This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |
Wire gauge is a measurement of wire diameter. This determines the amount of electric current the wire can safely carry, as well as its electrical resistance and weight.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |

Wire gauge is a measurement of wire diameter. This determines the amount of electric current the wire can safely carry, as well as its electrical resistance and weight.
Wire gauges may be broadly divided into two groups, the empirical and the geometric. The first includes all the older gauge measurements, notably the Birmingham gauge (B.W.G. or Stubs) and the Lancashire. The origin of the B.W.G. is obscure. The numbers of wire were in common use earlier than 1735 when the measurements were officially defined. [1] It is believed that they originally were based on the series of drawn wires, No. 1 being the original rod, and succeeding numbers corresponding with each draw, so that No. 10, for example, would have passed ten times through the draw plate. But the Birmingham and the Lancashire gauges, the latter being based on an averaging of the dimensions collated from a large number of the former in the possession of Peter Stubs of Warrington (1756-1806), [2] have long held the leading position, and are still retained and used probably to a greater extent than the more recent geometrical gauges.

The first attempt to adopt a geometrical system was made by Messrs Brown & Sharpe in 1855. They established a regular progression of thirty-nine steps between the English sizes, No. 0000 (460 thou or about 12 mm) and No. 36 (5 mils or about 0.13 mm). Each diameter was multiplied by 0.890526 to give the next lower size. This is now the American wire gauge (AWG), and is prevalent in North America and used to some extent in over 65 countries, with a market share of about 30% of all power and control wires and cables. [3]
The Imperial Standard Wire Gauge, which was sanctioned by the British Board of Trade in 1884, was formulated by J. Latimer Clark. Following one of its recommendations, it differs from pre-existing gauges scarcely more than they differ among themselves, and is based on a rational system, the basis being the circular mil. No. 7/0, the largest size, is 0.50 inches (500 mils or 12.7 mm) in diameter (250 000 circular mils in cross-sectional area), and the smallest, No. 50, is 0.001 inches (1 mil or 25.4 μm) in diameter (1 circular mil [cross-sectional area] or 0.7854 millionths of a square inch). Between each step the diameter, or thickness, diminishes by 10.557%, and the area and weight diminish by ~ 20%.
None of the above systems of measurement is part of the metric system.
The current British Standard for metallic materials including wire is BS 6722:1986, which is a solely metric standard, superseding 3737:1964, which used the SWG system.
The IEC 60228, used in most parts of the world, defines standard wire sizes based on their cross-sectional areas as expressed in mm2. [3] Each wire size has to respect a maximum resistivity value. [3]
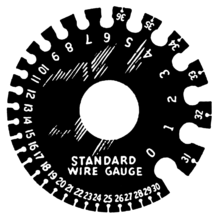
In commerce, the sizes of wire are estimated by devices, also called gauges, which consist of plates of circular or oblong form having notches of different widths around their edges to receive wire and sheet metals of different thicknesses. Each notch is stamped with a number, and the wire or sheet, which just fits a given notch, is stated to be of, say, No. 10, 11, 12, etc., of the wire gauge.
The circular forms of wire gauge measurement devices are the most popular, and are generally 3+3⁄4 inches (95 mm) in diameter, with thirty-six notches; many have the decimal equivalents of the sizes stamped on the back. Oblong plates are similarly notched. Rolling mill gauges are also oblong in form. Many gauges are made with a wedge-like slot into which the wire is thrust; one edge being graduated, the point at which the movement of the wire is arrested gives its size. The graduations are those of standard wire, or in thousandths of an inch. In some cases both edges are graduated differently in order to allow comparison between two systems of measurement. A few gauges are made with holes into which the wire has to be thrust. All gauges are hardened and ground to dimensions.
In some applications wire sizes are specified as the cross sectional area of the wire, usually in mm2. Advantages of this system include the ability to readily calculate the physical dimensions or weight of wire, ability to take account of non-circular wire, and ease of calculation of electrical properties.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures evolved by 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are noticeable differences between the systems.

In guns, particularly firearms, but not artillery, where a different definition may apply, caliber is the specified nominal internal diameter of the gun barrel bore – regardless of how or where the bore is measured and whether the finished bore matches that specification. It is measured in inches or in millimeters. In the United States it is expressed in hundredths of an inch; in the United Kingdom in thousandths; and elsewhere in millimeters. For example, a US "45 caliber" firearm has a barrel diameter of roughly 0.45 inches (11.43mm). Barrel diameters can also be expressed using metric dimensions. For example, a "9 mm pistol" has a barrel diameter of about 9 millimeters. Since metric and US customary units do not convert evenly at this scale, metric conversions of caliber measured in decimal inches are typically approximations of the precise specifications in non-metric units, and vice versa.
American Wire Gauge (AWG) is a logarithmic stepped standardized wire gauge system used since 1857, predominantly in North America, for the diameters of round, solid, nonferrous, electrically conducting wire. Dimensions of the wires are given in ASTM standard B 258. The cross-sectional area of each gauge is an important factor for determining its current-carrying capacity.

A screw thread is a helical structure used to convert between rotational and linear movement or force. A screw thread is a ridge wrapped around a cylinder or cone in the form of a helix, with the former being called a straight thread and the latter called a tapered thread. A screw thread is the essential feature of the screw as a simple machine and also as a threaded fastener.
Drill bits are the cutting tools of drilling machines. They can be made in any size to order, but standards organizations have defined sets of sizes that are produced routinely by drill bit manufacturers and stocked by distributors.

IEC 60228 is the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)'s international standard on conductors of insulated cables. As of 2023 the current version is Third Edition 2004-11 Among other things, it defines a set of standard wire cross-sectional areas:
Litz wire is a particular type of multistrand wire or cable used in electronics to carry alternating current (AC) at radio frequencies. The wire is designed to reduce the skin effect and proximity effect losses in conductors used at frequencies up to about 1 MHz.

Speaker wire is used to make the electrical connection between loudspeakers and audio amplifiers. Modern speaker wire consists of two or more electrical conductors individually insulated by plastic or, less commonly, rubber. The two wires are electrically identical, but are marked to identify the correct audio signal polarity. Most commonly, speaker wire comes in the form of zip cord.

Metrication in Canada began in 1970 and ceased in 1985. While Canada has converted to the metric system for many purposes, there is still significant use of non-metric units and standards in many sectors of the Canadian economy and everyday life. This is mainly due to historical ties with the United Kingdom, the traditional use of the imperial system of measurement in Canada, interdependent supply chains with the United States, and opposition to metrication during the transition period.
Ring size is a measurement used to denote the circumference of jewellery rings and smart rings.
British Standard Pipe (BSP) is a set of technical standards for screw threads that has been adopted internationally for interconnecting and sealing pipes and fittings by mating an external (male) thread with an internal (female) thread. It has been adopted as standard in plumbing and pipe fitting, except in North America, where NPT and related threads are used.

A circular mil is a unit of area, equal to the area of a circle with a diameter of one mil. It is equal to π/4 square mils or approximately 5.067×10−4 mm2. It is a unit intended for referring to the area of a wire with a circular cross section. As the definition of the unit contains π, it is easy to calculate area values in circular mils when the diameter in mils is known.
A thermoplastic-sheathed cable (TPS) consists of a toughened outer sheath of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) thermoplastic, covering one or more individual annealed copper conductors, themselves insulated with PVC. This type of wiring is commonly used for residential and light commercial construction in many countries. The flat version of the cable, with two insulated conductors and an uninsulated earth conductor, is referred to as twin and earth. In mainland Europe, a round equivalent is more common.

A thousandth of an inch is a derived unit of length in a system of units using inches. Equal to 1⁄1000 of an inch, a thousandth is commonly called a thou or, particularly in North America, a mil.

Jewelry wire is wire, usually copper, brass, nickel, aluminium, silver, or gold, used in jewelry making.
Wollaston wire is a very fine platinum wire clad in silver and used in electrical instruments. For most uses, the silver cladding is etched away by acid to expose the platinum core.

British Standard Wire Gauge is a unit for denoting wire size given by BS 3737:1964. It is also known as the Imperial Wire Gauge or British Standard Gauge. Use of SWG sizes has fallen greatly in popularity, but they are still used as a measure of thickness in guitar strings and some electrical wire. Cross sectional area in square millimetres is now the more usual size measurement for wires used in electrical installation cables. The current British Standard for metallic materials such as wire and sheet is BS 6722:1986, which is a solely metric standard.
The distinction between real value and nominal value occurs in many fields. From a philosophical viewpoint, nominal value represents an accepted condition, which is a goal or an approximation, as opposed to the real value, which is always present.
Body jewelry sizes express the thickness of an item of body jewelry, using one of several possible systems.

FASTON terminals or faston terminals are connectors that are widely used in electronic and electrical equipment. These terminals are manufactured by many companies, commonly using the terms "quick disconnect", "quick connect", "tab" terminals, "spade" terminals or blade connectors; without qualifiers, the first two could be mistaken for plumbing connections.