
Headphones are a pair of small loudspeaker drivers worn on or around the head over a user's ears. They are electroacoustic transducers, which convert an electrical signal to a corresponding sound. Headphones let a single user listen to an audio source privately, in contrast to a loudspeaker, which emits sound into the open air for anyone nearby to hear. Headphones are also known as earphones or, colloquially, cans. Circumaural and supra-aural headphones use a band over the top of the head to hold the drivers in place. Another type, known as earbuds or earpieces, consists of individual units that plug into the user's ear canal; within that category have been developed cordless air buds using wireless technology. A third type are bone conduction headphones, which typically wrap around the back of the head and rest in front of the ear canal, leaving the ear canal open. In the context of telecommunication, a headset is a combination of a headphone and microphone.

Noise-cancelling headphones are headphones that suppress unwanted ambient sounds using active noise control (ANC).

Acoustical engineering is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typically concerned with the design, analysis and control of sound.

A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as personal sound amplification products (PSAPs) or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids".
Occupational noise is the amount of acoustic energy received by an employee's auditory system when they are working in the industry. Occupational noise, or industrial noise, is often a term used in occupational safety and health, as sustained exposure can cause permanent hearing damage. Occupational noise is considered an occupational hazard traditionally linked to loud industries such as ship-building, mining, railroad work, welding, and construction, but can be present in any workplace where hazardous noise is present.

An earplug is a device that is inserted in the ear canal to protect the user's ears from loud noises, intrusion of water, foreign bodies, dust or excessive wind. Earplugs may be used as well to improve sleep quality or focus in noisy environments. Since they reduce the sound volume, earplugs may prevent hearing loss and tinnitus, in some cases.

Earmuffs refer to two different items. Both items consist of a thermoplastic or metal head-band that fits over the top or back of the head, and a cushion or cup at each end to usually cover both ears. The cups can either be clothing accessories designed to cover a person's ears for warmth or personal protective equipment designed to cover a person's ears for hearing protection.
Plantronics, Inc. is an American electronics company producing audio communications equipment for business and consumers. Its products support unified communications, mobile use, gaming and music. Plantronics is headquartered in Santa Cruz, California, and most of its products are produced in China and Mexico.
Aircraft marshalling is visual signalling between ground personnel and pilots on an airport, aircraft carrier or helipad.
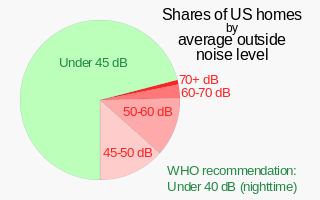
Noise health effects are the physical and psychological health consequences of regular exposure to consistent elevated sound levels. Noise from traffic, in particular, is considered by the World Health Organization to be one of the worst environmental stressors for humans, second only to air pollution. Elevated workplace or environmental noise can cause hearing impairment, tinnitus, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, annoyance, and sleep disturbance. Changes in the immune system and birth defects have been also attributed to noise exposure.

Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a hearing impairment resulting from exposure to loud sound. People may have a loss of perception of a narrow range of frequencies or impaired perception of sound including sensitivity to sound or ringing in the ears. When exposure to hazards such as noise occur at work and is associated with hearing loss, it is referred to as occupational hearing loss.

Hearing conservation programs are programs that should reduce the risk of hearing loss due to hazardous noise exposure, if implemented correctly and with high quality. Hearing conservation programs require knowledge about risk factors such as noise and ototoxicity, hearing, hearing loss, protective measures to prevent hearing loss at home, in school, at work, in the military and, and at social/recreational events, and legislative requirements. Regarding occupational exposures to noise, a hearing conservation program is required by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) "whenever employee noise exposures equal or exceed an 8-hour time-weighted average sound level (TWA) of 85 decibels (dB) measured on the A scale or, equivalently, a dose of fifty percent." This 8-hour time-weighted average is known as an exposure action value. While the Mine Safety and Health Administration (MSHA) also requires a hearing conservation program, MSHA does not require a written hearing conservation program. MSHA's hearing conservation program requirement can be found in 30 CFR § 62.150, and is very similar to the OSHA hearing conservation program requirements. Therefore, only the OSHA standard 29 CFR 1910.95 will be discussed in detail.
A noise-canceling microphone is a microphone that is designed to filter ambient noise.

A headset is a combination of headphone and microphone. Headsets connect over a telephone or to a computer, allowing the user to speak and listen while keeping both hands free. They are commonly used in customer service and technical support centers, where employees can converse with customers while typing information into a computer. They are also common among computer gamers and let them talk with each other and hear others while using their keyboards and mice to play the game.
Selective auditory attention, or selective hearing, is a process of the auditory system where an individual selects or focuses on certain stimuli for auditory information processing while other stimuli are disregarded. This selection is very important as the processing and memory capabilities for humans have a limited capacity. When people use selective hearing, noise from the surrounding environment is heard by the auditory system but only certain parts of the auditory information are chosen to be processed by the brain.

Doppler Labs was a San Francisco-based audio technology company, founded in 2013. The company designed and manufactured in-ear computing technology, including earplugs and wireless smart earbuds.

A hearing protection device, also known as a HPD, is an ear protection device worn in or over the ears while exposed to hazardous noise and provide hearing protection to help prevent noise-induced hearing loss. HPDs reduce the level of the noise entering the ear. HPDs can also protect against other effects of noise exposure such as tinnitus and hyperacusis. There are many different types of HPDs available for use, including earmuffs, earplugs, electronic hearing protection devices, and semi-insert devices.
Minuendo is a manufacturer of Hearing protection devices in the form of lossless Earplugs for the HSE and hearing health market. The products typically address users that are reliant on sound fidelity and spatial awareness while exposed to stressful or dangerous levels of sound. Examples of user groups are Musicians, sound engineers, Construction workers and child care professionals.
Elaine Saunders is an associate professor at the Swinburne University of Technology and executive director of Blamey Saunders, as well as an inventor, entrepreneur. She was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of Science Technology and Engineering in 2019. She is one of only nine women out of 160 to win the Clunies Ross award for entrepreneurship, and has won many other awards, as well as given numerous keynote addresses on the value of entrepreneurship and innovation in STEMM.

Safe listening is a framework for health promotion actions to ensure that sound-related recreational activities do not pose a risk to hearing.












