
A blade is the portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with an edge that is designed to puncture, chop, slice or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are to be used on. Historically, humans have made blades from flaking stones such as flint or obsidian, and from various metal such as copper, bronze and iron. Modern blades are often made of steel or ceramic. Blades are one of humanity's oldest tools, and continue to be used for combat, food preparation, and other purposes.

A pipe wrench is any of several types of wrench that are designed to turn threaded pipe and pipe fittings for assembly (tightening) or disassembly (loosening). The Stillson wrench, or Stillson-pattern wrench, is the usual form of pipe wrench, especially in North America. The Stillson name is that of the original patent holder, who licensed the design to a number of manufacturers. The patent expired decades ago. Another type of wrench often used on pipes, the plumber wrench, is also called a pipe wrench in some places.

Bread knives are used for cutting bread and are one of many kitchen knives used by cooks. The serrated blades of bread knives are able to cut soft bread without crushing it.

Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade.

A kitchen knife is any knife that is intended to be used in food preparation. While much of this work can be accomplished with a few general-purpose knives – notably a large chef's knife, a tough cleaver, a small paring knife and some sort of serrated blade – there are also many specialized knives that are designed for specific tasks. Kitchen knives can be made from several different materials.

A vise or vice is a mechanical apparatus used to secure an object to allow work to be performed on it. Vises have two parallel jaws, one fixed and the other movable, threaded in and out by a screw and lever.
A serrated blade is a type of blade used on saws and on some knives or scissors. It is also known as a dentated, sawtooth, or toothed blade.
The Portevin–Le Chatelier effect (PLC) describes a serrated stress–strain curve or jerky flow, which some materials exhibit as they undergo plastic deformation, specifically inhomogeneous deformation. This effect has been long associated with dynamic strain aging or the competition between diffusing solutes pinning dislocations and dislocations breaking free of this stoppage.

A locknut, also known as a lock nut, locking nut, self-locking nut, prevailing torque nut, stiff nut or elastic stop nut, is a nut that resists loosening under vibrations and torque. Elastic stop nuts and prevailing torque nuts are of the particular type where some portion of the nut deforms elastically to provide a locking action. The first type used fiber instead of nylon and was invented in 1931.

A tomato knife is a small serrated kitchen knife designed to slice through tomatoes. The serrated edge allows the knife to penetrate the tomatoes’ skin quickly and with a minimum of pressure without crushing the flesh. Many tomato knives have forked tips that allow the user to lift and move the tomato slices after they have been cut.

A flange nut is a nut that has a wide flange at one end that acts as an integrated washer. This serves to distribute the pressure of the nut over the part being secured, reducing the chance of damage to the part and making it less likely to loosen as a result of an uneven fastening surface. These nuts are mostly hexagonal in shape and are made up of hardened steel and often coated with zinc.

A T-nut, T nut, or tee nut is a type of nut used to fasten a wood, particle or composite materials workpiece, leaving a flush surface.

Columbia River Knife & Tool, Inc. (CRKT) is an American knife company established in 1994, and currently based in Tualatin, Oregon, United States. The company's president and sales executive is Rod Bremer and the finance executive is Peggy Bremer.

A nut is a type of fastener with a threaded hole. Nuts are almost always used in conjunction with a mating bolt to fasten multiple parts together. The two partners are kept together by a combination of their threads' friction, a slight stretching of the bolt, and compression of the parts to be held together.
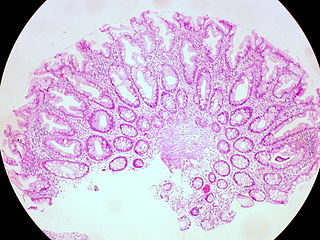
A hyperplastic polyp is a type of colorectal polyp.

A steak knife is a sharp table knife. Such knives often feature serrated blades and wooden handles, and are the only sharp knife commonly found at the modern table for use while eating.

Ostafrikasaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period of what is now Tanzania. It is known only from fossil teeth discovered sometime between 1909 and 1912, during an expedition to the Tendaguru Formation by the Natural History Museum of Berlin. Eight teeth were originally attributed to the dubious dinosaur genus Labrosaurus, and later to Ceratosaurus, both known from the North American Morrison Formation. Subsequent studies attributed two of these teeth to a spinosaurid dinosaur, and in 2012, Ostafrikasaurus crassiserratus was named by French palaeontologist Eric Buffetaut, with one tooth as the holotype, and the other referred to the same species. The generic name comes from the German word for German East Africa, the former name of the colony in which the fossils were found, while the specific name comes from the Latin words for "thick" and "serrated", in reference to the form of the animal's teeth.
Dryadissector is an extinct genus of varanoid lizard represented by the type species Dryadissector shilleri from the Late Cretaceous of Texas. Dryadissector is known only from isolated teeth, which may have been shed by living individuals. These teeth are common in early Campanian strata within the Aguja Formation, which date back about 80 to 82 million years. The teeth of Dryadissector are extremely similar to those of theropod dinosaurs, which led to them initially being misidentified as the remains of theropods. Like theropod teeth, the teeth of Dryadissector are recurved, laterally compressed, and serrated. However, their lizard affinities are made evident by serrations that are smaller and more numerous than those of theropods, as well as a bulge on the inner surface of the base of each tooth that is characteristic of varanoids.

Polymorphodon is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile from the Middle Triassic of Germany. The only known species is Polymorphodon adorfi, discovered in Lower Keuper deposits at a quarry in Eschenau, Germany. Polymorphodon is notable for its heterodont dentition, with long and conical premaxillary teeth followed by thin maxillary teeth with large serrations. Maxillary teeth near the back of the mouth are short and leaf-shaped, similar to some living and extinct reptiles with a herbivorous or omnivorous diet. This may suggest that Polymorphodon had some reliance on plants in its diet, a rarity among basal archosauriforms, most of which are carnivores.
Syntomiprosopus is an extinct genus of archosauriform, possibly a crocodylomorph from the Late Triassic period of Arizona. The type and only known species is S. sucherorum. Syntomiprosopus was unusually short-snouted, comparable to the Late Cretaceous notosuchian Simosuchus, and is regarded as an example of convergent evolution between Triassic stem-archosaurs and Cretaceous archosaurs.
















