The Mahabodhi Temple or the Mahābodhi Mahāvihāra, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is an ancient, but restored Buddhist temple in Bodh Gaya, Bihar, India, marking the location where the Buddha is said to have attained enlightenment. Bodh Gaya is 15 km from Gaya and is about 96 km (60 mi) from Patna. The site contains a descendant of the Bodhi Tree under which the Buddha gained enlightenment, and has been a major pilgrimage destination of Buddhists for over two thousand years.

Sanchi Stupa is a Buddhist complex, famous for its Great Stupa, on a hilltop at Sanchi Town in Raisen District of the State of Madhya Pradesh, India. It is located, about 23 kilometers from Raisen town, district headquarter and 46 kilometres (29 mi) north-east of Bhopal, capital of Madhya Pradesh.

In Buddhism, a stupa is a mound-like or hemispherical structure containing relics that is used as a place of meditation.

The Greco-Buddhist art or Gandhara art is the artistic manifestation of Greco-Buddhism, a cultural syncretism between Ancient Greek art and Buddhism. It had mainly evolved in the ancient region of Gandhara, located in the northwestern fringe of the Indian subcontinent.
The Shunga dynasty was the Fifth ruling dynasty of Magadha and controlled most of the northern Indian subcontinent from around 187 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pushyamitra, after taking the throne of Magadha from the Mauryas. The Shunga Empire's capital was Pataliputra, but later emperors such as Bhagabhadra also held court at Besnagar in eastern Malwa. This dynasty is also responsible for successfully fighting and resisting the Greeks in Shunga-Greek War.

The Heliodorus pillar is a stone column that was erected around 113 BCE in central India in Besnagar (Vidisha), Madhya Pradesh. The pillar was called the Garuda-standard by Heliodorus (ambassador), referring to the deity Garuda. The pillar is commonly named after Heliodorus, who was an ambassador of the Indo-Greek king Antialcidas from Taxila, and was sent to the Indian ruler Bhagabhadra. A dedication written in Brahmi script was inscribed on the pillar, venerating Vāsudeva (krishna), the Deva deva the "God of Gods" and the Supreme Deity. The pillar also glorifies the Indian ruler as "Bhagabhadra the savior". The pillar is a stambha which symbolizes joining earth, space and heaven, and is thought to connote the "cosmic axis" and express the cosmic totality of the Deity.

The pillars of Ashoka are a series of monolithic pillars dispersed throughout the Indian subcontinent, erected—or at least inscribed with edicts—by the 3rd Mauryan Emperor Ashoka the Great, who reigned from c. 268 to 232 BC. Ashoka used the expression Dhaṃma thaṃbhā, i.e. "pillars of the Dharma" to describe his own pillars. These pillars constitute important monuments of the architecture of India, most of them exhibiting the characteristic Mauryan polish. Twenty of the pillars erected by Ashoka still survive, including those with inscriptions of his edicts. Only a few with animal capitals survive of which seven complete specimens are known. Two pillars were relocated by Firuz Shah Tughlaq to Delhi. Several pillars were relocated later by Mughal Empire rulers, the animal capitals being removed. Averaging between 12 and 15 m in height, and weighing up to 50 tons each, the pillars were dragged, sometimes hundreds of miles, to where they were erected.

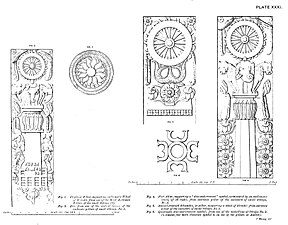
Bharhut is a village located in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh, central India. It is known for its famous relics from a Buddhist stupa. What makes Bharhut panels unique is that each panel is explicitly labelled in Brahmi characters mentioning what the panel depicts. The major donor for the Bharhut stupa was King Dhanabhuti.

Sculpture in the Indian subcontinent, partly because of the climate of the Indian subcontinent makes the long-term survival of organic materials difficult, essentially consists of sculpture of stone, metal or terracotta. It is clear there was a great deal of painting, and sculpture in wood and ivory, during these periods, but there are only a few survivals. The main Indian religions had all, after hesitant starts, developed the use of religious sculpture by around the start of the Common Era, and the use of stone was becoming increasingly widespread.

The Indo-Greeks practiced numerous religions during the time they ruled in the northwestern Indian subcontinent from the 2nd century BCE to the beginning of the 1st century CE. In addition to the worship of the Classical pantheon of the Greek deities found on their coins, the Indo-Greeks were involved with local faiths, particularly with Buddhism, but also with Hinduism and Zoroastrianism.

Indo-Greek art is the art of the Indo-Greeks, who reigned from circa 200 BCE in areas of Bactria and the Indian subcontinent. Initially, between 200 and 145 BCE, they remained in control of Bactria while occupying areas of Indian subcontinent, until Bactria was lost to invading nomads. After 145 BCE, Indo-Greek kings ruled exclusively in parts of ancient India, especially in Gandhara, in what is now present-day the northwestern Pakistan. The Indo-Greeks had a rich Hellenistic heritage and artistic proficiency as seen with the remains of the city of Ai-Khanoum, which was founded as a Greco-Bactrian city. In modern-day Pakistan, several Indo-Greeks cities are known such as Sirkap near Taxila, Barikot, and Sagala where some Indo-Greek artistic remains have been found, such as stone palettes.

Amarāvati Stupa is a ruined Buddhist stūpa at the village of Amaravathi, Palnadu district, Andhra Pradesh, India, probably built in phases between the third century BCE and about 250 CE. It was enlarged and new sculptures replaced the earlier ones, beginning in about 50 CE. The site is under the protection of the Archaeological Survey of India, and includes the stūpa itself and the Archaeological Museum.

Hellenistic influence on Indian art and architecture reflects the artistic and architectural influence of the Greeks on Indian art following the conquests of Alexander the Great, from the end of the 4th century BCE to the first centuries of the common era. The Greeks in effect maintained a political presence at the doorstep, and sometimes within India, down to the 1st century CE with the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom and the Indo-Greek Kingdoms, with many noticeable influences on the arts of the Maurya Empire especially. Hellenistic influence on Indian art was also felt for several more centuries during the period of Greco-Buddhist art.
The Northern Satraps, or sometimes Satraps of Mathura, or Northern Sakas, are a dynasty of Indo-Scythian ("Saka") rulers who held sway over the area of Punjab and Mathura after the decline of the Indo-Greeks, from the end of the 1st century BCE to the 2nd century CE. They are called "Northern Satraps" in modern historiography to differentiate them from the "Western Satraps", who ruled in Sindh, Gujarat and Malwa at roughly the same time and until the 4th century CE. They are thought to have replaced the last of the Indo-Greek kings in the Punjab region, as well as the Mitra dynasty and the Datta dynasty of local Indian rulers in Mathura.

The Art of Mathura refers to a particular school of Indian art, almost entirely surviving in the form of sculpture, starting in the 2nd century BCE, which centered on the city of Mathura, in central northern India, during a period in which Buddhism, Jainism together with Hinduism flourished in India. Mathura "was the first artistic center to produce devotional icons for all the three faiths", and the pre-eminent center of religious artistic expression in India at least until the Gupta period, and was influential throughout the sub-continent.
The Bharhut Yavana is a high relief of a warrior which was discovered among the reliefs of the railings around the Bharhut Stupa. It is dated to circa 100 BCE, with a range from 150 BCE to 80 BCE. The relief is currently in the Indian Museum in Kolkata. The man in the relief has been described as a Greek, called "Yavanas" among the Indians.

Bairat Temple is a freestanding Buddhist temple, a Chaityagriha, located about a mile southwest of the city Viratnagar, Rajasthan, India, on a hill locally called "Bijak-ki-Pahari". The temple is of a circular type, formed of a central stupa surrounded by a circular colonnade and an enclosing wall. It was built during the time of Ashoka in the 3rd century BCE, and near it were found two of Ashoka's Minor Rock Edicts, the Bairat and the Calcutta-Bairat Minor Rock Edicts. It is the earliest circular Buddhist shrine and therefore, Bairat temple is an important marker of the architecture of India.

Ancient Indian architecture ranges from the Indian Bronze Age to around 800 CE. By this endpoint Buddhism in India had greatly declined, and Hinduism was predominant, and religious and secular building styles had taken on forms, with great regional variation, which they largely retain even after some forceful changes brought about by the arrival of first Islam, and then Europeans.

Dhanabhūti or Vatsiputra Dhanabhūti was a 2nd or 1st-century BCE Buddhist king in Central India, and the most prominent donor for the Bharhut stupa. He appears in two or three major dedicatory inscriptions at the stupa of Bharhut, and possibly in another inscription at Mathura. Dhanabhuti may have been a feudatory of the Sunga Empire, or a ruler in a neighbouring territory, such as Kosala or Panchala, or possibly a northern king from Sughana in Haryana. or he may have also been part of the Mitra dynasty of Kosambi.

Indo-Scythian art developed under the various dynasties of Indo-Scythian rulers in northwestern India, from the 1st century BCE to the early 5th century CE, encompassing the productions of the early Indo-Scythians, the Northern Satraps and the Western Satraps. It follows the development of Indo-Greek art in northwestern India. The Scythians in India were ultimately replaced by the Kushan Empire and the Gupta Empire, whose art form appear in Kushan art and Gupta art.