
The British Antarctic Territory (BAT) is a sector of Antarctica claimed by the United Kingdom as one of its 14 British Overseas Territories, of which it is by far the largest by area. It comprises the region south of 60°S latitude and between longitudes 20°W and 80°W, forming a wedge shape that extends to the South Pole, overlapped by the Antarctic claims of Argentina and Chile.

The South Shetland Islands are a group of Antarctic islands with a total area of 3,687 km2 (1,424 sq mi). They lie about 120 kilometres north of the Antarctic Peninsula, and between 430 and 900 km southwest of the nearest point of the South Orkney Islands. By the Antarctic Treaty of 1959, the islands' sovereignty is neither recognized nor disputed by the signatories and they are free for use by any signatory for non-military purposes.

Alexander Island, which is also known as Alexander I Island, Alexander I Land, Alexander Land, Alexander I Archipelago, and Zemlja Alexandra I, is the largest island of Antarctica. It lies in the Bellingshausen Sea west of Palmer Land, Antarctic Peninsula from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. The George VI Ice Shelf entirely fills George VI Sound and connects Alexander Island to Palmer Land. The island partly surrounds Wilkins Sound, which lies to its west. Alexander Island is about 390 kilometres (240 mi) long in a north–south direction, 80 kilometres (50 mi) wide in the north, and 240 kilometres (150 mi) wide in the south. Alexander Island is the second-largest uninhabited island in the world, after Devon Island.

Petermann Island is a small, low and rounded island, lying off the northwest coast of Kyiv Peninsula in Graham Land, Antarctica, a short distance south of Booth Island and the Lemaire Channel. It is a popular tourist destination.

Adelaide Island is a large, mainly ice-covered island, 139 kilometres (75 nmi) long and 37 kilometres (20 nmi) wide, lying at the north side of Marguerite Bay off the west coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. The Ginger Islands lie off the southern end. Mount Bodys is the easternmost mountain on Adelaide Island, rising to over 1,220 m. The island lies within the Argentine, British and Chilean Antarctic claims.
Trinity Island or Île de la Trinité or Isla Trinidad is an island 24 km (15 mi) long and 10 km (6 mi) wide in the northern part of the Palmer Archipelago, Antarctica. It lies 37 km (23 mi) east of Hoseason Island, 72.6 km (45 mi) south of Deception Island in the South Shetland Islands, and 10.3 km (6 mi) north-northwest of Cape Andreas on the Antarctic Peninsula. The island was named by Otto Nordenskiöld, leader of the 1901-1904 Swedish Antarctic Expedition (SAE) in commemoration of Edward Bransfield's "Trinity Land" of 1820.

Snow Hill Island is an almost completely snowcapped island, 33 km (21 mi) long and 12 km (7.5 mi) wide, lying off the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from James Ross Island to the north-east by Admiralty Sound and from Seymour Island to the north by Picnic Passage. It is one of several islands around the peninsula known as Graham Land, which is closer to Argentina and South America than any other part of the Antarctic continent.

The Antarctic Place-names Commission was established by the Bulgarian Antarctic Institute in 1994, and since 2001 has been a body affiliated with the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Bulgaria.

Cape Evans is a rocky cape on the west side of Ross Island, Antarctica, forming the north side of the entrance to Erebus Bay.
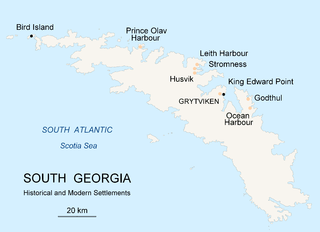
Prince Olav Harbour is a small harbour in the south west portion of Cook Bay, entered between Point Abrahamsen and Sheep Point, along the north coast of South Georgia.
Emperor Island is a small island in Marguerite Bay, lying close north-east of the Courtier Islands in the Dion Islands. The islands in this group were discovered and roughly charted in 1909 by the French Antarctic Expedition. This island was surveyed in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey and so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because a low rock and shingle isthmus at the south-eastern end of the island was the winter breeding site of emperor penguins.

Endurance Glacier is a broad glacier north of Mount Elder, draining south-east to the south coast of Elephant Island in the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica, and is the main discharge glacier on the island. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after HMS Endurance, which anchored off the glacier on several occasions in support of the Joint Services Expedition to Elephant Island, 1970–71.
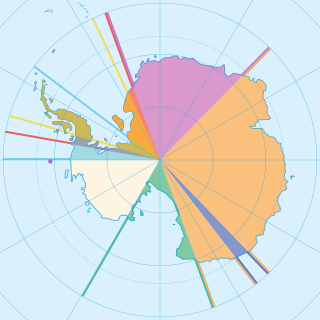
Seven sovereign states–Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the United Kingdom–have made territorial claims in Antarctica. These countries have tended to place their Antarctic scientific observation and study facilities within their respective claimed territories; however, a number of such facilities are located outside of the area claimed by their respective countries of operation, and countries without claims such as India, Italy, Pakistan, Russia, South Africa, Ukraine, and the United States have constructed research facilities within the areas claimed by other countries.

Bellisime Glacier is a glacier about 4 nautical miles (7 km) long flowing south from Thurston Island east of Myers Glacier. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Lynda B. Bellisime of the United States Geological Survey (USGS), Flagstaff, Arizona, part of the USGS team that compiled the 1:5,000,000-scale Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer maps of Antarctica and the 1:250,000-scale Landsat TM image maps of the Siple Coast area in the 1990s.
Wauwermans Islands is a group of small, low, snow-covered islands forming the northernmost group in the Wilhelm Archipelago. Discovered by a German expedition 1873–74, under Dallmann. Sighted by the Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1897–99, under Gerlache, and named for Lieutenant General Wauwermans, president of the Société Royale Belge de Géographie, a supporter of the expedition.

Deadmond Glacier is a glacier about 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing from the east side of Evans Peninsula on Thurston Island into Cadwalader Inlet. It was discovered by the U.S. Navy Bellingshausen Sea Expedition in February 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Commander Robert B. Deadmond, executive officer of USS Burton Island, forming part of this expedition.

Moe Island is an island 2 km (1.2 mi) long in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica, separated from the south-west end of Signy Island by Fyr Channel. It was charted by Captain Petter Sørlle in 1912–13, and named after M. Thoralf Moe of Sandefjord, Norway, a contemporary whaling captain who worked in this area. The northernmost point of the island is Spaull Point, named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Vaughan W. Spaull, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) biologist on Signy Island, 1969.

Hale Glacier is a glacier about 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, located just east of Mount Simpson on Thurston Island, Antarctica, and flowing southwest to the Abbot Ice Shelf in Peacock Sound. It was delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6 in January 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Lieutenant Bill J. Hale, U.S. Navy, a helicopter pilot aboard USS Burton Island who made exploratory flights to Thurston Island in February 1960.
Squires Glacier is a tributary glacier between the Playfair and Hutton Mountains, flowing east-northeast to Swann Glacier, in Palmer Land. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–67. Named by Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Peter L. Squires, glaciologist at Byrd Station, summer 1965–66.

Lagotellerie Island is an island 1.9 kilometres (1 nmi) long, lying 3.7 kilometres (2 nmi) west of Horseshoe Island in Marguerite Bay, off the west coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and named by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1908–10, under Jean-Baptiste Charcot.













