
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.

Reverse Polish notation (RPN), also known as reverse Łukasiewicz notation, Polish postfix notation or simply postfix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators follow their operands, in contrast to prefix or Polish notation (PN), in which operators precede their operands. The notation does not need any parentheses for as long as each operator has a fixed number of operands.

A slide rule is a hand-operated mechanical calculator consisting of slidable rulers for evaluating mathematical operations such as multiplication, division, exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is one of the simplest analog computers.
Scientific notation is a way of expressing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in decimal form, since to do so would require writing out an inconveniently long string of digits. It may be referred to as scientific form or standard index form, or standard form in the United Kingdom. This base ten notation is commonly used by scientists, mathematicians, and engineers, in part because it can simplify certain arithmetic operations. On scientific calculators, it is usually known as "SCI" display mode.

In mathematics, the common logarithm is the logarithm with base 10. It is also known as the decadic logarithm and as the decimal logarithm, named after its base, or Briggsian logarithm, after Henry Briggs, an English mathematician who pioneered its use, as well as standard logarithm. Historically, it was known as logarithmus decimalis or logarithmus decadis. It is indicated by log(x), log10(x), or sometimes Log(x) with a capital L; on calculators, it is printed as "log", but mathematicians usually mean natural logarithm (logarithm with base e ≈ 2.71828) rather than common logarithm when writing "log". To mitigate this ambiguity, the ISO 80000 specification recommends that log10(x) should be written lg(x), and loge(x) should be ln(x).
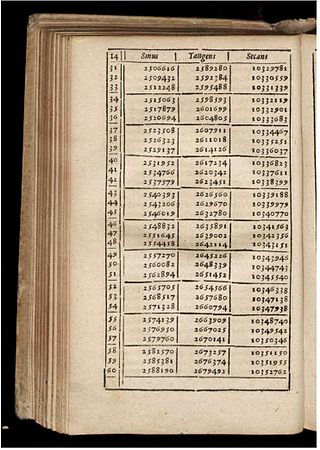
Mathematical tables are lists of numbers showing the results of a calculation with varying arguments. Trigonometric tables were used in ancient Greece and India for applications to astronomy and celestial navigation, and continued to be widely used until electronic calculators became cheap and plentiful in the 1970s, in order to simplify and drastically speed up computation. Tables of logarithms and trigonometric functions were common in math and science textbooks, and specialized tables were published for numerous applications.
Significant figures, also referred to as significant digits or sig figs, are specific digits within a number written in positional notation that carry both reliability and necessity in conveying a particular quantity. When presenting the outcome of a measurement, if the number of digits exceeds what the measurement instrument can resolve, only the number of digits within the resolution's capability are dependable and therefore considered significant.

A scientific calculator is an electronic calculator, either desktop or handheld, designed to perform calculations using basic and advanced mathematical operations and functions. They have completely replaced slide rules as well as books of mathematical tables and are used in both educational and professional settings.

The HP-35 was Hewlett-Packard's first pocket calculator and the world's first scientific pocket calculator: a calculator with trigonometric and exponential functions. It was introduced in 1972.

The HP-65 is the first magnetic card-programmable handheld calculator. Introduced by Hewlett-Packard in 1974 at an MSRP of $795, it featured nine storage registers and room for 100 keystroke instructions. It also included a magnetic card reader/writer to save and load programs. Like all Hewlett-Packard calculators of the era and most since, the HP-65 used Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) and a four-level automatic operand stack.

The HP-20S (F1890A) is an algebraic programmable scientific calculator produced by Hewlett-Packard from 1987 to 2000.

The TI-30 is a scientific calculator manufactured by Texas Instruments, the first model of which was introduced in 1976. While the original TI-30 was discontinued in 1983 after several design revisions, TI maintains the TI-30 designation as a branding for its low and mid-range scientific calculators.

The SR-50 was Texas Instruments' first scientific pocket calculator with trigonometric and logarithm functions. It enhanced their earlier SR-10 and SR-11 calculators, introduced in 1973, which had featured scientific notation, squares, square root, and reciprocals, but had no trig or log functions, and lacked other features. The SR-50 was introduced in 1974 and sold for US$170. It competed with the Hewlett-Packard HP-35.
There are various ways in which calculators interpret keystrokes. These can be categorized into two main types:

The HP-25 was a hand-held programmable scientific/engineering calculator made by Hewlett-Packard between early January 1975 and 1978. The HP-25 was introduced as a cheaper alternative to the ground-breaking HP-65.

The Sinclair Cambridge was a pocket-sized calculator introduced in August 1973 by Sinclair Radionics. It was available both in kit form to be assembled by the purchaser, or assembled prior to purchase. The range ultimately comprised seven models, the original "four-function" Cambridge – which carried out the four basic mathematical functions of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division – being followed by the Cambridge Scientific, Cambridge Memory, two versions of Cambridge Memory %, Cambridge Scientific Programmable and Cambridge Universal.

The HP-27 was a hand-held scientific and financial, but not programmable, calculator made by Hewlett-Packard between 1976 and 1978.
Sharp EL-500W series include a range of scientific calculators made by Sharp Corporation, capable of displaying 2 lines, with multi-line playback. It is the successor to the Sharp EL-500V series.

Texas Instruments TI-35 was a series of scientific calculators by Texas Instruments. The original TI-35 was notable for being one of Texas Instruments' first use of CMOS controller chips in their designs, and was at the time distinguished from the lower-end TI-30 line by the addition of some statistics functions.

The HP 35s (F2215A) is a Hewlett-Packard non-graphing programmable scientific calculator. Although it is a successor to the HP 33s, it was introduced to commemorate the 35th anniversary of the HP-35, Hewlett-Packard's first pocket calculator. HP also released a limited production anniversary edition with shiny black overlay and engraving "Celebrating 35 years".
















