
The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), often referred to as the "Milwaukee Road", was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwest and Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986.

The Seward neighborhood in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States, is geographically southeast of downtown, consisting of the land bordered by the Hiawatha Avenue industrial district to the west, Minneapolis Midtown Greenway to the south, the Mississippi River to the east, and Interstate 94 to the north. Seward's bordering neighborhoods are Cooper to the Southeast, Longfellow to the South, East Phillips to the Southwest, Ventura Village to the West, Cedar-Riverside to the North, and Prospect Park/East River Road across the Mississippi River to the East. It is one of the neighborhoods that is part of the larger Longfellow community. Seward was named after former New York senator, governor, and US Secretary of State William H. Seward.

The Minneapolis, Northfield and Southern Railway was an 87-mile (140 km) long American shortline railroad connecting Minneapolis and Northfield, Minnesota. It was incorporated in 1918 to take over the trackage of the former Minneapolis, St. Paul, Rochester and Dubuque Electric Traction Company, also known as the Dan Patch Lines. On June 2, 1982, it was acquired by the Soo Line Railroad, which operated it as a separate railroad until merging it on January 1, 1986 along with the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad.

Lake Street is a major east-west thoroughfare between 29th and 31st streets in Minneapolis, Minnesota United States. From its western most end at the city's limits, Lake Street reaches the Chain of Lakes, passing over a small channel linking Bde Maka Ska and Lake of the Isles, and at its eastern most end it reaches the Mississippi River. In May 2020, the Lake Street corridor suffered extensive damage during local unrest over the murder of George Floyd. In August of the same year, city officials designated East Lake Street as one of seven cultural districts to promote racial equity, preserve cultural identity, and promote economic growth.

Cedar Lake Trail is a 4.3-mile (6.9 km), shared-use path in the U.S. state of Minnesota, from downtown Minneapolis to the neighboring suburb of St. Louis Park. The trail begins at its eastern trailhead in downtown Minneapolis (44°59′11″N93°16′01″W) and continues west to Minnesota State Highway 100 in St. Louis Park (44°57′43″N93°20′36″W). At the trail's west end, a paved path continues for another 4.2 miles (6.8 km) through St. Louis Park to Hopkins under the former name of Hutchinson Spur Trail, but known as North Cedar Lake Regional Trail since 2009. In 2019, large portions of the Cedar Lake Trail were closed due to construction of the Southwest LRT extension with expected reopening in 2021 or 2022.

The Midtown Greenway is a 5.7-mile (9.2 km) rail trail in Minneapolis, Minnesota that follows the path of an abandoned route of the Milwaukee Road railway. It is considered under segregated cycle facilities.

Northern Pacific Bridge #9 is a deck truss bridge that spans the Mississippi River in Minneapolis, Minnesota, between the Seven Corners area and the University of Minnesota campus. It was built in 1924 and was designed by Frederick W. Cappelen. Railroad use of the bridge ended in 1981, and in 1999 the bridge was opened to bicycles and pedestrians. It replaced the former Northern Pacific "A Line" bridge.
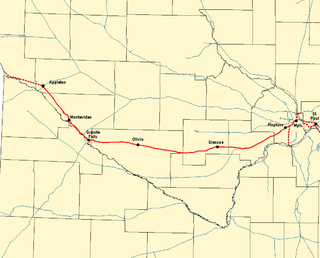
The Twin Cities and Western Railroad is a railroad operating in the U.S. state of Minnesota which started operations on July 27, 1991. Trackage includes the former Soo Line Railroad "Ortonville Line", originally built as the first part of the Pacific extension of the Milwaukee Road. This main line extends from Hopkins, Minnesota to Appleton, Minnesota. The line was originally built between Hopkins and Cologne, Minnesota in 1876 by Hastings and Dakota Railroad. In 1913, the Milwaukee Road rerouted it, reducing the curves. The line was eventually extended to the Pacific.

Longfellow is a defined community in Minneapolis, Minnesota which includes five smaller neighborhoods inside of it: Seward, Cooper, Hiawatha, Howe and Longfellow. The community is a mix of agri-industrial properties along the old Northern Pacific Railway, expansive parkland surrounding the famous Minnehaha Falls, and smaller residential areas.

The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Depot Freight House and Train Shed, now officially named The Depot, is a historic railroad depot in downtown Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States. At its peak, the station served 29 trains per day. Following decline, the station was closed and eventually adapted into various other uses.

The Minneapolis Great Northern Depot, also known as Great Northern Station, was a passenger railroad station which served Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA. It was built in 1913 and demolished in 1978. It was located on Hennepin Avenue next to the Hennepin Avenue Bridge and across the street from the main Minneapolis Post Office.

The River Subdivision or River Sub is a railway line along the Mississippi River that runs approximately 124 miles (200 km) from Saint Paul, Minnesota south to La Crescent. U.S. Highway 61 closely parallels the route between La Crescent and Red Wing. The line is operated by the Canadian Pacific Railway through its primary United States subsidiary, the Soo Line Railroad. BNSF Railway operates a complementary St. Croix Subdivision which traces the eastern side of the river in Minnesota and Wisconsin. The two routes share some track between Saint Paul and St. Croix Junction, near Hastings.

The Tomah Subdivision or Tomah Sub is a railway line that runs about 103 miles (166 km) from La Crosse, WI in the west to Portage, WI in the east.
The Canadian Pacific Railway's Merriam Park Subdivision or Merriam Park Sub, also known as the Short Line, is a railway line in Saint Paul, Minnesota. It is run by the Soo Line Railroad, a U.S. in-name-only division of CP. It runs from the Saint Paul Yard, also known as the Pigs Eye Yard, westward to the Short Line Bridge over the Mississippi River, where rails continue as part of the Minnesota Commercial Railway. It was named for John L. Merriam, a Minnesota banker and politician. Completed by the Chicago, Milwaukee and St. Paul Railroad in 1880, it shortened the route Milwaukee Road trains took between downtown Saint Paul and downtown Minneapolis. Previous trains would exit Saint Paul and follow the Mississippi River southwest until crossing at Fort Snelling, where they would follow the path of today's Hiawatha Avenue and the Metro Blue Line toward the Milwaukee Road Depot. Originally built as an interurban route, it was eventually converted for heavy rail traffic because the Twin City Rapid Transit streetcar system had taken over the local transit market.

The Watertown Subdivision or Watertown Sub is a 92.7-mile (149.2 km) railway line in Wisconsin operated by the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) through its primary United States subsidiary, the Soo Line Railroad. It meets CP's Tomah Subdivision in the west in Portage and runs to Milwaukee in the east where it meets the C&M Subdivision. The Watertown Subdivision had previously been operated by the Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad, though the Soo Line Railroad took it over when the Milwaukee Road folded. Canadian Pacific gained ownership via taking over the Soo Line.
The MN&S Spur is a 18.5-mile (29.8 km) railroad line operated by the Progressive Rail Inc. The route runs through suburbs immediately west of Minneapolis, Minnesota, from MN&S Junction in Crystal south to Auto Club Junction in Bloomington near the Minnesota River. This path is parallel to Minnesota State Highway 100, which is about half a mile east of the rail line.
The Bass Lake Spur is a railroad line owned by the Canadian Pacific Railway that runs 6.8 miles (10.9 km) from Minneapolis, Minnesota west to the suburb of Minnetonka. The primary operator on the line is the Twin Cities and Western Railroad which has trackage rights on the entire line and uses it to run trains from their main line to BNSF Railway's Wayzata Subdivision.

Hiawatha LRT Trail is a 4.7-mile (7.6 km), multi-use path adjacent to a light-rail transit line in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States, that is popular with bicycle commuters. Users travel along the Metro Blue Line and Hiawatha Avenue transit corridor, reaching downtown Minneapolis near an indoor sports stadium at the trail’s northern end, and reaching a bridge above Minnehaha Creek at the trail’s southern end. Hiawatha LRT Trail provides a vital link between several Minneapolis neighborhoods and the city’s downtown area.

Little Earth Trail is an approximately 1-mile (1.6 km), multi-use bicycle path in Minneapolis, Minnesota, United States, that links several neighborhoods, parks, businesses, and trails in the Phillips community. The trail begins at its northern end near the intersection of East Franklin Avenue and 16th Avenue South and eventually follows the west side of Hiawatha Avenue to the Midtown Greenway and Martin Olav Sabo Bridge. Named after the nearby Little Earth community, the shared-use pathway provides transportation and recreation opportunities, and is a frequent location of activism on social justice issues in Minneapolis.

Minneapolis is often considered one of the top biking and walking cities in the United States due to its vast network of trails and dedicated pedestrian areas. In 2020, Walk Score rated Minneapolis as 13th highest among cities over 200,000 people. Some bicycling ratings list Minneapolis at the top of all United States cities, while others list Minneapolis in the top ten. There are over 80 miles (130 km) of paved, protected pathways in Minneapolis for use as transportation and recreation. The city's Grand Rounds National Scenic Byway parkway system accounts for the vast majority of the city's shared-use paths at approximately 50 miles (80 km) of dedicated biking and walking areas. By 2008, other city, county, and park board areas accounted for approximately 30 miles (48 km) of additional trails, for a city-wide total of approximately 80 miles (130 km) of protected pathways. The network of shared biking and walking paths continued to grow into the late 2010s with the additions of the Hiawatha LRT Trail gap remediation, Min Hi Line pilot projects, and Samatar Crossing. The city also features several natural-surface hiking trails, mountain-biking paths, groomed cross-country ski trails in winter, and other pedestrian walkways.




















