
Dangriga, formerly known as Stann Creek Town, is a town in southern Belize, located on the Caribbean coast at the mouth of the North Stann Creek River. It is the capital of Belize's Stann Creek District. Dangriga is served by the Dangriga Airport. Commonly known as the "culture capital of Belize" due to its influence on punta music and other forms of Garifuna culture, Dangriga is the largest settlement in southern Belize.

Toledo District is the southernmost district in Belize, and Punta Gorda is the District capital. It is the least developed region in the country, and it features some of the most pristine rainforests, extensive cave networks, coastal lowland plains, and offshore cays. Toledo is home to a wide range of cultures: Mopan and Kekchi Maya, Creole, the Garifuna, East Indians, Mennonites, Mestizos, and descendants of US Confederate settlers.
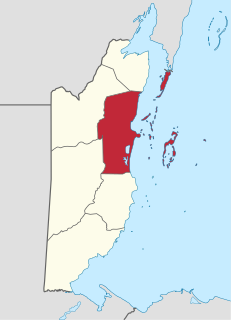
Belize District is a district of the nation of Belize. Its capital is Belize City.
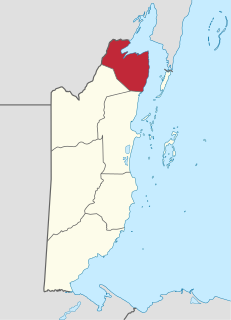
Corozal District is the northernmost district of the nation of Belize. The population was 33,894 in 2000. The district capital is Corozal Town.

Orange Walk District is a district in the northwest of the nation of Belize, with its district capital in Orange Walk Town.
Louisville is a village in the Corozal District of the nation of Belize, located at 18°19′N88°30′W. According to the 2000 census, it had a population of 655 people mainly from Maya Mestizo ancestry.

Xaibe is small rural settlement in the country of Belize mainly consisting of people from the Yucatec Maya ethnicity. It is located in Corozal District. The name Xaibe literally means 'crossroads'. The people of the Maya civilization often traversed across the village to reach other Maya villages. The population of the village is very small. The last available data of the population of Xaibe in 2010 revealed that it had a modest population of approximately 1,575 people. There is, however, evidence of the fact that the people belonging to the Maya civilization resided in the Xaibe village. These people then gradually shifted to Mexico, just across the border at the time of the Caste War of Yucatán. The village is known for celebrating the Maya tradition Hanal Pixan which means "food for the souls" also known as Day of the Dead.

Nim Li Punit is a Maya Classic Period site in the Toledo District of the nation of Belize, located 40 kilometres north of the town of Punta Gorda, at 16° 19' N, 88° 47' 60W. Nim Li Punit is sometimes known as Big Hat or Top Hat; the name is Kekchi Maya for "Big Hat", referring to the large elaborate head-dress on a stela sculpture found on site depicting one of the site's ancient kings.

Lubaantun is a pre-Columbian ruined city of the Maya civilization in southern Belize, Central America. Lubaantun is in Belize's Toledo District, about 42 kilometres (26 mi) northwest of Punta Gorda, and approximately 3.2 kilometres (2 mi) from the village of San Pedro Columbia, at an elevation of 61 metres (200 ft) feet above mean sea level. One of the most distinguishing features of Lubaantun is the large collection of miniature ceramic objects found on site; these detailed constructs are thought to have been charmstones or ritual-accompanying accoutrements.

San Pedro is a town on the southern part of the island of Ambergris Caye in the Belize District of the nation of Belize, in Central America. According to the 2015 mid-year estimates, the town has a population of about 16,444. It is the second-largest town in the Belize District and largest in the Belize Rural South constituency. The once sleepy fishing village was granted the status of a town in 1984.

Silver Creek is a village in the Toledo District of Belize. According to the 2000 census, Silver Creek had a population of 1,326 people. There is also a stream named Silver Creek at this same location. Near the village of Silver Creek is an ancient Maya civilization site. Nearby there is a larger Maya site from at least as early as 700 AD, Lubaantun.

Roaring Creek is a small village in the Cayo District of Belize, just north-west of Belmopan. Its name is derived from the creek waterfalls which flow into the Belize River next to the Guanacaste Park area.

Indian Church is a small remote village in the Orange Walk District of Belize. It is located on the west bank of New River, neighbouring the town of San Carlos to its south, and the Maya ruins of Lamanai to its north. According to the 2010 census, Indian Church has a population of 267 people in 66 households. The village is named for the historic Spanish churches recovered among the ancient Maya ruins. The residents lived among the ruins until 1991 when the Government of Belize established the 2-square-mile (5.2 km2) Lamanai Archaeological Reserve maintained by Belize's Institute of Archaeology.

Monkey River is a coastal watercourse in southern Belize that rises in the Maya Mountains and discharges to the Caribbean Sea near Monkey River Town. One of Belize's major rivers, Monkey River has northern headwaters which originate in the Cockscomb Basin Wildlife Sanctuary, where the Swasey Branch drains the East Basin of that wildlife sanctuary. Further south, the Bladen Branch watercourse drains the eastern slopes of the Maya Mountains including the ancient Mayan settlement areas of Lubaantun and Nim Li Punit. These two watercourses join to form the Monkey River approximately 16 kilometres upstream from the mouth of the Monkey River. The Monkey River is readily navigated throughout the year using small boats, but navigation above the major confluence becomes more difficult due to lack of depth when the dry season starts about February. Habitats in this watershed provide cover for such diverse species as the ocelot, jaguar, Guatemalan black howler, bare-throated tiger heron, Morelet's crocodile, fer-de-lance and manatee.
The History of Belize dates back thousands of years. The Maya civilization spread into the area of Belize between 1500 BC to 1200 BC and flourished until about 1000 AD. Several Maya ruin sites, including Cahal Pech, Caracol, Lamanai, Lubaantun, Altun Ha, and Xunantunich reflect the advanced civilization and much denser population of that period. The first recorded European incursions in the region were made by Spanish conquistadors and missionaries in the 16th century, secondly there was a demand. great cabinestmakers like sheraton shipbuild industry was beginning to use mahogany.
Cotton Tree Lodge is a jungle lodge in the Toledo District of Belize. The lodge was built in 2006 and opened January 2007. The property is situated 12 miles (19 km) west of the nearest major town, Punta Gorda, between the two Maya villages of Santa Ana and San Felipe, and on the banks of the Moho River.
Norman Hammond is a British archaeologist, academic and Mesoamericanist scholar, noted for his publications and research on the pre-Columbian Maya civilization.

Hispanic Belizeans, Latin Belizean or Belizean Mestizos are Belizeans of Hispanic and mestizo descent. Currently, they comprise around 52.9% of Belize's population.

The extensive trade networks of the Ancient Maya contributed largely to the success of their civilization spanning three millennia. The Maya royals control and wide distribution of foreign and domestic commodities for both population sustenance and social affluence are hallmarks of the Maya visible throughout much of the iconography found in the archaeological record. In particular, moderately long distance trade of foreign commodities from the Caribbean and Gulf Coasts provided the larger inland Maya cities with the resources they needed to sustain settled population levels in the several thousands. Though the ruling class essentially controlled the trade economy, a middle merchant class supervised import and export from cities and trade ports. Not much is known of the Maya merchant class; however, merchants of royal lineage are sometimes represented in the iconography. Notably, a canoe paddle often accompanies the royal merchant depictions, signifying their association with marine resources. Water lilies are also a recognizable feature of Maya iconography, appearing on ceramics and murals in landlocked cities like Palenque where the lilies cannot grow, further indicating the important political symbolism of water connections. The dugout style canoes of the Maya and other small watercraft are also represented in various codices, sometimes ferrying royal figures or deities. The rich tradition of maritime trade has continued into the modern era, exemplified by the resource exploitation of the coastal lagoons and cay locations along the Caribbean coast of Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. Eventually, the intensification of maritime trade reliance aided in the collapse of interior Maya power regimes, shifting political influence to coastal polities such as Uxmal and Chichen Itza in the Terminal Classic. A seaborne trade economy would continue to dominate the Maya civilization until the period of European Contact.
Jaime José Awe is a Belizean archaeologist who specializes in the ancient Maya, an Associate Professor of Anthropology at Northern Arizona University, and the Director of the Belize Valley Archaeological Reconnaissance Project.












