South Africa is divided into nine provinces. On the eve of the 1994 general election, South Africa's former homelands, also known as Bantustans, were reintegrated and the four existing provinces were divided into nine. The twelfth, thirteenth and sixteenth amendments to the constitution changed the borders of seven of the provinces.
A constitutional amendment is a modification of the constitution of a polity, organization or other type of entity. Amendments are often interwoven into the relevant sections of an existing constitution, directly altering the text. Conversely, they can be appended to the constitution as supplemental additions (codicils), thus changing the frame of government without altering the existing text of the document.

The Constitution of South Africa is the supreme law of the Republic of South Africa. It provides the legal foundation for the existence of the republic, it sets out the rights and duties of its citizens, and defines the structure of the Government. The current constitution, the country's fifth, was drawn up by the Parliament elected in 1994 in the South African general election, 1994. It was promulgated by President Nelson Mandela on 18 December 1996 and came into effect on 4 February 1997, replacing the Interim Constitution of 1993.

The Victorian Legislative Council (VLC) is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of Victoria, Australia; the lower house being the Legislative Assembly. Both houses sit at Parliament House in Spring Street, Melbourne. The Legislative Council serves as a house of review, in a similar fashion to its federal counterpart, the Australian Senate. Although it is possible for legislation to be first introduced in the Council, most bills receive their first hearing in the Legislative Assembly.

The National Council of Provinces (NCOP) is the upper house of the Parliament of South Africa under the (post-apartheid) constitution which came into full effect in 1997. It replaced the former Senate, but is very similar to that body, and to many other upper houses of legislatures throughout the world, in that its purpose is to represent the governments of the provinces, rather than directly representing the people.

The Parliament of Victoria is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of Victoria that follows a Westminster-derived parliamentary system. It consists of the Queen, represented by the Governor of Victoria, the Legislative Assembly and the Legislative Council. It has a fused executive drawn from members of both chambers. The parliament meets at Parliament House in the state capital Melbourne. The current Parliament was elected on 24 November 2018, sworn in on 19 December 2018 and is the 59th parliament in Victoria.
The Third Amendment of the Constitution Bill 1968 was a bill to amend the Constitution of Ireland to change the criteria for redistribution of constituencies for elections to Dáil Éireann, the lower house of the Oireachtas. The proposal was rejected in a referendum held on 16 October 1968.

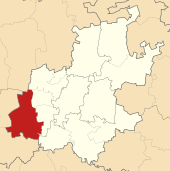
Merafong City Local Municipality is a local municipality in West Rand District Municipality, Gauteng, South Africa. Its boundaries encloses some of the richest gold mines in the world. It is situated about 65 km from Johannesburg and is serviced by a number of major roads, including the N12 from Johannesburg to Beaufort West and the N14.
The Sixth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa made a number of changes, most importantly giving the title of "Chief Justice" to the head of the Constitutional Court instead of the head of the Supreme Court of Appeal. It was passed by the National Assembly with the requisite two-thirds majority on 1 November 2001, and signed by President Thabo Mbeki on 20 November; it was published and came into force on the following day.
The Seventh Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa made various changes involving the financial management of national and provincial government. Most of its provisions came into force on 26 April 2002, and the remainder on 1 December 2003.
The Eighth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa allowed members of municipal councils to cross the floor from one political party to another without losing their seats. It came into force on 20 June 2002, and was effectively repealed on 17 April 2009 by the Fifteenth Amendment.
The Ninth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa modified the scheme for the allocation of seats in the National Council of Provinces, to account for the possibility of changes in the party makeup of provincial legislatures. This was necessary because of other legislation which had been introduced to allow members of the provincial legislatures to cross the floor without losing their seats. It came into force on 20 June 2002, and was effectively repealed on 17 April 2009 by the Fourteenth Amendment.
The Tenth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa altered the provisions relating to membership of the National Assembly and the provincial legislatures, to allow members of those bodies to cross the floor at certain times without losing their seats. It came into force on 20 March 2003, and was effectively repealed on 17 March 2009 by the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendments.
The Eleventh Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa renamed the Northern Province to Limpopo, altered the procedure for intervention by the national government in a failing provincial government and intervention by a provincial government in a failing municipality, and expanded the powers of the provincial executive when it intervenes in a municipality.
The Twelfth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa altered the boundaries of seven of South Africa's nine provinces. It also redefined all of the provinces' geographical areas in terms of the areas of district and metropolitan municipalities, and repealed the provisions introduced by the Third Amendment that allowed municipal areas to cross provincial boundaries. A number of the boundary changes were highly controversial and led to popular protest and court challenges.
The Thirteenth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa re-enacted provisions of the Twelfth Amendment which the Constitutional Court ruled had not been validly enacted. These provisions transferred the Matatiele Local Municipality from KwaZulu-Natal province to the Eastern Cape province.
The Fourteenth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa repealed some of the provisions inserted into the Constitution by the Ninth and Tenth Amendments which allowed for floor-crossing, that is, allowed members of legislative bodies to move from one political party to another without losing their seats. The remaining floor-crossing provisions were repealed by the Fifteenth Amendment, which was enacted at the same time.
The Fifteenth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa repealed some of the provisions inserted into the Constitution by the Eighth and Tenth Amendments which allowed for floor-crossing, that is, allowed members of legislative bodies to move from one political party to another without losing their seats. The remaining floor-crossing provisions were repealed by the Fourteenth Amendment, which was enacted at the same time.
The provincial councils were the legislatures of the four original provinces of South Africa. They were created at the foundation of the Union of South Africa in 1910, and abolished in 1986 when they were replaced by a strengthened executive appointed by the State President. The four provincial councils were the Cape Provincial Council, the Natal Provincial Council, the Transvaal Provincial Council and the Orange Free State Provincial Council.
The Seventeenth Amendment of the Constitution of South Africa made a number of changes to the structure of the South African judiciary. The bill for the amendment was passed by the National Assembly on 20 November 2012 with the required two-thirds majority; because it is a constitutional amendment not affecting the provinces it was not required to be voted on by the National Council of Provinces. The act was signed by President Jacob Zuma on 1 February 2013, and a presidential proclamation brought it into force on 23 August 2013. The amendment came into force simultaneously with the Superior Courts Act, 2013, which implemented a major rationalisation and restructuring of the judicial system.