Related Research Articles

The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, except for the headwaters and several bedrock gorges in the lower reaches.
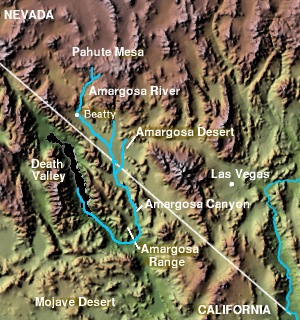
The Amargosa Valley is the valley through which the Amargosa River flows south, in Nye County, southwestern Nevada and Inyo County in the state of California. The south end is alternately called the "Amargosa River Valley'" or the "Tecopa Valley." Its northernmost point is around Beatty, Nevada and southernmost is Tecopa, California, where the Amargosa River enters into the Amargosa Canyon.
The State Scenic Highway System in the U.S. state of California is a list of highways, mainly state highways, that have been designated by the California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) as scenic highways. They are marked by the state flower, a California poppy, inside either a rectangle for state-maintained highways or a pentagon for county highways.

The Old Spanish Trail is a historical trade route that connected the northern New Mexico settlements of Santa Fe, New Mexico with those of Los Angeles, California and southern California. Approximately 700 mi (1,100 km) long, the trail ran through areas of high mountains, arid deserts, and deep canyons. It is considered one of the most arduous of all trade routes ever established in the United States. Explored, in part, by Spanish explorers as early as the late 16th century, the trail was extensively used by traders with pack trains from about 1830 until the mid-1850s. The area was part of Mexico from Mexican independence in 1821 to the Mexican Cession to the United States in 1848.
San Bernardino, California, was named in 1810.

The Mojave Road, also known as Old Government Road, is a historic route and present day dirt road across what is now the Mojave National Preserve in the Mojave Desert in the United States. This rough road stretched 147 miles (237 km) from Beale's Crossing, to Fork of the Road location along the north bank of the Mojave River where the old Mojave Road split off from the route of the Old Spanish Trail/Mormon Road.

The Salt Spring Hills are a low mountain range in the Mojave Desert, in northern San Bernardino County, California. They are just outside the southeastern corner of Death Valley National Park, southeast of the Saddle Peak Hills. The road between Shoshone and Baker passes through the hills.
Noonday Camp, also known as Mill City, Noonday City, and Tecopa, is a ghost town located in the Mojave Desert east of Tecopa in Inyo County, California.
Tule is a plant of the sedge family.

Elizabeth von Till Warren was an American historian and preservationist. She had expertise in the history of water development in the Mojave Desert and the Las Vegas Valley in particular. She also had expertise in the historical route of the Old Spanish Trail in Southern Nevada.
Dos Palmas Spring is an artesian spring in Riverside County, California where it lies at the foot of the Orocopia Mountains. It is only one of several such springs in the area that create an oasis in the Colorado Desert there.
Bitter Spring is a spring within the Fort Irwin National Training Center in San Bernardino County, California. It lies at an elevation of 1355 feet and is located in a valley between the Soda Mountains to the east, the Tiefort Mountains to the northwest, Alvord Mountain to the southwest and Cronese Mountains to the south and southeast.
Silurian Valley is a valley in the Mojave Desert, in San Bernardino County, California. The valley trends in a north–south direction, its mouth located just southeast of the south end of Death Valley at 35°37′17″N116°16′07″W. Its head is at 35°23′36″N116°08′02″W. The valley is drained by Salt Creek a tributary of the Amargosa River and contains Silurian Lake and Dry Sand Lake.
Red Pass is a gap in the Avawatz Mountains, in San Bernardino County, California. Red Pass, lies between the Silurian Valley and the valley drained by an as yet unnamed tributary of Salt Creek, which drains much of the area of Fort Irwin National Training Center, through Red Pass into the Silurian Valley and into the Amargosa River in Death Valley.
Camp Spring, is a spring, in Washington County, Utah. It lies at an elevation of 3,435 feet/1,047 meters in the reservation of the Shivwits Band of Paiutes.
Crowder Canyon, originally Coyote Canyon, is a valley in San Bernardino County, California. Its mouth was at an elevation of 2,999 feet / 914 meters at its confluence with Cajon Canyon. Its source was at an elevation of 4200 feet at 34°21′02″N117°26′04″W near Cajon Summit. The canyon runs southward just west of the top of Cajon Pass then turns southwestward to meet Cajon Canyon.
Fork of the Road was the locale along the Mojave River where the junction of the Mojave Trail / Mojave Road and the Old Spanish Trail / Mormon Road was located in San Bernardino County, California. The location of Fork of the Road was on the north side of the Mojave River, 18.75 miles southwest of Bitter Spring, about 14.5 miles east of Grapevine, and 10.9 miles west of Camp Cady. The location was an oasis where the Mojave River came to the surface. There travelers could get water, camp, rest and graze their animals before or after crossing the desert.
Salt Creek or Rio Salitroso is a tributary stream or wash of the Amargosa River, in San Bernardino County, California. It was named Rio Salitroso, on January 16, 1830, by Antonio Armijo, whose expedition subsequently followed it up towards the Mojave River, as they established the first route of the Old Spanish Trail.
Mormon Road, also known to the 49ers as the Southern Route, of the California Trail in the Western United States, was a seasonal wagon road pioneered by a Mormon party from Salt Lake City, Utah led by Jefferson Hunt, that followed the route of Spanish explorers and the Old Spanish Trail across southwestern Utah, northwestern Arizona, southern Nevada and the Mojave Desert of California to Los Angeles in 1847. From 1855, it became a military and commercial wagon route between California and Utah, called the Los Angeles – Salt Lake Road. In later decades this route was variously called the "Old Mormon Road", the "Old Southern Road", or the "Immigrant Road" in California. In Utah, Arizona and Nevada it was known as the "California Road".
Seventeen Mile Point is a mountain at the north end of the Old Dad Mountains in San Bernardino County, California. Its summit is at an altitude of 2,500 feet / 760 meters.
References
- ↑ Armijo's Journal, LeRoy R. Hafen and Antonio Armijo, Huntington Library Quarterly Vol. 11, No. 1 (Nov., 1947), University of California Press, DOI: 10.2307/3816035
- ↑ Gary L. Shumway, Larry Vredenburgh, Russell Hartill, Desert Fever: An Overview of Mining History of the California Desert Conservation Area, Prepared For: DESERT PLANNING STAFF BUREAU OF LAND MANAGEMENT U.S. DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR 3610 Central Avenue, Suite 402 Riverside, California 92506, February, 1980
- ↑ Reynolds, Robert E., Field Trip Guide, The Changing Face of the East Mojave Desert Abstracts from the 2001 Desert Symposium and Robert E. Reynolds, Editor, LSA Associates, Inc., 1650 Spruce Street, Suite 500, Riverside, California 92507. California State University, Desert Studies Consortium, Department of Biological Science, California State University, Fullerton, California 92834; in association with The Western Center for Archaeology & Paleontology, Western Center Community Foundation, 1160 University Avenue, Suite G, Riverside, California 92521, April 2001