
The genus Satyrium contains butterflies in the family Lycaenidae. The species of this genus are found in the Holarctic ecozone. For distribution information see Further reading "Le genre Satyrium".

Sericinus is a genus of swallowtail butterflies placed in the subfamily Parnassiinae. The genus has a complex history and a multiplicity of names have been applied to its single species.

Favonius is a Palearctic genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae.

Diacrisia sannio, the clouded buff, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae.

Katha depressa, the buff footman, is a moth of the family Erebidae found in Asia and Europe. It was first described by Eugenius Johann Christoph Esper in 1787.

Sinia is a genus of butterflies in the family Lycaenidae first described by Walter Forster in 1940. The species of this genus are found in the far eastern Palearctic realm.

Satyrium mera is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It is endemic to Japan. The larva on feeds on Rhamnus (Rhamnaceae). Satyrium mera is single brooded and overwinters as an egg.

Coenophila subrosea, the rosy marsh moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by James Francis Stephens in 1829. It is found from southern Great Britain, Italy and France, through central Europe north to Scandinavia, east to Russia, from Siberia to the Amur region, Ussuri and Sakhalin, south to northern China, east to Korea and northern Japan.

Diarsia brunnea, the purple clay, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. The species was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775. It is found in most of Europe, east to Transcaucasia, the Caucasus, central Asia, Siberia, the Kuriles, Amur, Ussuri, Sakhalin, Korea, Japan, and China, including China's Tibet region.
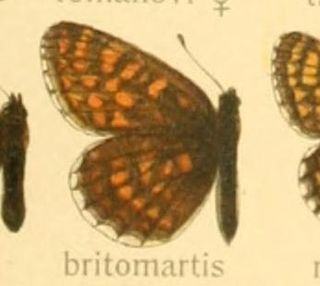
Melitaea britomartis, or Assmann's fritillary, is a butterfly in the family Nymphalidae. It has a wide geographic range and is represented by three subspecies.
Aemene taeniata is a moth of the family Erebidae first described by Johann Heinrich Fixsen in 1887. It is found in the Russian Far East and Korea.

Sephisa princeps is a species of butterfly of the family Nymphalidae. It was described by Johann Heinrich Fixsen in 1887. It is found in the Russian Far East, north-eastern China and Korea. The habitat consists of oak forests.

Satyrium prunoides is a butterfly of the family Lycaenidae. It was described by Otto Staudinger in 1887. It is found in the Russian Far East, Mongolia, north-eastern China and Korea.

Satyrium herzi is a butterfly of the subfamily Lycaeninae. It was described by Johann Heinrich Fixsen in 1887. It is found in the Russian Far East, north-eastern China and Korea.

Rapala arata is a small butterfly found in the East Palearctic that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family.

Chrysozephyrus brillantinus is a small butterfly found in the East Palearctic that belongs to the lycaenids or blues family.

Satyrium eximius is a butterfly found in the East Palearctic that belongs to the blues family.













