Brackish water is water having more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater with fresh water together, as in estuaries, or it may occur in brackish fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root "brak". Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it is damaging to the environment.

Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea to the west, Iran and Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the north-east, and Kazakhstan to the north-west. It is the southernmost republic of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the loose federation created at the end of 1991 by most of the Post-Soviet states.

Lake Chad is a historically large, shallow, endorheic lake in Africa, which has varied in size over the centuries. According to the Global Resource Information Database of the United Nations Environment Programme, it shrank by as much as 95% from about 1963 to 1998, but "the 2007 (satellite) image shows significant improvement over previous years." Lake Chad is economically important, providing water to more than 30 million people living in the four countries surrounding it on the edge of the Sahara. It is the largest lake in the Chad Basin.

An endorheic basin is a limited drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. Such a basin may also be referred to as a closed or terminal basin or as an internal drainage system or interior drainage basin.

A shrunken head is a severed and specially prepared human head that is used for trophy, ritual, or trade purposes.
In geomorphology, an outburst flood — a type of megaflood — is a high-magnitude, low-frequency catastrophic flood involving the sudden release of a large quantity of water. During the last deglaciation, numerous glacial lake outburst floods were caused by the collapse of either ice sheets or glaciers that formed the dams of proglacial lakes. Examples of older outburst floods are known from the geological past of the Earth and inferred from geomorphological evidence on Mars. Landslides, lahars, and volcanic dams can also block rivers and create lakes, which trigger such floods when the rock or earthen barrier collapses or is eroded. Lakes also form behind glacial moraines, which can collapse and create outburst floods.

Lake Urmia is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East and the sixth-largest saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately 5,200 km2 (2,000 sq mi), a length of 140 km (87 mi), a width of 55 km (34 mi), and a maximum depth of 16 m (52 ft). The lake has shrunk to 10% of its former size due to damming of the rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area.

Lake Algonquin was a proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, and Lake Nipissing.
Kazakhstan has serious environmental issues such as radiation from nuclear testing sites, the shrinking of the Aral sea, and desertification of former agricultural land. These issues are due in large part to Kazakhstan's years under the Soviet Union.

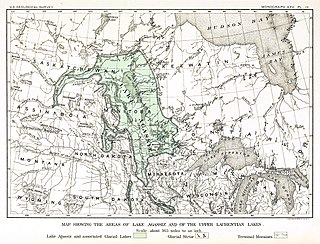
Lake Ojibway was a prehistoric lake in what is now northern Ontario and Quebec in Canada. Ojibway was the last of the great proglacial lakes of the last ice age. Comparable in size to Lake Agassiz, and north of the Great Lakes, it was at its greatest extent c. 8,500 years BP. The former lakebed forms the modern Clay Belt, an area of fertile land.

A beel is a billabong or a lake-like wetland with static water {in bengali}, in the Ganges - Brahmaputra flood plains of the Eastern Indian states of West Bengal, and Assam and in the country of Bangladesh. The term owes its origins to the word of the same pronunciation meaning "pond" and "lake" in the Bengali and Assamese languages.

The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.

The Traverse Gap is an ancient river channel occupied by Lake Traverse, Big Stone Lake and the valley connecting them at Browns Valley, Minnesota. It is located on the border of the U.S. states of Minnesota and South Dakota. Traverse Gap has an unusual distinction for a valley: it is crossed by a continental divide, and in some floods water has flowed across that divide from one drainage basin to the other. Before the Anglo-American Convention of 1818 it marked the border between British territory in the north and U.S. – or earlier, French – territory in the south.

Once upon a time, Hyderabad was known as City of Lakes. Some of these lakes are natural and various are manmade bodies. As per various sources only a few decades back, Hyderabad had a large number of water bodies such as lakes, reservoirs, rivers, streams, aquaculture ponds, tanks etc.. Most of these lakes have totally disappeared and the surface area of most of the surviving lakes have shrunken and turned to tiny ponds and cesspool. Some of the lakes which have totally disappeared are Tigal Kunta, Somajiguda Tank, Mir Jumla tank, Pahar Tigal Kunta, Kunta Bhawani Das, Nawab Saheb Kunta, Afzalsagar, Nallakunta, Masab Tank etc. Hussainsagar Lake, Kunta Mallaiyapalli have shrunk drastically. Out of thousands of water bodies those were existing in 1970s in various sizes in and around Hyderabad, today only about 70 to 500 of them have survived. Most of them have disappeared due to encroachment or have been illegally drained for real estate projects by private or government agencies. The existing lakes have been used to dump garbage and sewage water. Most of these lakes and tanks were built during the regime of Qutub Shah in 16th and 17th century and later by Nizams as a source of drinking water for the residents of Hyderabad. The area of Hussain Sagar, which is the largest lake in Hyderabad shrunk by more than 40% i.e. from 550 ha to 349 ha in just 30 years. This lake was built in 1575 AD and since 1930 is not being used as a source for drinking water.
Manali aeri, or Mathur aeri or Madhavaram aeri, is a 150-acre lake in the Manali-Mathur-Madavaram area of Chennai, India. Due to indiscriminate dumping of garbage and sewage, the lake has shrunk to less than 100 acres.
The phenomenon of paleoflooding is apparent in the geologic record over various spatial and temporal scales. It often occurred on a large scale, and was the result of either glacial ice melt causing large outbursts of freshwater, or high sea levels breaching bodies of freshwater. If a freshwater outflow event was large enough that the water reached the ocean system, it caused changes in salinity that potentially affected ocean circulation and global climate. Freshwater flows could also accumulate to form continental glacial lakes, and this is another indicator of large-scale flooding. In contrast, periods of high global sea level could cause marine water to breach natural dams and flow into bodies of freshwater. Changes in salinity of freshwater and marine bodies can be detected from the analysis of organisms that inhabited those bodies at a given time, as certain organisms are more suited to live in either fresh or saline conditions.