humans evolved outside of Africa. It is unclear how A. africanus relates to other hominins, being variously placed as ancestral to Homo and Paranthropus, to just Paranthropus, or to just P. robustus. The specimen "Little Foot" is the most completely preserved early hominin, with 90% of the skeleton intact, and the oldest South African australopith. However, it is controversially suggested that it and similar specimens be split off into "A. prometheus".
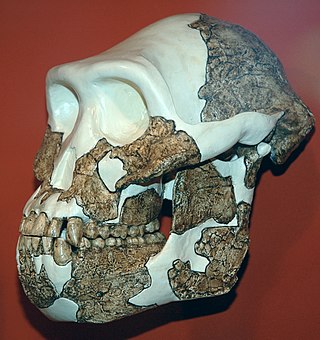
Australopithecus anamensis is a hominin species that lived approximately between 4.2 and 3.8 million years ago and is the oldest known Australopithecus species, living during the Plio-Pleistocene era.

The Taung Child is the fossilised skull of a young Australopithecus africanus. It was discovered in 1924 by quarrymen working for the Northern Lime Company in Taung, South Africa. Raymond Dart described it as a new species in the journal Nature in 1925.

Paranthropus robustus is a species of robust australopithecine from the Early and possibly Middle Pleistocene of the Cradle of Humankind, South Africa, about 2.27 to 0.87 million years ago. It has been identified in Kromdraai, Swartkrans, Sterkfontein, Gondolin, Cooper's, and Drimolen Caves. Discovered in 1938, it was among the first early hominins described, and became the type species for the genus Paranthropus. However, it has been argued by some that Paranthropus is an invalid grouping and synonymous with Australopithecus, so the species is also often classified as Australopithecus robustus.
Orthograde is a term derived from Greek ὀρθός, orthos + Latin gradi that describes a manner of walking which is upright, with the independent motion of limbs. Both New and Old World monkeys are primarily arboreal, and they have a tendency to walk with their limbs swinging in parallel to one another. This differs from the manner of walking demonstrated by the apes.

Ronald John Clarke is a paleoanthropologist most notable for the discovery of "Little Foot", an extraordinarily complete skeleton of Australopithecus, in the Sterkfontein Caves. A more technical description of various aspects of his description of the Australopithecus skeleton was published in the Journal of Quaternary Science.

STS 71 is a fossilized skull of the species Australopithecus africanus. It was discovered in Sterkfontein, South Africa by Robert Broom in 1947. In 1972 John Wallace connected STS 71 with STS 36, a lower jaw found in the same layer, by matching the wear patterns on the teeth.

"Little Foot" is the nickname given to a nearly complete Australopithecus fossil skeleton found in 1994–1998 in the cave system of Sterkfontein, South Africa.

Selam (DIK-1/1) is the fossilized skull and other skeletal remains of a three-year-old Australopithecus afarensis female hominin, whose bones were first found in Dikika, Ethiopia in 2000 and recovered over the following years. Although she has often been nicknamed Lucy's baby, the specimen has been dated at 3.3 million years ago, approximately 100,000 years older than "Lucy".
Gladysvale Cave is a fossil-bearing breccia filled cave located about 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) northeast of the well-known South African hominid-bearing sites of Sterkfontein and Swartkrans and about 45 kilometres (28 mi) north-northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is situated within the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site and is itself a South African National Heritage Site.

Australopithecus sediba is an extinct species of australopithecine recovered from Malapa Cave, Cradle of Humankind, South Africa. It is known from a partial juvenile skeleton, the holotype MH1, and a partial adult female skeleton, the paratype MH2. They date to about 1.98 million years ago in the Early Pleistocene, and coexisted with Paranthropus robustus and Homo ergaster / Homo erectus. Malapa is interpreted as having been a natural death trap, the base of a long vertical shaft which creatures could accidentally fall into. A. sediba was initially described as being a potential human ancestor, and perhaps the progenitor of Homo, but this is contested and it could also represent a late-surviving population or sister species of A. africanus which had earlier inhabited the area.

Malapa is a fossil-bearing cave located about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) northeast of the well known South African hominid-bearing sites of Sterkfontein and Swartkrans and about 45 kilometres (28 mi) north-northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa. It is situated within the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site.

André Werner Keyser, was a South African palaeontologist and geologist noted for his discovery of the Drimolen hominid site and of numerous hominid remains.

StW 505 is the most complete hominin cranium discovered in Sterkfontein Member 4 since Broom's excavations. It was found in situ in Member 4 breccia in 1989 and is larger, on the whole, than any other cranium from Sterkfontein that has comparable parts.
John Talbot Robinson FRSSAf was a distinguished South African hominin paleontologist. His most famous discovery was the nearly complete fossil skull of the hominin species Australopithecus africanus, known as Mrs. Ples.
















