Stanley is an unincorporated community in northern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. [1] The community is on Oklahoma State Highway 2 seven miles southwest of Clayton. The Kiamichi River flows past the southeast side of the site. [2]

Stanley is an unincorporated community in northern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. [1] The community is on Oklahoma State Highway 2 seven miles southwest of Clayton. The Kiamichi River flows past the southeast side of the site. [2]

A United States Post Office was established at Stanley, Indian Territory on August 20, 1906, and was named for William Eugene Stanley (1844–1910), Governor of Kansas, 1899–1903, and member of the Dawes Commission to the Five Civilized Tribes, 1903–1904. He is buried in Highland Cemetery in Wichita, Kansas. The Dawes Commission was appointed by the U.S. Government to prepare the Choctaw Nation and its sister Five Civilized Tribes for statehood. [3]
During the 1880s the St. Louis-San Francisco Railway, more popularly known as the “Frisco”, built a line from north to south through the Choctaw Nation, connecting Fort Smith, Arkansas with Paris, Texas. The railroad paralleled the Kiamichi River throughout much of its route in present-day Pushmataha County, Oklahoma. Train stations were established every few miles to aid in opening up the land and, more particularly, to serve as the locations of section houses. Supervisors for their respective miles of track lived in the section houses to administer the track and its right-of-way. These stations also served as points at which the trains could draw water.
The site of Stanley was selected because of its proximity to the Kiamichi River, with its abundant water supply. Adjacent station stops were established to the north and south.
The sparsely populated area, at that time known as Jack’s Fork County, a part of the Pushmataha District of the Choctaw Nation, in the Indian Territory, [4] was home to Choctaw Indians who farmed or subsisted on the land.
Few roads or trails existed. Transportation was provided by the Frisco Railroad, which offered six trains per day—three in each direction—until it closed to passenger traffic during the late 1950s. It continued freight operations until 1981, when it closed altogether and its rails were removed. The loss of passenger rail coincided with the construction of Oklahoma State Highway 2.
Stanley is located in one of the most scenic places in Oklahoma. It is surrounded by the Kiamichi Mountains to its east and west, with summits to Stanley’s immediate west reaching 1,600 feet in elevation. The summits to Stanley’s east are lower. The relatively flat valley floor stretches to Stanley’s northeast and southwest. [5]

Pushmataha County is a county in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 10,812. Its county seat is Antlers.

Latimer County is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Oklahoma. Its county seat is Wilburton. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,444. The county was created at statehood in 1907 and named for James L. Latimer, a delegate from Wilburton to the 1906 state Constitutional Convention. Prior to statehood, it had been for several decades part of Gaines County, Sugar Loaf County, and Wade County in the Choctaw Nation.

Choctaw County is a county located in the U.S. state of Oklahoma. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,204. Its county seat is Hugo.

Hugo is a city in and the county seat of Choctaw County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located in southeastern Oklahoma, approximately 9 miles (14 km) north of the Texas state line. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 5,310.
Albion is a town in northeast Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States, approximately 2 miles (3.2 km) south of the Pushmataha-Latimer county line. The population was 106 at the 2010 census. When Albion was established, before Oklahoma became a state, the community was located in Wade County, Choctaw Nation, in what was then known as Indian Territory.

Antlers is a city in and the county seat of Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. The population was 2,453 at the 2010 census, a 3.9 percent decline from 2,552 in 2000. The town was named for a kind of tree that becomes festooned with antlers shed by deer, and is taken as a sign of the location of a spring frequented by deer.

The Kiamichi River is a river in southeastern Oklahoma, United States of America. A tributary of the Red River of the South, its headwaters rise on Pine Mountain in the Ouachita Mountains near the Arkansas border. From its source in Polk County, Arkansas, it flows approximately 177 miles (285 km) to its confluence with the Red River at Hugo, Oklahoma.

Tuskahoma is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in northern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States, four miles east of Clayton. It was the former seat of the Choctaw Nation government prior to Oklahoma statehood. The population at the 2010 census was 151.
Moyers is an unincorporated community located in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States.
Kosoma is a ghost town and former railroad station in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. It is located just off Oklahoma State Highway 2, approximately 10 miles (16 km) north of Antlers.
Kellond is an unincorporated community and former railroad station in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. Kellond is located approximately three miles northwest of Antlers on Oklahoma State Highway 2.
Dunbar is a community in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States, 17 miles north of Antlers.
Eubanks is a former community in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. It is 13 miles north of Antlers.
Honobia is an unincorporated community on the border between western LeFlore County and eastern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States, 15 miles southeast of Talihina.
Kiamichi is a former community in northern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. It is six miles east of Tuskahoma.
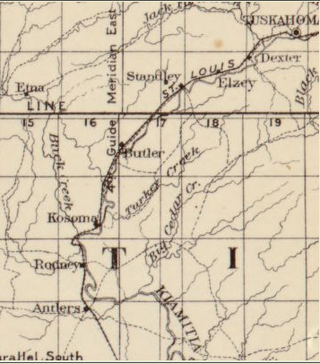
Rodney is a former community in Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States, five miles north of Antlers.
Sardis was a community in northern Pushmataha County, Oklahoma. United States. The location is six miles northwest of Clayton.
Hamden is an unincorporated community in northern Choctaw County, Oklahoma, United States. It is seven miles southeast of Antlers.
The Pushmataha County Historical Society is a historical society devoted to collecting and preserving the history of Pushmataha County, Oklahoma, United States. It is headquartered in the historic Frisco Depot in Antlers, Oklahoma, which it operates as a public museum.

Pushmataha County was a proposed political subdivision created by the Sequoyah Constitutional Convention. The convention, meeting in Muskogee, Indian Territory in 1905, established the political and administrative layout of a prospective U.S. state it called the State of Sequoyah.