
Paint is a material or mixture that, when applied to a solid material and allowed to dry, adds a film-like layer. As art, this is used to create an image or images known as a painting. Paint can be made in many colors and types. Most paints are either oil-based or water-based, and each has distinct characteristics.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+ and hydroxide anions OH−.

Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula C
10H
8. It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is the main ingredient of traditional mothballs.

Dry cleaning is any cleaning process for clothing and textiles using a solvent other than water. Clothes are instead soaked in a water-free liquid solvent. Perchloroethylene is the most commonly used solvent, although alternative solvents such as hydrocarbons, and supercritical CO2 are also used.

Varnish is a clear transparent hard protective coating or film. It is not to be confused with wood stain. It usually has a yellowish shade due to the manufacturing process and materials used, but it may also be pigmented as desired. It is sold commercially in various shades.

In metallurgy, a flux is a chemical reducing agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.

Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH3)2SO. This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a relatively high boiling point. DMSO is metabolised to compounds that leave a garlic-like taste in the mouth after DMSO is absorbed by skin.

Urinal deodorizer blocks are small disinfectant blocks or tablets that are added to urinals. As these products originally contained para-dichlorobenzene (pDCB) they may also be called para blocks. Besides disinfecting, the purpose of these materials is to deodorize restroom urinals. They are placed above the urinal drain, often in the confines of a small plastic device called a urinal screen that prevents loss down the drain when they dissolve down to a small size.

White spirit (AU, UK and Ireland) or mineral spirits (US, Canada), also known as mineral turpentine (AU/NZ/ZA), turpentine substitute, and petroleum spirits, is a petroleum-derived clear liquid used as a common organic solvent in painting. There are also terms for specific kinds of white spirit, including Stoddard solvent and solvent naphtha (petroleum). White spirit is often used as a paint thinner, or as a component thereof, though paint thinner is a broader category of solvent. Odorless mineral spirits (OMS) have been refined to remove the more toxic aromatic compounds, and are recommended for applications such as oil painting.

Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish removers. Methyl acetate is occasionally used as a solvent, being weakly polar and lipophilic, but its close relative ethyl acetate is a more common solvent being less toxic and less soluble in water. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or aqueous acids. Methyl acetate is not considered a VOC in the USA.

A primer or undercoat is a preparatory coating put on materials before painting. Priming ensures better adhesion of paint to the surface, increases paint durability, and provides additional protection for the material being painted.

Hot-melt adhesive (HMA), also known as hot glue, is a form of thermoplastic adhesive that is commonly sold as solid cylindrical sticks of various diameters designed to be applied using a hot glue gun. The gun uses a continuous-duty heating element to melt the plastic glue, which the user pushes through the gun either with a mechanical trigger mechanism on the gun, or with direct finger pressure. The glue squeezed out of the heated nozzle is initially hot enough to burn and even blister skin. The glue is sticky when hot, and solidifies in a few seconds to one minute. Hot-melt adhesives can also be applied by dipping or spraying, and are popular with hobbyists and crafters both for affixing and as an inexpensive alternative to resin casting.
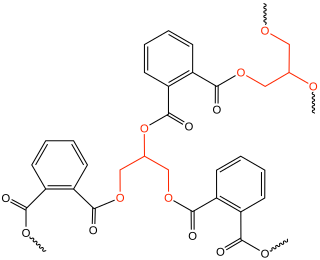
An alkyd is a polyester resin modified by the addition of fatty acids and other components. Alkyds are derived from polyols and organic acids including dicarboxylic acids or carboxylic acid anhydride and triglyceride oils. The term alkyd is a modification of the original name "alcid", reflecting the fact that they are derived from alcohol and organic acids. The inclusion of a fatty acid confers a tendency to form flexible coatings. Alkyds are used in paints, varnishes and in moulds for casting. They are the dominant resin or binder in most commercial oil-based coatings. Approximately 200,000 tons of alkyd resins are produced each year. The original alkyds were compounds of glycerol and phthalic acid sold under the name Glyptal. These were sold as substitutes for the darker-colored copal resins, thus creating alkyd varnishes that were much paler in colour. From these, the alkyds that are known today were developed.

Pressure-sensitive adhesive is a type of nonreactive adhesive which forms a bond when pressure is applied to bond the adhesive with a surface. No solvent, water, or heat is needed to activate the adhesive. It is used in pressure-sensitive tapes, labels, glue dots, stickers, sticky note pads, automobile trim, and a wide variety of other products.

Dimethoxymethane, also called methylal, is a colorless flammable liquid with a low boiling point, low viscosity and excellent dissolving power. It has a chloroform-like odor and a pungent taste. It is the dimethyl acetal of formaldehyde. Dimethoxymethane is soluble in three parts water and miscible with most common organic solvents.

Cellulose acetate phthalate (CAP), also known as cellacefate (INN) and cellulosi acetas phthalas, is a commonly used polymer phthalate in the formulation of pharmaceuticals, such as the enteric coating of tablets or capsules and for controlled release formulations. It is a cellulose polymer where about half of the hydroxyls are esterified with acetyls, a quarter are esterified with one or two carboxyls of a phthalic acid, and the remainder are unchanged. It is a hygroscopic white to off-white free-flowing powder, granules, or flakes. It is tasteless and odorless, though may have a weak odor of acetic acid. Its main use in pharmaceutics is with enteric formulations. It can be used together with other coating agents, e.g. ethyl cellulose. Cellulose acetate phthalate is commonly plasticized with diethyl phthalate, a hydrophobic compound, or triethyl citrate, a hydrophilic compound; other compatible plasticizers are various phthalates, triacetin, dibutyl tartrate, glycerol, propylene glycol, tripropionin, triacetin citrate, acetylated monoglycerides, etc.

Automotive paint is paint used on automobiles for both protective and decorative purposes. Water-based acrylic polyurethane enamel paint is currently the most widely used paint for reasons including reducing paint's environmental impact.

The environmental impact of paint can vary depending on the type of paint used and mitigation measures. Traditional painting materials and processes can have harmful effects on the environment, including those from the use of lead and other additives. Measures can be taken to reduce its environmental effects, including accurately estimating paint quantities so waste is minimized, and use of environmentally preferred paints, coating, painting accessories, and techniques.

Fabric treatments are processes that make fabric softer, or water resistant, or enhance dye penetration after they are woven. Fabric treatments get applied when the textile itself cannot add other properties. Treatments include, scrim, foam lamination, fabric protector or stain repellent, anti microbial and flame retardant.
Waterborne resins are sometimes called water-based resins. They are resins or polymeric resins that use water as the carrying medium as opposed to solvent or solvent-less. Resins are used in the production of coatings, adhesives, sealants, elastomers and composite materials. When the phrase waterborne resin is used, it usually describes all resins which have water as the main carrying solvent. The resin could be water-soluble, water reducible or water dispersed.


















