The inch is a unit of length in the British Imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to 1/36 yard or 1/12 of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth"), the word inch is also sometimes used to translate similar units in other measurement systems, usually understood as deriving from the width of the human thumb.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures evolved by 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

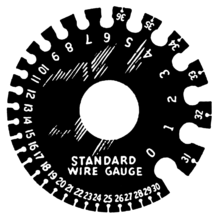
A wire is a flexible, round, bar of metal. Wires are commonly formed by drawing the metal through a hole in a die or draw plate. Wire gauges come in various standard sizes, as expressed in terms of a gauge number or cross-sectional area.

A micrometer, sometimes known as a micrometer screw gauge (MSG), is a device incorporating a calibrated screw widely used for accurate measurement of components in mechanical engineering and machining as well as most mechanical trades, along with other metrological instruments such as dial, vernier, and digital calipers. Micrometers are usually, but not always, in the form of calipers (opposing ends joined by a frame). The spindle is a very accurately machined screw and the object to be measured is placed between the spindle and the anvil. The spindle is moved by turning the ratchet knob or thimble until the object to be measured is lightly touched by both the spindle and the anvil.

In guns, particularly firearms, but not artillery, where a different definition may apply, caliber is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore matches that specification. It is measured in inches or in millimeters. In the United States it is expressed in hundredths of an inch; in the United Kingdom in thousandths; and elsewhere in millimeters. For example, a US "45 caliber" firearm has a barrel diameter of roughly 0.45 inches (11.43mm). Barrel diameters can also be expressed using metric dimensions. For example, a "9 mm pistol" has a barrel diameter of about 9 millimeters. Since metric and US customary units do not convert evenly at this scale, metric conversions of caliber measured in decimal inches are typically approximations of the precise specifications in non-metric units, and vice versa.

American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a logarithmic stepped standardized wire gauge system used since 1857, predominantly in North America, for the diameters of round, solid, nonferrous, electrically conducting wire. Dimensions of the wires are given in ASTM standard B 258. The cross-sectional area of each gauge is an important factor for determining its current-carrying capacity.
Resistance thermometers, also called resistance temperature detectors (RTDs), are sensors used to measure temperature. Many RTD elements consist of a length of fine wire wrapped around a heat-resistant ceramic or glass core but other constructions are also used. The RTD wire is a pure material, typically platinum (Pt), nickel (Ni), or copper (Cu). The material has an accurate resistance/temperature relationship which is used to provide an indication of temperature. As RTD elements are fragile, they are often housed in protective probes.

A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener.

A milliradian is an SI derived unit for angular measurement which is defined as a thousandth of a radian (0.001 radian). Milliradians are used in adjustment of firearm sights by adjusting the angle of the sight compared to the barrel. Milliradians are also used for comparing shot groupings, or to compare the difficulty of hitting different sized shooting targets at different distances. When using a scope with both mrad adjustment and a reticle with mrad markings, the shooter can use the reticle as a ruler to count the number of mrads a shot was off-target, which directly translates to the sight adjustment needed to hit the target with a follow-up shot. Optics with mrad markings in the reticle can also be used to make a range estimation of a known size target, or vice versa, to determine a target size if the distance is known, a practice called "milling".
Drill bits are the cutting tools of drilling machines. They can be made in any size to order, but standards organizations have defined sets of sizes that are produced routinely by drill bit manufacturers and stocked by distributors.

IEC 60228 is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)'s international standard on conductors of insulated cables. As of 2023 the current version is Third Edition 2004-11 Among other things, it defines a set of standard wire cross-sectional areas:

Wire gauge is a measurement of wire diameter. This determines the amount of electric current the wire can safely carry, as well as its electrical resistance and weight.

A sound level meter is used for acoustic measurements. It is commonly a hand-held instrument with a microphone. The best type of microphone for sound level meters is the condenser microphone, which combines precision with stability and reliability. The diaphragm of the microphone responds to changes in air pressure caused by sound waves. That is why the instrument is sometimes referred to as a sound pressure level meter (SPL). This movement of the diaphragm, i.e. the sound pressure, is converted into an electrical signal. While describing sound in terms of sound pressure, a logarithmic conversion is usually applied and the sound pressure level is stated instead, in decibels (dB), with 0 dB SPL equal to 20 micropascals.
British Standard Pipe (BSP) is a set of technical standards for screw threads that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipes and fittings by mating an external (male) thread with an internal (female) thread. It has been adopted as standard in plumbing and pipe fitting, except in North America, where NPT and related threads are used.

A circular mil is a unit of area, equal to the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil. It is equal to π/4 square mils or approximately 5.067×10−4 mm2. It is a unit intended for referring to the area of a wire with a circular cross section. As the definition of the unit contains π, it is easy to calculate area values in circular mils when the diameter in mils is known.
A thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) consists of a toughened outer sheath of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) thermoplastic, covering one or more individual annealed copper conductors, themselves insulated with PVC. This type of wiring is commonly used for residential and light commercial construction in many countries. The flat version of the cable, with two insulated conductors and an uninsulated earth conductor, is referred to as twin and earth. In mainland Europe, a round equivalent is more common.

A thousandth of an inch is a derived unit of length in a system of units using inches. Equal to 1⁄1000 of an inch, a thousandth is commonly called a thou or, particularly in North America, a mil.

Jewelry wire is wire, usually copper, brass, nickel, aluminium, silver, or gold, used in jewelry making.
The distinction between real value and nominal value occurs in many fields. From a philosophical viewpoint, nominal value represents an accepted condition, which is a goal or an approximation, as opposed to the real value, which is always present.
Body jewelry sizes express the thickness of an item of body jewelry, using one of several possible systems.