
Caelum is a faint constellation in the southern sky, introduced in the 1750s by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille and counted among the 88 modern constellations. Its name means "chisel" in Latin, and it was formerly known as Caelum Sculptorium ; It is a rare word, unrelated to the far more common Latin caelum, meaning "sky", "heaven", or "atmosphere". It is the eighth-smallest constellation, and subtends a solid angle of around 0.038 steradians, just less than that of Corona Australis.

Telescopium is a minor constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, one of twelve named in the 18th century by French astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille and one of several depicting scientific instruments. Its name is a Latinized form of the Greek word for telescope. Telescopium was later much reduced in size by Francis Baily and Benjamin Gould.

Pictor is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, located between the star Canopus and the Large Magellanic Cloud. Its name is Latin for painter, and is an abbreviation of the older name Equuleus Pictoris. Normally represented as an easel, Pictor was named by Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in the 18th century. The constellation's brightest star is Alpha Pictoris, a white main-sequence star around 97 light-years away from Earth. Pictor also hosts RR Pictoris, a cataclysmic variable star system that flared up as a nova, reaching apparent (visual) magnitude 1.2 in 1925 before fading into obscurity.

T Pyxidis is a recurrent nova and nova remnant in the constellation Pyxis. It is a binary star system and its distance is estimated at about 4,783 parsecs from Earth. It contains a Sun-like star and a white dwarf. Because of their close proximity and the larger mass of the white dwarf, the latter draws matter from the larger, less massive star. The influx of matter on the white dwarf's surface causes periodic thermonuclear explosions to occur.

The American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO) is an international nonprofit organization. Founded in 1911, the organization focuses on coordinating, analyzing, publishing, and archiving variable star observations made largely by amateur astronomers. The AAVSO creates records that establish light curves depicting the variation in brightness of a star over time. The AAVSO makes these records available to professional astronomers, researchers, and educators.
Beta Pictoris is the second brightest star in the constellation Pictor. It is located 63.4 light-years (19.4 pc) from the Solar System, and is 1.75 times as massive and 8.7 times as luminous as the Sun. The Beta Pictoris system is very young, only 20 to 26 million years old, although it is already in the main sequence stage of its evolution. Beta Pictoris is the title member of the Beta Pictoris moving group, an association of young stars which share the same motion through space and have the same age.
A flare star is a variable star that can undergo unpredictable dramatic increases in brightness for a few minutes. It is believed that the flares on flare stars are analogous to solar flares in that they are due to the magnetic energy stored in the stars' atmospheres. The brightness increase is across the spectrum, from X-rays to radio waves. Flare activity among late-type stars was first reported by A. van Maanen in 1945, for WX UMa and YZ CMi. However, the best-known flare star is UV Ceti, first observed to flare in 1948. Today similar flare stars are classified as UV Ceti type variable stars in variable star catalogs such as the General Catalogue of Variable Stars.

RR Pictoris, also known as Nova Pictoris 1925, is a cataclysmic variable star system that flared up as a nova that lit up in the constellation Pictor in 1925. It was discovered by South African amateur astronomer R. Watson who lived in Beaufort West. At 05:50 AM on 25 May 1925, Mr. Watson was walking to work and noticed a star that he did not recognize in line with the stars α Crucis and β Carinae. He consulted his copy of Norton's Star Atlas, and realized that the unfamiliar star was a nova. Fortuitously, Mr. Watson was employed as a telegraph operator, and he promptly sent a telegram describing his discovery to the Royal Observatory at Cape Town. This quick reporting of the event allowed southern observatories to obtain spectra of the nova before it had reached maximum brightness.
A Lambda Eridani Variable is a class of Be stars that show small amplitude variations of a few hundredths of a magnitude. The variations are highly regular with periods between 0.5 and 2.0 days, and they were initially described as periodic Be stars. Lambda Eridani is an example and the prototype. This has been ascribed to non-radial pulsations, inhomogeneous rotating discs, or the rotation of the star itself.

R Virginis is a Mira variable in the constellation Virgo. Located approximately 530 parsecs (1,700 ly) distant, it varies between magnitudes 6.1 and 12.1 over a period of approximately 146 days. Its variable nature was discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding in 1809.

S Virginis is a Mira-type variable star in the constellation Virgo. Located approximately 700 parsecs (2,300 ly) distant, it varies between magnitudes 6.3 and 13.2 over a period of approximately 375 days.

R Serpentis is a Mira variable type star in the equatorial constellation of Serpens. It ranges between apparent magnitude 5.16 and 14.4, and spectral types M5e to M8e, over a period of 356.41 days. The variability of this star was discovered in 1826 by Karl Ludwig Harding.
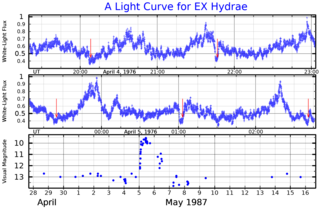
EX Hydrae is a variable star classified as an eclipsing intermediate polar-type cataclysmic variable, specifically of the DQ Herculis type. The system varies in apparent magnitude from 9.6 to 14. The system consists of a white dwarf primary and an M-type secondary, of masses of 0.4–0.7 M☉ and 0.07–0.10 M☉ respectively. The orbital period is 98.25696 minutes (0.068233846 days). The system is 65±11 parsecs distant, making EX Hya one of the closest cataclysmic variable stars. The cataclysmic outbursts appear to be caused by accretion of material from the M-star to the white dwarf.
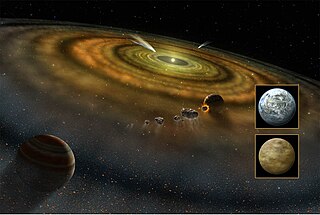
An exocomet, or extrasolar comet, is a comet outside the Solar System, which includes rogue comets and comets that orbit stars other than the Sun. The first exocomets were detected in 1987 around Beta Pictoris, a very young A-type main-sequence star. There are now a total of 27 stars around which exocomets have been observed or suspected.

R Pictoris is a semiregular variable type star in the constellation Pictor. It ranges between apparent magnitude 5.1 and 14.4, and spectral types M1IIe to M4IIe, over a period of 168 days.
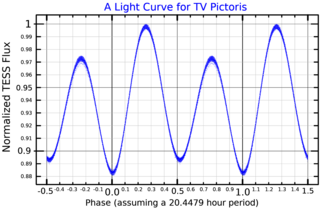
TV Pictoris is a rotating ellipsoidal variable star in the constellation Pictor. It ranges between apparent magnitude 7.37 - 7.53 over a period of 0.85 days. It was first discovered to be variable in 1987. The system is inclined at an angle of 54 degrees to observers on Earth. It is composed of a primary star that has a radius 4.3 times that of the sun and 1.2 times its mass, and an effective (surface) temperature of 8300 K, and a secondary star with a radius 2.1 times that of the sun and 40% of its mass, and an effective temperature of 7000 K. Both stars are less massive than expected for a main sequence star of their temperatures. The secondary rotates much faster than the primary.

BH Crucis, also known as Welch's Red Variable, is a star in the constellation Crux. A long period (Mira-type) variable, its apparent magnitude ranges from 6.6 to 9.8 over 530 days. Hence at its brightest it is barely visible with the unaided eye in a rural sky. A red giant, it had been classified ranging between spectral types SC4.5/8-e and SC7/8-e, but appears to have evolved into a C-type spectrum by 2011.

R Leonis Minoris is a Mira variable type star in the constellation Leo Minor. It ranges between apparent magnitude 6.3 and 13.2, and spectral types M6.5e to M9.0e (Tc:), over a period of 372 days.
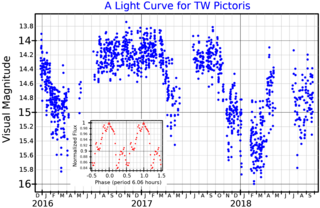
TW Pictoris is a 14th magnitude cataclysmic variable star system in the southern constellation of Pictor. It is located at a distance of approximately 1,430 light-years based on parallax measurements. Photometric observations in the visual band suggest a binary system with an orbital period of 6.06 hours. One of the components is an accreting white dwarf.

V Coronae Borealis is a Mira-type long period variable star and carbon star in the constellation Corona Borealis. Its apparent magnitude varies between 6.9 and 12.6 over a period of 357 days


















