
The River Waveney is a river which forms the boundary between Suffolk and Norfolk, England, for much of its length within The Broads. The earliest attestation of the name is from 1275, Wahenhe, from *wagen + ea, meaning the river by a quagmire.

Reedham is a village and civil parish in the English county of Norfolk and within The Broads. It is on the north bank of the River Yare, 12 miles (19 km) east of the city of Norwich, 8 mi (13 km) south-west of the town of Great Yarmouth and the same distance north-west of the Suffolk town of Lowestoft. The village's name means 'reedy homestead/village' or 'reedy hemmed-in land'.

Lowestoft is a coastal town and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk, England. As the most easterly UK settlement, it is 38 miles (61 km) north-east of Ipswich and 22 miles (35 km) south-east of Norwich, and the main town in its district. The estimated population in the built-up area exceeds 70,000. Its development grew with the fishing industry and as a seaside resort with wide sandy beaches. As fishing declined, oil and gas exploitation in the North Sea in the 1960s took over. While these too have declined, Lowestoft is becoming a regional centre of the renewable energy industry.

Somerleyton is a village and former civil parish, now in the parish of Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet, in the East Suffolk district, in the north of the English county of Suffolk. It is 4.5 miles (7.2 km) north-west of Lowestoft and 5.5 miles (8.9 km) south-west of Great Yarmouth. The village is closely associated with Somerleyton Hall and was largely rebuilt as a model village in the 19th century at the direction of Samuel Morton Peto. The parish was combined with Herringfleet and Ashby to create the parish of "Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet" on 1 April 1987.

Herringfleet is a place and former civil parish, now in the parish of Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet, in the East Suffolk district, in the north of the English county of Suffolk. It is located 5.5 miles (8.9 km) north-west of Lowestoft. The parish was combined with Somerleyton and Ashby to create the parish of "Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet" on 1 April 1987.

The River Wensum is a chalk river in Norfolk, England and a tributary of the River Yare, despite being the larger of the two rivers. The river is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest and Special Area of Conservation.

A swing bridge is a movable bridge that can be rotated horizontally around a vertical axis. It has as its primary structural support a vertical locating pin and support ring, usually at or near to its center of gravity, about which the swing span can then pivot horizontally as shown in the animated illustration to the right.
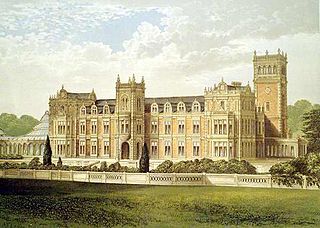
Baron Somerleyton, of Somerleyton in the County of Suffolk, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. It was created on 26 June 1916 for the Liberal Unionist politician and former Paymaster General Sir Savile Crossley, 2nd Baronet. The titles are currently held by his great-grandson, the fourth Baron, who succeeded his father in 2012.

The East Suffolk line is an un-electrified 49-mile secondary railway line running between Ipswich and Lowestoft in Suffolk, England. The traffic along the route consists of passenger services operated by Greater Anglia, while nuclear flask trains for the Sizewell nuclear power stations are operated by Direct Rail Services.

Banavie railway station is a railway station on the West Highland Line serving the village of Banavie, although it is much closer to Caol, Scotland. It is sited between Corpach and Fort William, 0 miles 22 chains (0.44 km) from Banavie Junction, just north of Fort William. To continue on to the next station at Corpach, trains must pass over the Caledonian Canal at Neptune's Staircase, a popular tourist attraction. ScotRail provide all services at, and manage, the station.

Somerleyton railway station is on the Wherry Lines in the east of England, serving the village of Somerleyton, Suffolk. It is 18 miles (29 km) down the line from Norwich on the route to Lowestoft, and is less than 2 miles (3.2 km) from Somerleyton Hall on foot. Its three-letter station code is SYT.

The Loughor railway viaduct carries the West Wales Line across the River Loughor. It is adjacent, and runs parallel to, the Loughor road bridge. The 1880 viaduct was granted Grade II listed building status. Before it was demolished in early 2013, the viaduct was the last remaining timber viaduct designed by Isambard Kingdom Brunel.

Trowse Bridge is a single-track railway bridge which carries the Great Eastern Main Line over the River Wensum just outside Norwich in England at grid reference TG245076.
The Yarmouth–Beccles line was a railway line which linked the Suffolk market town of Beccles with the Norfolk coastal resort of Yarmouth. Forming part of the East Suffolk Railway, the line was opened in 1859 and closed 100 years later in 1959.

Flixton is a civil parish in the north of the English county of Suffolk. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) north-east of Lowestoft in the East Suffolk district.

Reedham Swing Bridge, on the site of a Victorian swing bridge, is still in use at Reedham, Norfolk, England.

Sheepwash Channel connects the River Thames to the west and the Castle Mill Stream next to the Oxford Canal to the east, in west Oxford, England. To the north are Cripley Meadow and Fiddler's Island. To the south are Osney Island and the Botley Road.

Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet is a civil parish in the north of the English county of Suffolk. It is 5 miles (8.0 km) north-west of Lowestoft and the same distance south-west of Great Yarmouth and is in the East Suffolk district. The parish is made up of the villages of Somerleyton, Ashby and Herringfleet and at the 2011 United Kingdom census had a population of 427.

Oulton is a civil parish on the western edge of the town of Lowestoft in the north of the English county of Suffolk. It is in the East Suffolk district. The eastern part of the parish forms part of the suburbs of Lowestoft, whilst the western section extends into The Broads national park, reaching the River Waveney and Oulton Dyke.

Gull Wing Bridge is a road bridge being built to span Lake Lothing in the town of Lowestoft, Suffolk, England, which is claimed to be the largest rolling bascule bridge in the world lifted using hydraulic cylinders. The bridge is planned to be completed and open to traffic in the summer of 2024.



















