
Hogmanay is the Scots word for the last day of the old year and is synonymous with the celebration of the New Year in the Scottish manner. It is normally followed by further celebration on the morning of New Year's Day and, in some cases, 2 January—a Scottish bank holiday. In a few contexts, the word Hogmanay is used more loosely to describe the entire period consisting of the last few days of the old year and the first few days of the new year. For instance, not all events held under the banner of Edinburgh's Hogmanay take place on 31 December.

Loch is a word meaning "lake" or "sea inlet" in Scottish and Irish Gaelic, subsequently borrowed into English. In Irish contexts, it often appears in the anglicized form "lough".

The Oxford English Dictionary (OED) is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first edition in 1884, traces the historical development of the English language, providing a comprehensive resource to scholars and academic researchers, and provides ongoing descriptions of English language usage in its variations around the world.

A warlock is a male practitioner of witchcraft.

The letter yogh (ȝogh) was used in Middle English and Older Scots, representing y and various velar phonemes. It was derived from the Insular form of the letter g, Ᵹᵹ.
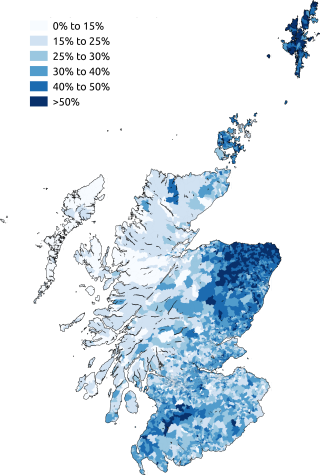
Scots is an Anglic language variety in the West Germanic language family, spoken in Scotland and parts of Ulster in the north of Ireland. Most commonly spoken in the Scottish Lowlands, Northern Isles, and northern Ulster, it is sometimes called Lowland Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Goidelic Celtic language that was historically restricted to most of the Scottish Highlands, the Hebrides, and Galloway after the sixteenth century; or Broad Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Standard English. Modern Scots is a sister language of Modern English, as the two diverged independently from the same source: Early Middle English (1150–1350).

The Norsemen were a North Germanic linguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the predecessor of the modern Germanic languages of Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a large-scale expansion in all directions, giving rise to the Viking Age. In English-language scholarship since the 19th century, Norse seafaring traders, settlers and warriors have commonly been referred to as Vikings. Historians of Anglo-Saxon England distinguish between Norse Vikings (Norsemen) from Norway, who mainly invaded and occupied the islands north and north-west of Britain, as well as Ireland and western Britain, and Danish Vikings, who principally invaded and occupied eastern Britain.

Wyrd is a concept in Anglo-Saxon culture roughly corresponding to fate or personal destiny. The word is ancestral to Modern English weird, whose meaning has drifted towards an adjectival use with a more general sense of "supernatural" or "uncanny", or simply "unexpected".
Lallans, is a term that was traditionally used to refer to the Scots language as a whole. However, more recent interpretations assume it refers to the dialects of south and central Scotland, while Doric, a term once used to refer to Scots dialects in general, is now generally seen to refer to the Mid Northern Scots dialects spoken in the north-east of Scotland.
Scottish English is the set of varieties of the English language spoken in Scotland. The transregional, standardised variety is called Scottish Standard English or Standard Scottish English (SSE). Scottish Standard English may be defined as "the characteristic speech of the professional class [in Scotland] and the accepted norm in schools". IETF language tag for "Scottish Standard English" is en-scotland.
Mackem, Makem or Mak'em is a nickname for residents of and people from Sunderland, a city in North East England. It is also a name for the local dialect and accent ; and for a fan, of whatever origin, of Sunderland A.F.C. It has been used by the people of Sunderland to describe themselves since the 1980s, prior to which it was mainly used in Tyneside as a disparaging exonym. An alternative name for a Mackem is a Wearsider.

Shortbread or shortie is a traditional Scottish biscuit usually made from one part white sugar, two parts butter, and three to four parts plain wheat flour. Shortbread does not contain any leavening, such as baking powder or baking soda. Shortbread is widely associated with Christmas and Hogmanay festivities in Scotland, and some Scottish brands are exported around the world.

A spinnaker is a sail designed specifically for sailing off the wind on courses between a reach to downwind. Spinnakers are constructed of lightweight fabric, usually nylon, and are often brightly colored. They may be designed to perform best as either a reaching or a running spinnaker, by the shaping of the panels and seams. They are attached at only three points and said to be flown.

An ell is a northwestern European unit of measurement, originally understood as a cubit. The word literally means "arm", and survives in the modern English word "elbow" (arm-bend). Later usage through the 19th century refers to several longer units, some of which are thought to derive from a "double ell".

The Gallowglass were a class of elite mercenary warriors who were principally members of the Norse-Gaelic clans of Ireland and Scotland between the mid 13th century and late 16th century. It originally applied to Scots, who shared a common background and language with the Irish, but as they were descendants of 10th-century Norse settlers who had intermarried with the local population in western Scotland, the Irish called them Gall Gaeil.

Modern Scots comprises the varieties of Scots traditionally spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster, from 1700.

A windjammer is a commercial sailing ship with multiple masts that may be square rigged, or fore-and-aft rigged, or a combination of the two. The informal term "windjammer" arose during the transition from the Age of Sail to the Age of Steam during the 19th century. The Oxford English Dictionary records the word "windjamming" from 1886 and "windjammer" with reference to a ship from 1892. The term has evolved to include such a vessel, carrying passengers on overnight cruises in the Caribbean, the U.S. state of Maine and elsewhere.














