
Dieffenbachia is a genus of tropical flowering plants in the family Araceae. It is native to the New World Tropics from Mexico and the West Indies south to Argentina. Some species are widely cultivated as ornamental plants, especially as houseplants, and have become naturalized on a few tropical islands.

Anthurium, is a genus of about 1000 species of flowering plants, the largest genus of the arum family, Araceae. General common names include anthurium, tailflower, flamingo flower, and laceleaf.

Dracontium is a genus of flowering plants similar to those of Amorphophallus. It is native to South America, Central America, southern Mexico, and the West Indies.

Quercus costaricensis is a species of oak native to Central America. It is often found with Quercus copeyensis in the upper montane forests, to 3100 meters elevation. The leaves are tough and leathery with a short petiole and toothed margin. Wind is the primary pollinator. Squirrels are their main seed predator but also their main disperser as they commonly lose their buried seeds.

Prestoea is a genus of palms native to the Caribbean, Central and South America. Its range extends from Nicaragua and the Greater Antilles in the north to Brazil and Bolivia in the south.
- Prestoea acuminata(Willd.) H.E.Moore - Central America, West Indies, northwestern South America
- Prestoea carderi(W.Bull) Hook.f. - Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru
- Prestoea decurrensH.E.Moore - Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador
- Prestoea ensiformis(Ruiz & Pav.) H.E.Moore - Costa Rica, Peru, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador
- Prestoea longipetiolata(Oerst.) H.E.Moore - Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia, Venezuela
- Prestoea pubensH.E.Moore - Panama, Colombia
- Prestoea pubigera(Griseb. & H.Wendl.) Hook.f. - Venezuela, Trinidad
- Prestoea schultzeana(Burret) H.E.Moore - Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador. Peru, Brazil
- Prestoea simplicifoliaGaleano - Antioquia region of Colombia
- Prestoea tenuiramosa(Dammer) H.E.Moore - Venezuela, Guyana, Brazil

Spathiphyllum silvicola is a flowering plant of the genus Spathiphyllum in the family Araceae. It is native to Colombia and Costa Rica.
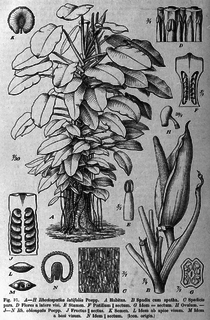
Rhodospatha is a genus of plant in family Araceae. It is native to South America, Central America, and southern Mexico.

Stenospermation is a genus of plant in family Araceae native to South America and Central America.

Welfia is a genus of palms found in Central America and northwestern South America. Only two species are currently recognized: Welfia regia and Welfia alfredii.

Neonicholsonia is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family native to Central America. The genus and species names honor George Nicholson, a former curator of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and his successor William Watson.

Holochlamys is a monotypic genus of flowering plants in the Araceae family. Holochlamys beccarii is the only species in the genus Holochlamys. It is native to New Guinea and the Bismarck Archipelago and is found growing in mud near lowland streams or rocky streambeds at high elevations.

Urospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae that consists of approximately 10 known species. They are found growing in South America and Central America in swamps, wet savannahs, and brackish water. The leaves of the species in this genus are upward pointing and sagittate (arrow-shaped). The inflorescences are quite unique; the spathe is mottled and elongated with a spiral twist at the end. The seeds are distributed by water and have a texture similar to cork that allows them to float. They also quickly germinate in water.
Chlorospatha is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae. Chlorospatha can be found from Costa Rica, Panama, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.

Spathicarpa is a genus of flowering plants in the family Araceae, all of which are endemic to South America. Spathicarpa species are notable for the fact that the entirety of their spadix is fused to the spathe. The genus is believed to be closely related to Spathantheum. The tribe Spathicarpeae is named after the genus Spathicarpa.

Monstera epipremnoides is a species of flowering plant in the Araceae family, endemic to Costa Rica.

Benzingia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to mountains of Central America and northwestern South America from Costa Rica to Peru.

Cischweinfia is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It was named after Harvard orchidologist Charles Schweinfurth. It has eleven currently recognized species, all native to Central America and northwestern South America.
- Cischweinfia colombianaGaray - Colombia
- Cischweinfia dasyandra(Rchb.f.) Dressler & N.H.Williams - Colombia, Ecuador, Panama, Costa Rica
- Cischweinfia donrafaeDressler & Dalström - Costa Rica
- Cischweinfia jaraeDodson & D.E.Benn.- Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia
- Cischweinfia nanaDressler - Panama
- Cischweinfia parva(C.Schweinf.) Dressler & N.H.Williams - Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Colombia
- Cischweinfia platychilaGaray - Colombia
- Cischweinfia popowianaKöniger - Ecuador
- Cischweinfia pusilla(C.Schweinf.) Dressler & N.H.Williams - Colombia, Panama, Costa Rica
- Cischweinfia pygmaea(Pupulin, J.Valle & G.Merino) M.W.Chase - Ecuador
- Cischweinfia rostrataDressler & N.H.Williams - Colombia, Ecuador

Nephthytis swainei is a species of flowering plants in the family Araceae, native to tropical West Africa.
Monstera standleyana, the five holes plant is a species of flowering plant from Araceae family which can be found in Costa Rica, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. It was described by G.S. Bunting in 1967.




















