Related Research Articles
The Long March rockets are a family of expendable launch system rockets operated by the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation. The rockets are named after the Chinese Red Army's 1934–35 Long March military retreat during the Chinese Civil War.

The space program of the People's Republic of China is directed by the China National Space Administration (CNSA). China's space program has overseen the development and launch of ballistic missiles,thousands of artificial satellites,manned spaceflight,an indigenous space station,and has stated plans to explore the Moon,Mars,and the broader Solar System.
Dongfanghong was a satellite program of the People's Republic of China. The program started in August 1965 as Project 651—a less ambitious successor to the earlier Project 581—with the goal of launching a satellite heavier than both Sputnik 1 and Explorer 1 into space,and developing all the necessary technologies to do so.

The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation,or CASC,is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has subsidiaries which design,develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft,launch vehicles,strategic and tactical missile systems,and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive,having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.

The National Space Research and Development Agency (NASRDA) is the national space agency of Nigeria. It is a parastatal under Federal Ministry of Science and Technology. The agency is based in the Nigerian capital city of Abuja in the Lugbe district and has a ground receiving station,among various other sites. It has had cooperation in space technology with the United Kingdom,China,Ukraine and Russia. The agency has struggled with meeting its financial plans and some of its facilities are rundown. Despite this,the space agency is one of the most advanced space agencies in Africa,boasting of four satellites and very grand ambitions. Nigeria's satellites have been praised for their high-resolution images. NASRDA is host to one of UN-SPIDER's Regional Support Offices (RSO) in Africa.
Dong Fang Hong 2 was the primary television satellite used by China during the later part of the 20th century. It was developed at the Chinese Academy of Space Technology (CAST) and had a design life 4.5 years. The first operational satellite in this group was launched into a geosynchronous orbit on 8 April 1984.
NigComSat-1 was a Nigerian communication satellite. The initial contract to build the satellite was signed in 2004. It was launched in China by Nasrda and became the third African geosynchronous communication satellite,when it was launched at 16:01 UTC on 13 May 2007,aboard a Chinese Long March 3B carrier rocket,from the Xichang Satellite Launch Centre in China. The spacecraft was operated by Nigerian Communications Satellite Ltd (NIGCOMSAT). On November 11,2008,NigComSat-1 failed in orbit after running out of power due to an anomaly in its solar array.
Nigerian Communications Satellite (NIGCOMSAT) Limited is a company under the supervision of the Federal Ministry of Communications and Digital Economy.
ChinaSat is the brand name of communications satellites operated by China Satellite Communications.
The Long March 3B,also known as the CZ-3B and LM-3B,is a Chinese orbital launch vehicle. Introduced in 1996,it is launched from Launch Area 2 and 3 at the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Sichuan. A three-stage rocket with four strap-on liquid rocket boosters,it is currently the second most powerful member of the Long March rocket family after the Long March 5 and the heaviest of the Long March 3 rocket family,and is mainly used to place communications satellites into geosynchronous orbits.
ChinaSat 9,also known as ZX-9,is a Chinese communications satellite.
Paksat-1R is a geosynchronous,communications satellite that was manufactured by China Great Wall Industry Corporation (CGWIC) and operated by the Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission (SUPARCO),an executive space authority of the Government of Pakistan.
ChinaSat 10 previously known as SinoSat 5 is a Chinese communications satellite. It was launched at 16:13 UTC on 20 June 2011 on a Long March 3B rocket.

ChinaSat 12 communications satellite is wholly owned by China Satellite Communications,with part of its communications payload leased or rented by SupremeSAT,a Sri Lankan company to be marketed to potential users as SupremeSAT-I. Once operational,it will provide communications services for the China,Sri Lanka,East Asia,South Asia,Middle East,Africa,Australia and China sea area,the Indian Ocean region.

APT Satellite Holdings Limited is a Bermuda-incorporated holding company. Its Hong Kong-incorporated subsidiary APT Satellite Co.,Ltd. is the operator of the Apstar satellite constellation. APT Satellite Holdings and APT Satellite are headquartered in Hong Kong.
China Satellite Communications Co.,Ltd. known as China Satcom is a Chinese aerospace company that provides services via satellites. The company was a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
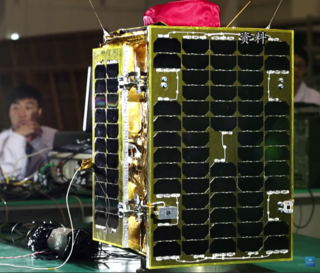
Jilin-1 is China's first self-developed commercial remote sensing satellite system. The satellites are operated by Chang Guang Satellite Technology Corporation and named after Jilin Province where the company is headquartered. The first set of satellites were launched by Long March 2D in Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on 7 October 2015,at 04:13 UTC. All launched Jilin-1 satellites are in sun-synchronous orbit (SSO).
Tianlian also known as CTDRS,is a Chinese data relay communication satellite constellation. The constellation serves to relay data from ground stations to spacecraft and rockets,most significantly China's crewed spaceflight program. The system currently consists of seven satellites in two generations,with the first satellite being launched in 2008.
References
- 1 2 "About us". Sino Satellite Communications. Archived from the original on 2 April 2007. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- 1 2 "2007 Annual Report" (PDF). CASC (in Chinese). chinabond.com.cn. 2008. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ "First Chinese Satellite Conglomerate Beams into Operation". Space Daily. Xinhua News Agency. 2 January 2008. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- ↑ "2009 Annual Report" (PDF). CSAC (in Chinese). chinabond.com.cn. 2010. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ "2016 Annual Report" (PDF). Shenglu Telecommunication (in Chinese). Shenzhen Stock Exchange. 28 April 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "北京宇信电子有限公司30%股权(编号 G316BJ1007416 )" (in Chinese). zhonghua-pe.com. 20 September 2016. Archived from the original on 6 May 2017. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- 1 2 "合作资源" (in Chinese). Sino Satellite Communications. Archived from the original on 7 September 2008. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ Krebs, Gunter. "Sinosat-2". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved 25 March 2009.
- ↑ "中星10号" (in Chinese). China Satellite Communications. 2 December 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ↑ "中星6A" (in Chinese). China Satellite Communications. 2 December 2014. Retrieved 25 July 2017.