
A bacteriophage, also known informally as a phage, is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaea. The term was derived from "bacteria" and the Greek φαγεῖν, meaning "to devour". Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structures that are either simple or elaborate. Their genomes may encode as few as four genes and as many as hundreds of genes. Phages replicate within the bacterium following the injection of their genome into its cytoplasm.
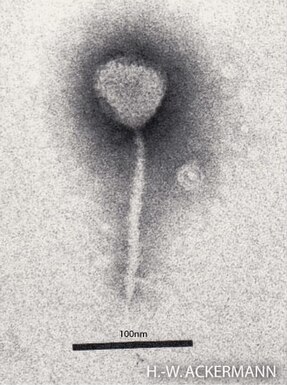
Enterobacteria phage λ is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli. It was discovered by Esther Lederberg in 1950. The wild type of this virus has a temperate life cycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase, during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring. Lambda strains, mutated at specific sites, are unable to lysogenize cells; instead, they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell.

Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. Formed in 1945 and led by Delbrück along with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey, the Phage Group made substantial headway unraveling important aspects of genetics. The three shared the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the replication mechanism and the genetic structure of viruses". He was the first physicist to predict what is now called Delbrück scattering.

Alfred Day Hershey was an American Nobel Prize–winning bacteriologist and geneticist.

Eric Francis Wieschaus is an American evolutionary developmental biologist and 1995 Nobel Prize-winner.

Filamentous bacteriophage is a family of viruses (Inoviridae) that infect bacteria. The phages are named for their filamentous shape, a worm-like chain, about 6 nm in diameter and about 1000-2000 nm long. The coat of the virion comprises five types of viral protein, which are located during phage assembly in the inner membrane of the host bacteria, and are added to the nascent virion as it extrudes through the membrane. The simplicity of this family makes it an attractive model system to study fundamental aspects of molecular biology, and it has also proven useful as a tool in immunology and nanotechnology.

Franklin (Frank) William Stahl is an American molecular biologist and geneticist. With Matthew Meselson, Stahl conducted the famous Meselson-Stahl experiment showing that DNA is replicated by a semiconservative mechanism, meaning that each strand of the DNA serves as a template for production of a new strand.
Allan M. Campbell was an American microbiologist and geneticist whose pioneering work on Lambda phage has helped advance molecular biology in the late 20th century.
Barbara J. Meyer is a biologist and genetist, noted for her pioneering research on lambda phage, a virus that infects bacteria; discovery of the master control gene involved in sex determination; and studies of gene regulation, particularly dosage compensation. Meyer’s work has revealed mechanisms of sex determination and dosage compensation—that balance X-chromosome gene expression between the sexes in Caenorhabditis elegans that continue to serve as the foundation of diverse areas of study on chromosome structure and function today.

Mark Ptashne is a molecular biologist. He is the Ludwig Chair of Molecular Biology at Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center in New York City.
Lynn W. Enquist is Professor Emeritus in Molecular Biology at Princeton University, as well as founding editor of the journal Annual Review of Virology. His research focuses on neuroinvasive alpha-herpesviruses.
Gisela Mosig was a German-American molecular biologist best known for her work with enterobacteria phage T4. She was among the first investigators to recognize the importance of recombination intermediates in establishing new DNA replication forks, a fundamental process in DNA replication.
Armin Dale Kaiser was an American biochemist, molecular geneticist, molecular biologist and developmental biologist.

Susan Gottesman is a microbiologist at the National Cancer Institute (NCI), which is part of the National Institutes of Health. Gottesman has been the editor of the Annual Review of Microbiology since 2008.

cII or transcriptional activator II is a DNA-binding protein and important transcription factor in the life cycle of lambda phage. It is encoded in the lambda phage genome by the 291 base pair cII gene. cII plays a key role in determining whether the bacteriophage will incorporate its genome into its host and lie dormant (lysogeny), or replicate and kill the host (lysis).

Grete Kellenberger-Gujer (1919–2011) was a Swiss molecular biologist known for her discoveries on genetic recombination and restriction modification system of DNA. She was a pioneer in the genetic analysis of bacteriophages and contributed to the early development of molecular biology.
Nat L. Sternberg was an American molecular biologist and bacteriophage researcher, particularly known for his work on DNA recombination and the phage P1.
Sushil Kumar was an Indian geneticist and academic, known for his Plant and microbial genetical genomics, especially the studies on Escherichia coli and Lambda phage as well as on the mutants of Rhizobium. He was a former director of the Central Institute of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research and an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, National Academy of Agricultural Sciences, National Academy of Sciences, India, and Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards, in 1981, for his contributions to biological sciences.

Helios Murialdo is a Chilean-Canadian molecular biologist, fiction writer, and ecologist. His research in the field of the assembly and structure of bacterial viruses contributed to the development of the first system for the cloning of human genes. He has published six novels and is a member of a group of conservationists that established a Natural Reserve in the central part of the Chilean Biodiversity Hotspot. Son of an Italian immigrant father and a Chilean mother of French descent, he has a brother and a sister. He is a member of the board of directors of the non-profit Fundación Ciencia & Vida, a scientific and technological institution with headquarters in Santiago, Chile. He is president of the NGO Corporación Altos de Cantillana, which manages the 26,000 acres of the Altos de Cantillana Natural Reserve in the coastal mountains of central Chile. He makes his home in this Natural Reserve, and spends the rest of the year in Toronto, Canada.
Anna Marie (Ann) Skalka is an American virologist, molecular biologist and geneticist who is Professor Emeritus and Senior Advisor to the President at the Fox Chase Cancer Center. She is a co-author of a textbook on virology, Principles of Virology.












