
Rafflesia is a genus of parasitic flowering plants in the family Rafflesiaceae. The species have enormous flowers, the buds rising from the ground or directly from the lower stems of their host plants; one species has the largest flower in the world. Plants of the World Online lists up to 41 species from this genus, all of them are found throughout Southeast Asia.

The bay cat, also known as the Bornean bay cat, is a small wild cat endemic to the island of Borneo that appears to be relatively rare compared to sympatric wild cats, based on the paucity of historical, as well as recent records. Since 2002, it has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List because it is estimated that fewer than 2,500 mature individuals exist, and that the population declined in the past. The bay cat has been recorded as rare and seems to occur at relatively low density, even in pristine habitat.

Nepenthes tentaculata, or the fringed pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant with a wide distribution across Borneo and Sulawesi. It grows at altitudes of 400–2550 m.
Datin Anthea Phillipps B.Sc. is a British botanist based in Sabah, Malaysia, specialising in pitcher plants and rhododendrons.

Nepenthes lowii, or Low's pitcher-plant, is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to Borneo. It is named after Hugh Low, who discovered it on Mount Kinabalu. This species is perhaps the most unusual in the genus, being characterised by its strongly constricted upper pitchers, which bear a greatly reduced peristome and a reflexed lid with numerous bristles on its lower surface.

Hanguana is a genus of flowering plants with a dozen known species. It is the only genus in the family Hanguanaceae.
Mount Trusmadi or Trus Madi is a mountain located at the Interior Division of Sabah, Malaysia. It is considered as the second highest mountain in both Sabah and Malaysia at 2,642 metres (8,668 ft), after Mount Kinabalu with Trusmadi offering a tougher climbing challenge than the latter.

The Borneo peat swamp forests ecoregion, within the tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests biome, are on the island of Borneo, which is divided between Brunei, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Anisophyllea nitida is a tree of Borneo in the family Anisophylleaceae. The specific epithet nitida is from the Latin meaning "polished", referring to the shiny appearance of the upper leaf surface.
Canarium pseudopimela is a tree of Borneo in the incense tree family Burseraceae. The specific epithet pseudopimela is from the Latin meaning "false pimela", referring to the species' resemblance to Canarium pimela.

Homalomena is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. Homalomena are found in southern Asia and the southwestern Pacific. Many Homalomena have a strong smell of anise. The name derives apparently from a mistranslated Malayan vernacular name, translated as homalos, meaning flat, and mene = moon.

Schismatoglottis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. Members of the genus are similar in appearance and growth habit to those of the genus Homalomena, but the two genera are not closely related. The primary difference is that the leaves of Schismatoglottis are not aromatic. Schismatoglottis are found primarily in tropical parts of Southeast Asia, New Guinea, and Melanesia. The majority of the species are native to the Island of Borneo.

Bucephalandra is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. There are 30 species of Bucephalandra which have been discovered in Borneo and have been formally described by S.Y. Wong and P.C. Boyce. Most of the species are found in Borneo. Bucephalandra are usually found growing as dense mats over stones or rocks in streams or rivers in moist tropical forest.

The Green Connection is an aquarium and science discovery center in Kota Kinabalu, Sabah, Malaysia. The Green Connection opened in May 2010 and is located just outside downtown Kota Kinabalu in the Northwest corner of the island of Borneo.

The island of Borneo is located on the Sunda Shelf, which is an extensive region in Southeast Asia of immense importance in terms of biodiversity, biogeography and phylogeography of fauna and flora that had attracted Alfred Russel Wallace and other biologists from all over the world.
Dacryodes elmeri is a tree in the family Burseraceae. It is named for the American botanist Adolph Elmer.
Vesta is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, formally described in 2018. It contains only one known species, Vesta longifolia, native to Perak in Peninsular Malaysia and to Brunei and Sarawak on the island of Borneo.
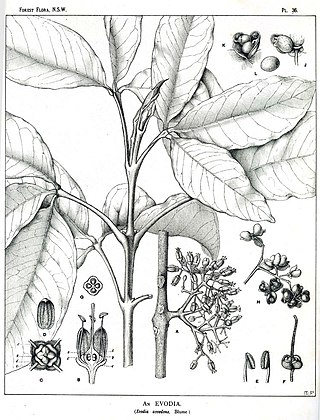
Melicope accedens is a plant in the family Rutaceae.
Alocasia melo is a species of flowering plant in the family Araceae, native to Sabah state in Malaysia. It grows on ultramafic soils. In the houseplant trade it is often sold as "Alocasia rugosa" due to its highly rugose leaves.
Schismatoglottis prietoi is an aquatic and semi-aquatic plant species in the family Araceae. It is endemic to the Philippines in fast-flowing freshwater rivers in lowland forests. It is the only known species in the genus Schismatoglottis that can grow in a fully aquatic habitat. It is a small plant, growing only up to 2 to 8 cm tall. The pale green to green leaves are smooth and are around 3 to 4 cm long and 1 to 2 cm wide. They are oblong to elliptical in shape with sharply pointed tips and broadly wavy edges. It bears a single white flower that produces an unpleasant odor at the base, reminiscent of spoiled milk. It is colonial, growing in dense clumps through stolons.











