
Erosion is the action of surface processes that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distinct from weathering which involves no movement. Removal of rock or soil as clastic sediment is referred to as physical or mechanical erosion; this contrasts with chemical erosion, where soil or rock material is removed from an area by dissolution. Eroded sediment or solutes may be transported just a few millimetres, or for thousands of kilometres.

Landslides, also known as landslips, or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of environments, characterized by either steep or gentle slope gradients, from mountain ranges to coastal cliffs or even underwater, in which case they are called submarine landslides.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits.

Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in a moving medium, such as water, wind, or ice. Types of mass wasting include creep, solifluction, rockfalls, debris flows, and landslides, each with its own characteristic features, and taking place over timescales from seconds to hundreds of years. Mass wasting occurs on both terrestrial and submarine slopes, and has been observed on Earth, Mars, Venus, Jupiter's moon Io, and on many other bodies in the Solar System.

In geology, a hummock is a small knoll or mound above ground. They are typically less than 15 meters (50 ft) in height and tend to appear in groups or fields. Large landslide avalanches that typically occur in volcanic areas are responsible for formation of hummocks. From the initiation of the landslide to the final formation, hummocks can be characterized by their evolution, spatial distribution, and internal structure. As the movement of landslide begins, the extension faulting results in formation of hummocks with smaller ones at the front of the landslide and larger ones in the back. The size of the hummocks is dependent on their position in the initial mass. As this mass spreads, the hummocks further modify to break up or merge to form larger structures. It is difficult to make generalizations about hummocks because of the diversity in their morphology and sedimentology. An extremely irregular surface may be called hummocky.

A submarine canyon is a steep-sided valley cut into the seabed of the continental slope, sometimes extending well onto the continental shelf, having nearly vertical walls, and occasionally having canyon wall heights of up to 5 km (3 mi), from canyon floor to canyon rim, as with the Great Bahama Canyon. Just as above-sea-level canyons serve as channels for the flow of water across land, submarine canyons serve as channels for the flow of turbidity currents across the seafloor. Turbidity currents are flows of dense, sediment laden waters that are supplied by rivers, or generated on the seabed by storms, submarine landslides, earthquakes, and other soil disturbances. Turbidity currents travel down slope at great speed, eroding the continental slope and finally depositing sediment onto the abyssal plain, where the particles settle out.

A fault scarp is a small step-like offset of the ground surface in which one side of a fault has shifted vertically in relation to the other. The topographic expression of fault scarps results from the differential erosion of rocks of contrasting resistance and the displacement of land surface by movement along the fault. Differential movement and erosion may occur either along older inactive geologic faults, or recent active faults.

A rockslide is a type of landslide caused by rock failure in which part of the bedding plane of failure passes through compacted rock and material collapses en masse and not in individual blocks. Note that a rockslide is similar to an avalanche because they are both slides of debris that can bury a piece of land. While a landslide occurs when loose dirt or sediment falls down a slope, a rockslide occurs only when solid rocks are transported down slope. The rocks tumble downhill, loosening other rocks on their way and smashing everything in their path. Fast-flowing rock slides or debris slides behave similarly to snow avalanches, and are often referred to as rock avalanches or debris avalanches.
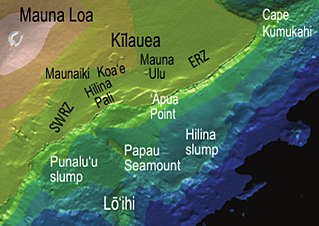
The Hilina Slump, on the south flank of the Kīlauea Volcano on the southeast coast of the Big Island of Hawaiʻi, is the most notable of several landslides that ring each of the Hawaiian Islands. These landslides are the means by which material deposited at a volcano's vents are transferred downward and seaward, eventually spilling onto the seabed to broaden the island.

A mudflow, also known as mudslide or mud flow, is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris and dirt that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/second. Mudflows contain a significant proportion of clay, which makes them more fluid than debris flows, allowing them to travel farther and across lower slope angles. Both types of flow are generally mixtures of particles with a wide range of sizes, which typically become sorted by size upon deposition.
There have been known various classifications of landslides. Broad definitions include forms of mass movement that narrower definitions exclude. For example, the McGraw-Hill Encyclopedia of Science and Technology distinguishes the following types of landslides:
Landslide mitigation refers to several human-made activities on slopes with the goal of lessening the effect of landslides. Landslides can be triggered by many, sometimes concomitant causes. In addition to shallow erosion or reduction of shear strength caused by seasonal rainfall, landslides may be triggered by anthropic activities, such as adding excessive weight above the slope, digging at mid-slope or at the foot of the slope. Often, individual phenomena join to generate instability over time, which often does not allow a reconstruction of the evolution of a particular landslide. Therefore, landslide hazard mitigation measures are not generally classified according to the phenomenon that might cause a landslide. Instead, they are classified by the sort of slope stabilization method used:

An earthflow is a downslope viscous flow of fine-grained materials that have been saturated with water and moves under the pull of gravity. It is an intermediate type of mass wasting that is between downhill creep and mudflow. The types of materials that are susceptible to earthflows are clay, fine sand and silt, and fine-grained pyroclastic material.

The interaction between erosion and tectonics has been a topic of debate since the early 1990s. While the tectonic effects on surface processes such as erosion have long been recognized, the opposite has only recently been addressed. The primary questions surrounding this topic are what types of interactions exist between erosion and tectonics and what are the implications of these interactions. While this is still a matter of debate, one thing is clear, Earth's landscape is a product of two factors: tectonics, which can create topography and maintain relief through surface and rock uplift, and climate, which mediates the erosional processes that wear away upland areas over time. The interaction of these processes can form, modify, or destroy geomorphic features on Earth's surface.

Submarine landslides are marine landslides that transport sediment across the continental shelf and into the deep ocean. A submarine landslide is initiated when the downwards driving stress exceeds the resisting stress of the seafloor slope material, causing movements along one or more concave to planar rupture surfaces. Submarine landslides take place in a variety of different settings, including planes as low as 1°, and can cause significant damage to both life and property. Recent advances have been made in understanding the nature and processes of submarine landslides through the use of sidescan sonar and other seafloor mapping technology.

River bank failure can be caused when the gravitational forces acting on a bank exceed the forces which hold the sediment together. Failure depends on sediment type, layering, and moisture content.
The Truttman Sink is an earthflow within the Humboldt Lagoons State Park, along the coast of Humboldt County, California. It is located between Trinidad to the south and Orick to the north. It deposits materials into the northern end of Big Lagoon and the Pacific Ocean, especially during periods of heavy rain. The soil characteristics, geology, and vegetation along the slope of this mass-wasting feature suggest a combination of an earthflow movement and a rotational slump.
Retrogressive thaw slumps (RTS), are a type of landslide that occur in the terrestrial Arctic's permafrost region of the circumpolar Northern Hemisphere when an ice-rich section thaws. RTSs develop quickly and can extend across several hectares modifying Arctic coastlines and permafrost terrain. They are the most active and dynamic feature of thermokarst—the collapse of the land surface as ground ice melts. They are thermokarst slope failures due to abrupt thawing of ice-rich permafrost or glaciated terrains. These horseshoe-shaped landslides contribute to the thawing of hectares of permafrost annually and are considered to be one of the most active and dynamic features of thermokarst—the "processes and landforms that involve collapse of the land surface as a result of the melting of ground ice." They are found in permafrost or glaciated regions of the Northern Hemisphere—the Tibetan Plateau, Siberia, from the Himalayas to northern Greenland, and in northern Canada's Northwest Territories (NWT), the Yukon Territories, Nunavut, and Nunavik and in the American state of Alaska. The largest RTS in the world is in Siberia—the Batagaika Crater, also called a "megaslump", is one-kilometre-long and 100 metres (330 ft) deep and it grows a 100 feet (30 m) annually. The land began to sink, and the Batagaika Crater began to form in the 1960s, following clear-cutting of a section of forested area.

The area of Oeschinen Lake and Kander river valley in Switzerland have been subject of multiple large landslides during the Holocene. Both the number and timing of landslides is controversial, with the most recent estimates stating that the large Kander landslide occurred about 3,210 years ago and the smaller Oeschinen Lake landslide 2,300 years ago. Both may have been caused by earthquakes, and the latter landslide generated the Oeschinen Lake. More recent landslides have occurred, and unstable rock masses occur in the landslide area.

















