
In biology and biochemistry, a lipid is a micro biomolecule that is soluble in nonpolar solvents. Non-polar solvents are typically hydrocarbons used to dissolve other naturally occurring hydrocarbon lipid molecules that do not dissolve in water, including fatty acids, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, and phospholipids.

Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main purposes of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism. In various diseases, such as type II diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cancer, normal metabolism is disrupted.
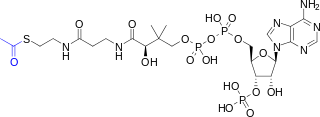
Acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production. Coenzyme A consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid (B5) through an amide linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. The acetyl group of acetyl-CoA is linked to the sulfhydryl substituent of the β-mercaptoethylamine group. This thioester linkage is a "high energy" bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).

Oleic acid is a fatty acid that occurs naturally in various animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is an odorless, colorless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 cis-9. It has the formula CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH. The name derives from the Latin word oleum, which means oil. It is the most common fatty acid in nature. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates.
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to produce malonyl-CoA through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase (BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes and in the chloroplasts of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm of most eukaryotes. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—ACACA and ACACB.
Lipogenesis is the conversion of fatty acid and glycerol into fats OR metabolic process through which acetyl-CoA is converted to triglyceride for storage in fat. The triglycerides in fat are packaged within cytoplasmic lipid droplets. The process Lipogenesis encompasses both fatty acid and triglyceride synthesis, with the latter being the process by which fatty acids are esterified to glycerol before being packaged into very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). Fatty acids are produced in the cytoplasm of cells by repeatedly adding two-carbon units to acetyl-CoA. Triacyglycerol synthesis on the other hand, occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane of cells by bonding three fatty acid molecules to a glycerol molecule. Both processes take place mainly in liver and adipose tissue. Nevertheless, it also occurs to some extent in other tissues such as the gut and kidney. A review on lipogenes in the brain was published in 2008 by Lopez and Vidal-Puig. After being packaged into VLDL in the liver, the resulting lipoprotein is then secreted directly into the blood for delivery to peripheral tissues.

Stearoyl-CoA desaturase (Δ-9-desaturase) is an endoplasmic reticulum enzyme that catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the formation of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), specifically oleate and palmitoleate from stearoyl-CoA and palmitoyl-CoA. Oleate and palmitoleate are major components of membrane phospholipids, cholesterol esters and alkyl-diacylglycerol. In humans, the enzyme is encoded by the SCD gene.
A fatty acid desaturase is an enzyme that removes two hydrogen atoms from a fatty acid, creating a carbon/carbon double bond. These desaturases are classified as:

Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase, long chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACADL gene.
The liver X receptor (LXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors and is closely related to nuclear receptors such as the PPARs, FXR and RXR. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are important regulators of cholesterol, fatty acid, and glucose homeostasis. LXRs were earlier classified as orphan nuclear receptors, however, upon discovery of endogenous oxysterols as ligands they were subsequently deorphanized.
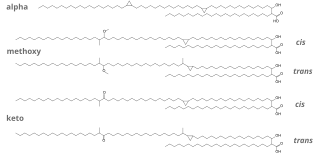
Cyclopropane fatty acids (CPA) are a subgroup of fatty acids that contain a cyclopropane group. Although they are usually rare, the seed oil from lychee contains nearly 40% CPAs in the form of triglycerides.
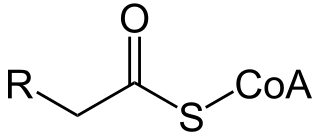
Acyl-CoA is a group of coenzymes that metabolize fatty acids. Acyl-CoA's are susceptible to beta oxidation, forming, ultimately, acetyl-CoA. The acetyl-CoA enters the citric acid cycle, eventually forming several equivalents of ATP. In this way, fats are converted to ATP, the universal biochemical energy carrier.
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine to form triglycerides, the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed. Phospholipids form the bulk of the lipid bilayers that make up cell membranes and surround the organelles within the cells

In enzymology, an acyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] desaturase (EC 1.14.19.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a linoleoyl-CoA desaturase (also Delta 6 desaturase, EC 1.14.19.3) is an enzyme that converts between types of fatty acids, which are essential nutrients in the human body. The enzyme mainly catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase (EC 1.14.19.1) is an enzyme used to produce the monounsaturated fatty acid oleic acid from the saturated fatty acid stearic acid. It catalyzes the chemical reaction

Fatty acid desaturase 2 (FADS2) is encoded by the FADS2 gene, the associated enzyme is sometimes known as FADS2 as well. Its main associated enzyme is Delta 6 desaturase (D6D) however the human enzyme been shown to also catalyze some delta-8 and delta-4 desaturases in spite of naming conventions.

Fatty acid desaturase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FADS1 gene.

Very long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SLC27A2 gene.

CYP4F22 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP4F22 gene.












