In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.
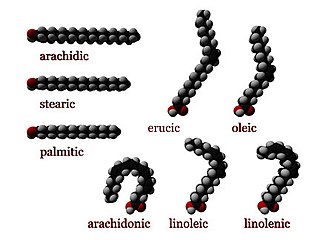
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are a major component of the lipids in some species such as microalgae but in some other organisms are not found in their standalone form, but instead exist as three main classes of esters: triglycerides, phospholipids, and cholesteryl esters. In any of these forms, fatty acids are both important dietary sources of fuel for animals and important structural components for cells.

Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology.

A triglyceride is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids. Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as well as vegetable fat. They are also present in the blood to enable the bidirectional transference of adipose fat and blood glucose from the liver, and are a major component of human skin oils.
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of other enzymes, particularly lipases.

Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.
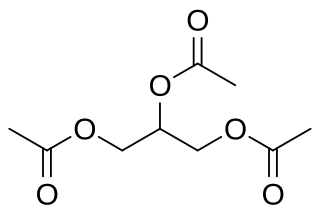
Glycerides, also known as acylglycerols, are esters formed from glycerol and fatty acids, and are generally very hydrophobic.
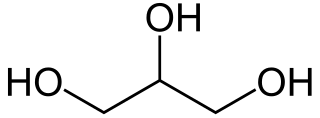
A diol is a chemical compound containing two hydroxyl groups. An aliphatic diol is also called a glycol. This pairing of functional groups is pervasive, and many subcategories have been identified.
Biodiesel production is the process of producing the biofuel, biodiesel, through the chemical reactions of transesterification and esterification. This involves vegetable or animal fats and oils being reacted with short-chain alcohols. The alcohols used should be of low molecular weight. Ethanol is the most used because of its low cost, however, greater conversions into biodiesel can be reached using methanol. Although the transesterification reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases, the base-catalyzed reaction is more common. This path has lower reaction times and catalyst cost than those acid catalysis. However, alkaline catalysis has the disadvantage of high sensitivity to both water and free fatty acids present in the oils. August 10 is international biodiesel day
In organic chemistry, butyl is a four-carbon alkyl radical or substituent group with general chemical formula −C4H9, derived from either of the two isomers (n-butane and isobutane) of butane.

Saponification value or saponification number represents the number of milligrams of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH) required to saponify one gram of fat under the conditions specified. It is a measure of the average molecular weight of all the fatty acids present in the sample in form of triglycerides. The higher the saponification value, the lower the fatty acids average length, the lighter the mean molecular weight of triglycerides and vice versa. Practically, fats or oils with high saponification value are more suitable for soap making.
Fatty acid metabolism consists of various metabolic processes involving or closely related to fatty acids, a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient category. These processes can mainly be divided into (1) catabolic processes that generate energy and (2) anabolic processes where they serve as building blocks for other compounds.
In chemistry, acid value is a number used to quantify the acidity of a given chemical substance. It is the quantity of base, expressed as milligrams of KOH required to neutralize the acidic constituents in 1 gram of a sample. The acid value measures the acidity of water-insoluble substances like oils, fats, waxes and resins, which do not have a pH value.
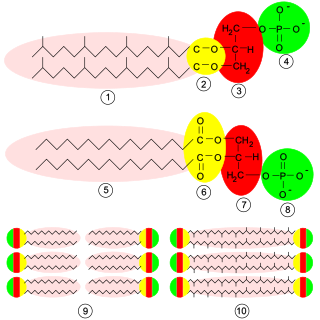
Glycerophospholipids or phosphoglycerides are glycerol-based phospholipids. They are the main component of biological membranes in eukaryotic cells. They are a type of lipid, of which its composition affects membrane structure and properties. Two major classes are known: those for bacteria and eukaryotes and a separate family for archaea.
In biochemistry, lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acids and glycerol into fats, or a metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, with the latter being the process by which fatty acids are esterified to glycerol before being packaged into very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Fatty acids are produced in the cytoplasm of cells by repeatedly adding two-carbon units to acetyl-CoA. Triacylglycerol synthesis, on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue. Nevertheless, it also occurs to some extent in other tissues such as the gut and kidney. A review on lipogenesis in the brain was published in 2008 by Lopez and Vidal-Puig. After being packaged into VLDL in the liver, the resulting lipoprotein is then secreted directly into the blood for delivery to peripheral tissues.
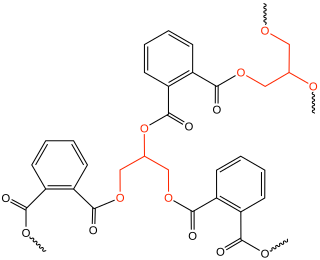
An alkyd is a polyester resin modified by the addition of fatty acids and other components. Alkyds are derived from polyols and organic acids including dicarboxylic acids or carboxylic acid anhydride and triglyceride oils. The term alkyd is a modification of the original name "alcid", reflecting the fact that they are derived from alcohol and organic acids. The inclusion of a fatty acid confers a tendency to form flexible coatings. Alkyds are used in paints, varnishes and in moulds for casting. They are the dominant resin or binder in most commercial oil-based coatings. Approximately 200,000 tons of alkyd resins are produced each year. The original alkyds were compounds of glycerol and phthalic acid sold under the name Glyptal. These were sold as substitutes for the darker-colored copal resins, thus creating alkyd varnishes that were much paler in colour. From these, the alkyds that are known today were developed.
Lipid metabolism is the synthesis and degradation of lipids in cells, involving the breakdown and storage of fats for energy and the synthesis of structural and functional lipids, such as those involved in the construction of cell membranes. In animals, these fats are obtained from food and are synthesized by the liver. Lipogenesis is the process of synthesizing these fats. The majority of lipids found in the human body from ingesting food are triglycerides and cholesterol. Other types of lipids found in the body are fatty acids and membrane lipids. Lipid metabolism is often considered as the digestion and absorption process of dietary fat; however, there are two sources of fats that organisms can use to obtain energy: from consumed dietary fats and from stored fat. Vertebrates use both sources of fat to produce energy for organs such as the heart to function. Since lipids are hydrophobic molecules, they need to be solubilized before their metabolism can begin. Lipid metabolism often begins with hydrolysis, which occurs with the help of various enzymes in the digestive system. Lipid metabolism also occurs in plants, though the processes differ in some ways when compared to animals. The second step after the hydrolysis is the absorption of the fatty acids into the epithelial cells of the intestinal wall. In the epithelial cells, fatty acids are packaged and transported to the rest of the body.
Neutral fats, also known as true fats, are simple lipids that are produced by the dehydration synthesis of one or more fatty acids with an alcohol like glycerol. Neutral fats are also known as triacylglycerols, these lipids are dense as well as hydrophobic due to their long carbon chain and are there main function is to store energy. Neutral fats can be made from the compact packing of fatty acids. Triacylglycerols can also serve to part of lipid membranes, which serve to provide flexibility to the membranes, they can also serve as parts for signaling molecules. Many types of neutral fats are possible both because of the number and variety of fatty acids that could form part of it and because of the different bonding locations for the fatty acids. An example is a monoglyceride, which has one fatty acid combined with glycerol, a diglyceride, which has two fatty acids combined with glycerol, or a triglyceride, which has three fatty acids combined with glycerol.
Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate from precursors other than glucose. Usually, glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, in the liquid of the cell's cytoplasm. Glyceroneogenesis is used when the concentrations of glucose in the cytosol are low, and typically uses pyruvate as the precursor, but can also use alanine, glutamine, or any substances from the TCA cycle. The main regulator enzyme for this pathway is an enzyme called phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which catalyzes the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate. Glyceroneogenesis is observed mainly in adipose tissue, and in the liver. A significant biochemical pathway regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes.
The Criegee oxidation is a glycol cleavage reaction in which vicinal diols are oxidized to form ketones and aldehydes using lead tetraacetate. It is analogous to the use of periodate but uses a milder oxidant. This oxidation was discovered by Rudolf Criegee and coworkers and first reported in 1931 using ethylene glycol as the substrate.