The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territorial waters. Known among Russians in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the current name of the sea is after the historical Dutch navigator Willem Barentsz.
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.

A floating production storage and offloading (FPSO) unit is a floating vessel used by the offshore oil and gas industry for the production and processing of hydrocarbons, and for the storage of oil. An FPSO vessel is designed to receive hydrocarbons produced by itself or from nearby platforms or subsea template, process them, and store oil until it can be offloaded onto a tanker or, less frequently, transported through a pipeline. FPSOs are preferred in frontier offshore regions as they are easy to install, and do not require a local pipeline infrastructure to export oil. FPSOs can be a conversion of an oil tanker or can be a vessel built specially for the application. A vessel used only to store oil is referred to as a floating storage and offloading (FSO) vessel.

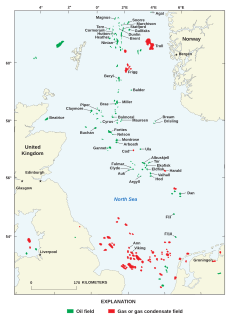
Ekofisk is an oil field in block 2/4 of the Norwegian sector of the North Sea about 320 km (200 mi) southwest of Stavanger. Discovered in 1969 by Phillips Petroleum Company, it remains one of the most important oil fields in the North Sea. This was the first discovery of oil after the drilling of over 200 exploration wells in the North Sea "triggered" by the Groningen gas field discovery. In 1971, Phillips started producing directly to tankers from four subsea wells. Oil production is planned to continue until at least 2050.

The Statfjord oil field is a large oil and gas field covering 580 km2 in the U.K.-Norwegian boundary of the North Sea at a water depth of 145 m, discovered in 1974 by Mobil and since 1987 operated by Equinor.
Oseberg is an offshore oil field with a gas cap in the North Sea located 140 km (87 mi) northwest of the city of Bergen on the southwestern coast of Norway. The field, which is 25 km long by 7 km wide, was discovered in 1979 and its development is known to be one of the significant milestones in emergence of Norway's independent oil and gas industry. The Oseberg field was named after Oseberg ship, one of Norway's most significant archeological discoveries. The ancient Viking ship from the early 9th century was discovered in a 1904 historical excavation of a burial mound at the Oseberg Farm, south of Oslo.

The Heidrun oil field is an oil and gas field discovered in 1985 in the Norwegian sector of the Norwegian Sea, named after the goat Heiðrún from Norse mythology.

Valhall is an oil field in the Norwegian sector of the North Sea. Discovered in 1975, production began in 1982 and is expected to continue until 2050. Valhall is located in 70 metres of water. It produces from chalk in the Tor and Hod Formations of Late Cretaceous age. The reservoir depth is approximately 2 400 metres.
This is a list of oil and gas fields operated by BP.

Equinor ASA is a Norwegian state-owned multinational energy company headquartered in Stavanger. It is primarily a petroleum company, operating in 36 countries with additional investments in renewable energy. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Equinor was ranked as the 169th-largest public company in the world. As of 2021, the company has 21,126 employees.

Frigg gas field is a natural gas field on Norwegian block 25/1 in the North Sea, on the boundary between the United Kingdom and Norway. The field is named after the goddess Frigg. King Olav V of Norway officially opened production on 8 May 1978. Production was closed on 26 October 2004. The field is situated 230 kilometres (140 mi) northwest of Stavanger. Operator for the field was the French oil company Elf Aquitaine, which merged and changed name to Total S.A.

Grane is an offshore oil field in the North Sea located 185 km (115 mi) west of the city of Haugesund on the western coast of Norway. It is Norway's first heavy crude oil production field and Statoil's largest heavy oil field in the Norwegian continental shelf. The oil from the field, located in Block 25/11 is transported to Sture terminal via Grane oil pipeline. The injection gas is imported to Grane oil field from the Heimdal, located just north the field.
Heimdal is an offshore natural gas field in the North Sea located 212 kilometres (132 mi) northwest of the Stavanger, Norway. Heimdal serves as a connection hub for processing and distribution of natural gas from satellite fields.
Vale is an offshore gas field in the North Sea located 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) north of the Heimdal gas field. The depth of the water in the field area is 115 metres (377 ft). Vale is considered a satellite to Heimdal field and is connected to it by a pipeline. Estimated reserves at Vale stand at 2.5 billion cubic metres of natural gas and 21 million barrels (3,300,000 m3) of gas condensate. Vale gas field is expected to produce 1.6 million cubic metres per day of natural gas and 2,600 barrels per day (410 m3/d) of condensate.
Skirne which also includes the Byggve deposit is an offshore gas field in the North Sea located 24 kilometres (15 mi) east of the Heimdal gas field and 140 kilometres (87 mi) from Stavanger, Norway. The depth of the water in the field area is 120 metres (390 ft). Both Skirne and Byggve are considered satellites to Heimdal field and are connected to it by subsea pipelines. TotalFinaElf which is the operator had received the approval from Norwegian Ministry of Petroleum and Energy for development of the fields in 2002. The company holds 40% interest in the project. Other stakeholders are Petoro and Centrica. Both Skirne and Byggve have an estimated 230 billion cubic feet of natural gas and about 10 million barrels of condensate, combined.

Gjøa oilfield is an oilfield in the Norwegian section of the North Sea. It lies about 70 kilometres (43 mi) off the Troll field.
Ula is an offshore oil field located in the southern Norwegian section of North Sea along with Gyda, Tambar and Tambar East fields making up the UGT area, usually attributed to DONG Energy's main areas of exploration and production activity.

Goliat field is an offshore oil field in the Norwegian sector of the Barents Sea. It is located 85 kilometres (53 mi) northwest of Hammerfest. The license is owned by Vår Energi AS and Equinor ASA (35%). It was awarded in 1997. Oil was discovered in 2000. The field development concept was approved by the Government of Norway on 8 May 2009. The field will be developed by using Goliat FPSO, a floating production storage and offloading unit.
Nzizi Power Station is a planned 100 MW (130,000 hp) natural gas-fired thermal power plant in Uganda.

Rex International Holding is an oil and gas company headquartered in Singapore. The company's main activity is in offshore oil and gas exploration and production in assets located in Oman and Norway.