
Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.
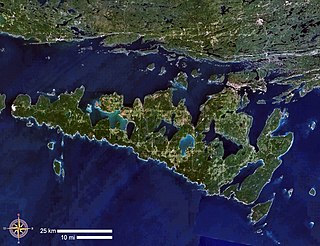
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of 2,766 km2 (1,068 sq mi), it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 lakes itself. In addition to the historic Anishinaabe and European settlement of the island, archaeological discoveries at Sheguiandah have demonstrated Paleo-Indian and Archaic cultures dating from 10,000 BC to 2,000 BC.
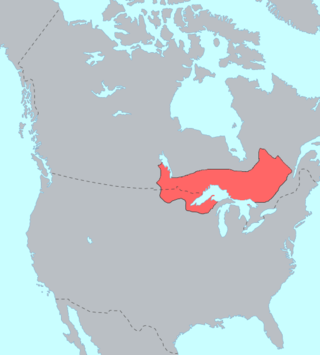
The Ojibwe are an Anishinaabe people whose homeland covers much of the Great Lakes region and the northern plains, extending into the subarctic and throughout the northeastern woodlands. The Ojibwe, being Indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands and of the subarctic, are known by several names, including Ojibway or Chippewa. As a large ethnic group, several distinct nations also consider themselves Ojibwe, including the Saulteaux, Nipissings, and Oji-Cree.

The Potawatomi, also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie, are a Native American people of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquian family. The Potawatomi call themselves Neshnabé, a cognate of the word Anishinaabe. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibwe and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother". Their people are referred to in this context as Bodéwadmi, a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples.
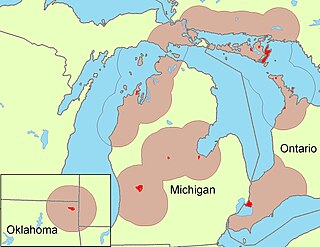
The Odawa are an Indigenous American people who primarily inhabit land in the Eastern Woodlands region, now in jurisdictions of the northeastern United States and southeastern Canada. Their territory long preceded the creation of the current border between the two countries in the 18th and 19th centuries.
The Council of Three Fires is a long-standing Anishinaabe alliance of the Ojibwe, Odawa, and Potawatomi North American Native tribes.
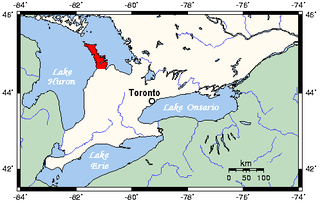
The Bruce Peninsula is a peninsula in Ontario, Canada, that divides Georgian Bay of Lake Huron from the lake's main basin. The peninsula extends roughly northwestwards from the rest of Southwestern Ontario, pointing towards Manitoulin Island, with which it forms the widest strait joining Georgian Bay to the rest of Lake Huron. The Bruce Peninsula contains part of the geological formation known as the Niagara Escarpment. The entire peninsula and nearby communities to the south along Lake Huron are located within Bruce County, Ontario.

Sauble Beach is a beach community and unincorporated area in the town of South Bruce Peninsula, Bruce County, in the northern area of southwestern Ontario, Canada. It is on the Bruce Peninsula, along the eastern shore of Lake Huron, on the north edge of the Saugeen First Nation. The beach takes its name from that given by early French explorers to the sandy Sauble River, originally "La Rivière Au Sable" also indicating that the river emptied into Lake Huron at a sandy beach. The river was labelled with the French name on maps until 1881, when it became the Sauble River; in early years, a sawmill was built on the river, and later, a hydro electric plant.

The Anishinaabe are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe, Odawa, Potawatomi, Mississaugas, Nipissing, and Algonquin peoples. The Anishinaabe speak Anishinaabemowin, or Anishinaabe languages that belong to the Algonquian language family.
Saugeen First Nation is an Ojibway First Nation band located along the Saugeen River and Bruce Peninsula in Ontario, Canada. The band states that their legal name is the "Chippewas of Saugeen". Organized in the mid-1970s, Saugeen First Nation is the primary "political successor apparent" to the Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory; the other First Nation that is a part of Chippewas of Saugeen Ojibway Territory is Cape Croker. The Ojibway are of the Algonquian languages family. The First Nation consist of four reserves: Chief's Point 28, Saugeen 29, Saugeen Hunting Grounds 60A, and Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1.
First Nations in Ontario constitute many nations. Common First Nations ethnicities in the province include the Anishinaabe, Haudenosaunee, and the Cree. In southern portions of this province, there are reserves of the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca and Tuscarora.

The Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa Indians is a federally recognized Native American tribe located in northwest Michigan on the Leelanau Peninsula. Sandra Witherspoon is the current tribal chairperson, elected in May 2024 to a four-year term after succeeding David Arroyo, who served a single term from 2020 to 2024.
The Robinson Treaties are two treaties signed between the Ojibwa chiefs and the Crown in 1850 in the Province of Canada. The first treaty involved Ojibwa chiefs along the north shore of Lake Superior, and is known as the Robinson Superior Treaty. The second treaty, signed two days later, included Ojibwa chiefs from along the eastern and northern shores of Lake Huron, and is known as the Robinson Huron Treaty. The Wiikwemkoong First Nation did not sign either treaty, and their land is considered "unceded".

Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation is an Anishinaabek First Nation from the Bruce Peninsula region in Ontario, Canada. Along with the Saugeen First Nation, they form the Saugeen Ojibway Nation. The Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation had a registered membership of 2758 individuals, as of December 2020. Approximately 700 members live on the main reserve, Neyaashiinigmiing 27. The First Nation has 3 reserves, Neyaashiinigmiing 27, Cape Croker Hunting Ground 60B and Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1. The size of all reserves is 8083.70 hectares.

Basil H. Johnston was an Anishinaabe (Ojibwa) and Canadian writer, storyteller, language teacher and scholar.
Peggy J. Blair is a Canadian lawyer and author. Blair has been a member of the Law Society of Upper Canada since 1990 and is a past member of the Law Society of Alberta (1982–1999). Blair is considered an expert in Indigenous legal issues. After leaving active law practice, Blair has become a mystery writer.
Anishinaabe tribal political organizations are political consortiums of Anishinaabe nations that advocate for the political interests of their constituencies. Anishinaabe people of Canada are considered as First Nations, and of the United States as Native Americans.
Saugeen may refer to the following in Ontario, Canada:

The Caldwell First Nation is a First Nations band government whose land base is located in Leamington, Ontario, Canada. They are an Anishinaabe group, part of the Three Fires Confederacy, comprising the bands Potawatomi, Odawa, and Ojibwa, whose members are originally of the Mikinaak (Turtle) and the Makwa (Bear) dodems. The Caldwell First Nation are a distinct and federally recognized Indian band and used to be referred to by such names as the "Chippewas of Pelee", "Point Pelee Indians" and "Caldwell's band of Indians."
Saugeen and Cape Croker Fishing Islands 1 is a First Nations reserve consisting of 89 islands in Lake Huron off the western coast of the Bruce Peninsula in Ontario. They extend north of Chief's Point 28 for 11 miles (18 km) up to Pike Bay. These islands are shared between the Chippewas of Nawash Unceded First Nation and Saugeen First Nation.











