
The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word Acropolis is from the Greek words ἄκρον and πόλις. The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was also more properly known as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king.

Mount Lykaion is a mountain in Arcadia, Greece. Lykaion has two peaks: Stefani to the north and St. Ilias to the south where the altar of Zeus is located.

The Temple of Olympian Zeus, also known as the Olympieion or Columns of the Olympian Zeus, is a colossal temple in the centre of Athens, now in ruins. It was dedicated to "Olympian" Zeus, a name originating from his position as head of the Olympian gods. Construction began in the 6th century BC during the rule of the Athenian tyrants, who envisioned building the greatest temple in the ancient world, but it was not completed until the reign of Roman Emperor Hadrian in the 2nd century AD, some 638 years after the project had begun. During the Roman period, the temple, which included 104 colossal columns, was renowned as the largest temple in Greece and housed one of the largest cult statues in the ancient world.

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Hestia is the virgin goddess of the hearth and the home. In myth, she is the firstborn child of the Titans Cronus and Rhea, and one of the Twelve Olympians.

Pandrosos or Pandrosus was known in Greek myth as one of the three daughters of Cecrops I, the first king of Athens, and Aglaurus, daughter of King Actaeus.

Cecrops was a legendary king of Attica which derived from him its name Cecropia, according to the Parian Chronicle having previously borne the name of Acte or Actice. He was the founder and the first king of Athens itself though preceded in the region by the earth-born king Actaeus of Attica. Cecrops was a culture hero, teaching the Athenians marriage, reading and writing, and ceremonial burial.

The Erechtheion or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple on the north side of the Acropolis, Athens, which was primarily dedicated to the goddess Athena.

The Pnyx is a hill or hillside in central Athens, the capital of Greece. Beginning as early as 507 BC, the Athenians gathered on the Pnyx to host their popular assemblies, thus making the hill one of the earliest and most important sites in the creation of democracy.

The Temple of Athena Nike is a temple on the Acropolis of Athens, dedicated to the goddesses Athena and Nike. Built around 420 BC, the temple is the earliest fully Ionic temple on the Acropolis. It has a prominent position on a steep bastion at the south west corner of the Acropolis to the right of the entrance, the Propylaea. In contrast to the Acropolis proper, a walled sanctuary entered through the Propylaea, the Victory Sanctuary was open, entered from the Propylaea's southwest wing and from a narrow stair on the north. The sheer walls of its bastion were protected on the north, west, and south by the Nike Parapet, named for its frieze of Nikai celebrating victory and sacrificing to their patroness, Athena and Nike.
In ancient Greece, the Buphonia denoted a sacrificial ceremony performed at Athens as part of the Dipolieia, a religious festival held on the 14th of the midsummer month Skirophorion—in June or July—at the Acropolis. In the Buphonia a working ox was sacrificed to Zeus Polieus, Zeus protector of the city, in accordance with a very ancient custom. A group of oxen was driven forward to the altar at the highest point of the Acropolis. On the altar a sacrifice of grain had been spread by members of the family of the Kentriadae, on whom this duty devolved hereditarily. When one of the oxen began to eat, thus selecting itself for sacrifice, one of the family of the Thaulonidae advanced with an axe, slayed the ox, then immediately threw aside the axe and fled the scene of his guilt-laden crime.

Lycosura was a city in the ancient Parrhasia region of south Arcadia said by Pausanias to be the oldest city in the world, although there is no evidence for its existence before the fourth century BCE. Its current significance is chiefly associated with the sanctuary of the goddess Despoina, which contained a colossal sculptural group that Pausanias wrote was made by Damophon of Messene. This group comprises acrolithic-technique statues of Despoina and Demeter seated on a throne, with statues of Artemis and the Titan Anytos standing on either side of them – all in Pentelic marble. The dates of both the temple and the sculptural group have occasioned some dispute. Remains of a stoa, altars, and other structures have been found at the site as well. The Sanctuary of Despoina at Lycosoura is located 9 km WSW of Megalopolis, 6.9 km SSE of Mount Lykaion, and 160 km SW of Athens. There is a small museum at the archaeological site housing small finds as well as part of the cult group, while the remains of the cult statues of Despoina and Demeter are displayed at the National Archaeological Museum of Athens.

The Brauroneion was the sanctuary of Artemis Brauronia on the Athenian Acropolis, located in the southwest corner of the Acropolis plateau, between the Chalkotheke and the Propylaea in Greece. It was originally dedicated during the reign of Peisistratos. Artemis Brauronia, protector of women in pregnancy and childbirth, had her main sanctuary at Brauron, a demos on the east coast of Attica.

The Pandroseion was a sanctuary dedicated to Pandrosus, one of the daughters of Cecrops I, the first king of Attica Greece, located on the Acropolis of Athens. It occupied the space adjacent to the Erechtheum and the old Temple of Athena Polias.
In Ancient Greece, the Lykaia was an archaic festival with a secret ritual on the slopes of Mount Lykaion, the tallest peak in Arcadia. The rituals and myths of this primitive rite of passage centered upon an ancient threat of cannibalism and the possibility of a werewolf transformation for the epheboi who were the participants. The festival occurred yearly, probably at the beginning of May.

The Sanctuary of Apollo Maleatas is located on a low hill on Mount Kynortion, east of the sanctuary of Asklepios at Epidaurus.
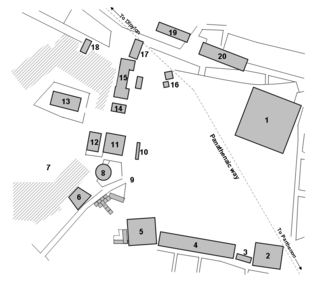
The Altar of the Twelve Gods, was an important altar and sanctuary at Athens, located in the northwest corner of the Classical Agora. The Altar was set up by Pisistratus the Younger, during his archonship, in 522/1 BC. It marked the central point from which distances from Athens were measured and was a place of supplication and refuge.

In Greek mythology, Gaia, also spelled Gaea, is the personification of Earth. Gaia is the ancestral mother—sometimes parthenogenic—of all life. She is the mother of Uranus (Sky), from whose sexual union she bore the Titans, the Cyclopes, and the Giants, as well as of Pontus (Sea), from whose union she bore the primordial sea gods. Her equivalent in the Roman pantheon was Terra.
Scambonidae or Skambonidai was a deme of ancient Attica, located in the city of Athens. It was located within the Themistoclean Wall, north of the Acropolis.

The Temple of Athena Lindia was a sanctuary in Lindos in Rhodes, dedicated to the goddess Athena. It was a significant Pan-Hellenic shrine of Athena and arguably the regional center of her cult.
The Cave Sanctuaries of the Acropolis of Athens are the natural fissures in the rock of the Acropolis hill that were used as sites of worship for deities of the Panhellenic pantheon in antiquity. Traditionally a sharp distinction has been drawn between the state religion practised on the summit of the Acropolis and the cult practice of the shrines on the lower slopes. Recently, however, interest has burgeoned in the individual religious experience or personal piety in Greek society of which these cult sites may be the expression. The proceeding description follows the order of the shrines from the Klepsydra at the northwest face of the Acropolis clockwise via the Peripatos round to the foot of the Nike bastion.

















