
A tricycle, sometimes abbreviated to trike, is a human-powered three-wheeled vehicle.

The Ackermann steering geometry is a geometric arrangement of linkages in the steering of a car or other vehicle designed to solve the problem of wheels on the inside and outside of a turn needing to trace out circles of different radii.

Steering is the control of the direction of motion or the components that enable its control. Steering is achieved through various arrangements, among them ailerons for airplanes, rudders for boats, cylic tilting of rotors for helicopters, and many more.

There have been many human powered vehicles designed and constructed specifically for transporting loads since their earliest appearance in the 20th century. They are referred to variously depending on the number of wheels — typically two, three, or four — and by their specific use. Adjectives used to describe the tasks to which the bicycles, dicycles, tricycles, or quadracycles are put include cargo cycles, freight cycles, box cycles, carrier cycles, and so on. Sometimes they are also called cycletrucks, which uses a sense of the word 'truck' predating the automobile.

Suspension is the system of tires, tire air, springs, shock absorbers and linkages that connects a vehicle to its wheels and allows relative motion between the two. Suspension systems must support both road holding/handling and ride quality, which are at odds with each other. The tuning of suspensions involves finding the right compromise. The suspension is crucial for maintaining consistent contact between the road wheel and the road surface, as all forces exerted on the vehicle by the road or ground are transmitted through the tires' contact patches. The suspension also protects the vehicle itself and any cargo or luggage from damage and wear. The design of front and rear suspension of a car may be different.

An anti-roll bar is an automobile suspension part that helps reduce the body roll of a vehicle during fast cornering or over road irregularities. It links opposite front or rear wheels to a torsion spring using short lever arms for anchors. This increases the suspension's roll stiffness—its resistance to roll in turns.
Power steering is a system for reducing a driver's effort to turn a steering wheel of a motor vehicle, by using a power source to assist steering.
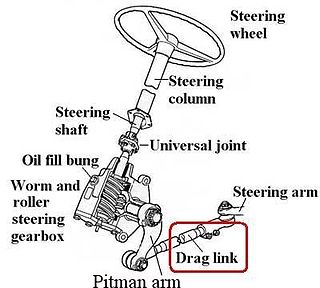
A drag link converts rotary motion from a crank arm, to a second bellcrank, usually in an automotive steering system.

A beam axle, rigid axle, or solid axle is a dependent suspension design in which a set of wheels is connected laterally by a single beam or shaft. Beam axles were once commonly used at the rear wheels of a vehicle, but historically, they have also been used as front axles in four-wheel-drive vehicles. In most automobiles, beam axles have been replaced with front (IFS) and rear independent suspensions (IRS).

Ford Model AA is a truck from Ford. As the Model T and TT became obsolete and needed to be replaced, Henry Ford began initial designs on the Model A and Model AA in 1926. Basic chassis layout was done rapidly and mechanical development was moved forward quickly. Body design and style was developed and then outsourced to various body manufacturers, including Briggs and Murray. The designs of the Model A shared parts and materials with the Model AA Ford, notably the body, engine and interior. The AA usually received plainer interiors than their car counterparts. The Model AA followed similar design changes to the Model A during the AA's four years in production, often delayed anywhere from three to nine months. The mechanical changes and upgrades were done during production of the vehicles. Body changes that occurred between 1929 and 1930 were also integrated into AA production, but leftover parts were used longer in the heavy commercial trucks.

In an automobile, ball joints are spherical bearings that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles, and are used on virtually every automobile made. They bionically resemble the ball-and-socket joints found in most tetrapod animals.
DIRAVI is the name given by Citroën to its proprietary power steering system, first seen in 1970.
The Chevrolet Engineering Research Vehicle (CERV) is a series of Chevrolet experimental cars. Chevrolet Staff engineer, designer, and race car driver Zora Arkus-Duntov started development of the CERV I in 1959, and began work on the CERV II in 1963. Chevrolet chief engineer Don Runkle and Lotus' Tony Rudd discussed creating a new show car to demonstrate their engineering expertise in 1985; It would become the CERV III. Corvette chief engineer Dave Hill unveiled the CERV IV in 1993, a test vehicle for the 1997 C5 Corvette.
A motorcycle's suspension serves a dual purpose: contributing to the vehicle's handling and braking, and providing safety and comfort by keeping the vehicle's passengers comfortably isolated from road noise, bumps and vibrations.

The rocker-bogie system is the suspension arrangement developed in 1988 for use in NASA's Mars rover Sojourner, and which has since become NASA's favored design for rovers. It has been used in the 2003 Mars Exploration Rover mission robots Spirit and Opportunity, on the 2012 Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission's rover Curiosity, the Mars 2020 rover Perseverance and ISRO's Chandrayaan-3 rover Pragyan in 2023.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to automobiles:

Bicycle suspension is the system, or systems, used to suspend the rider and bicycle in order to insulate them from the roughness of the terrain. Bicycle suspension is used primarily on mountain bikes, but is also common on hybrid bicycles.

A rowing cycle is a wheeled vehicle propelled by a rowing motion of the body. Steering, braking, and shifting are usually done by the handlebars. Feet are on symmetrical foot rests, as opposed to rotating pedals. Unlike many rowing boats, the rider faces forward. Rowing cycles exist in numerous designs, particularly with respect to frames and drive mechanisms. Commercial production numbers for rowing cycles are small compared to that of standard bicycles.

The Yamaha Niken is a 845 cc tilting three-wheeler motorcycle, manufactured since 2018 by Yamaha Motor and sold worldwide.














