Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Romanesque is characterized by semicircular arches, while the Gothic is marked by the pointed arches. The Romanesque emerged nearly simultaneously in multiple countries ; its examples can be found across the continent, making it the first pan-European architectural style since Imperial Roman architecture. Similarly to Gothic, the name of the style was transferred onto the contemporary Romanesque art.

The Cathedral of Saint Mary of Burgos is a Catholic church dedicated to the Virgin Mary located in the historical center of the Spanish city of Burgos. Its official name is the Holy Metropolitan Cathedral Basilica Church of St Mary of Burgos.

Santa María de Regla de León Cathedral is a Catholic church, the episcopal see of the diocese of León in the city of León, Castile and León, north-western Spain, consecrated under the name of the Virgin Mary. It was the first monument declared by the Royal Order of Spain on August 28, 1844.

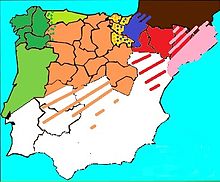
One of the first streams of Romanesque architecture in Europe from the 10th century and the beginning of 11th century is called First Romanesque or Lombard Romanesque. It took place in the region of Lombardy and spread into Catalonia and into the south of France. Its principal decoration for the exterior, bands of ornamental blind arches are called Lombard bands. It was characterized by thick walls and lack of sculpture in facades, and with interiors profusely painted with frescoes.

The Isabelline style, also called the Isabelline Gothic, or Castilian late Gothic, was the dominant architectural style of the Crown of Castile during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon in the late-15th century to early-16th century. The Frenchman Émile Bertaux named the style after Queen Isabella.

Spanish Renaissance architecture emerged in the late 15th century as Renaissance ideals reached Spain, blending with existing Gothic forms. Rooted in Renaissance humanism and a renewed interest inClassical architecture, the style became distinguished by a synthesis of Gothic and Italian Renaissance elements. The style is a creation of uniquely Spanish phases notable because of both rich ornamentation and restrained minimalism. The period saw contributions from the patronage of noble families, notably the House of Mendoza, and architects like Lorenzo Vázquez de Segovia, whose works in places like the Colegio Mayor Santa Cruz in Valladolid, incorporated Tuscan-Roman motifs alongside Gothic forms.

The Cathedral of Zamora is a Catholic cathedral in Zamora, in Castile and León, Spain, located above the right bank of the Duero It remains surrounded by its old walls and gates.

Portuguese Gothic architecture is the architectural style prevalent in Portugal in the Late Middle Ages. As in other parts of Europe, Gothic style slowly replaced Romanesque architecture in the period between the late 12th and the 13th century. Between the late 15th and early 16th century, Gothic was replaced by Renaissance architecture through an intermediate style called Manueline.

Mozarabic art is an early medieval artistic style that is part of the pre-Romanesque style and is linked to the kingdom of León. It was developed by the Hispanic Christians who lived in Arab-Muslim territory and in the expansion territories of the León crown, in the period from the Arab-Islamic Conquest of the Iberian Peninsula (711) to the end of the 11th century. During this period, disciplines such as painting, goldsmithing and architecture with marked Caliphate influences were cultivated in a context of medieval coexistence - Christian, Hebrew and Muslim - in which the territories were constantly changing in size and status. Other names for this artistic style are Leonese art or repopulation art.

The Monastery of Santa Maria de Ripoll is a Benedictine monastery, built in the Romanesque style, located in the town of Ripoll in Catalonia, Spain. Although much of the present church is 19th century rebuilding, the sculptured portico is a renowned work of Romanesque art.

The Monastery of Sant Jeroni de Cotalba is a monastic building of Valencian Gothic, Mudéjar, Renaissance, Baroque and Neoclassical styles constructed between the 14th and 18th centuries, located in the municipal area of Alfauir, (Valencia), Spain, about 8 km. from the well-known city of Gandia.

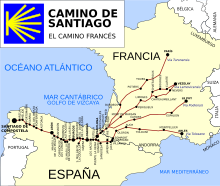
The Church of Saint Martin of Tours, in Frómista, province of Palencia, Spain, was built in the 11th century in Romanesque style. It is located on the Way of St. James to Santiago de Compostella.

The Master of Taüll is considered the greatest mural painter of the 12th century in Catalonia, as well as one of the most important Romanesque painters in Europe. His main work is the church of Sant Climent de Taüll, with the famous apse painting now moved to the Museu Nacional d'Art de Catalunya in Barcelona.

Romanesque architecture in Spain is the architectural style reflective of Romanesque architecture, with peculiar influences both from architectural styles outside the Iberian Peninsula via Italy and France as well as traditional architectural patterns from within the peninsula. Romanesque architecture was developed in and propagated throughout Europe for more than two centuries, ranging approximately from the late tenth century until the thirteenth century.

Valencian Gothic is an architectural style. It occurred under the Kingdom of Valencia between the 13th and 15th centuries, which places it at the end of the European Gothic period and at the beginning of the Renaissance. The term "Valencian Gothic" is confined to the Kingdom of Valencia and its area of influence, which has its own characteristics.

The Church of San Andrés is a Catholic church located in the town of Cuéllar, province of Segovia, in the autonomous community of Castile and León, Spain. Located outside the walls of the town and in the neighborhood to which it gives its name, during the Middle Ages it was the head of a small suburb that over time merged with the town.