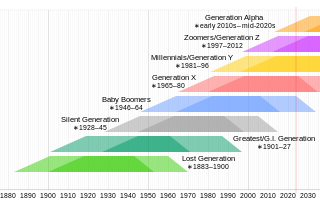
Generation X is the demographic cohort following the Baby Boomers and preceding Millennials. Researchers and popular media often use the mid-1960s as its starting birth years and the late 1970s as its ending birth years, with the generation being generally defined as people born from 1965 to 1980. By this definition and U.S. Census data, there are 65.2 million Gen Xers in the United States as of 2019. Most of Generation X are the children of the Silent Generation and early Baby Boomers; Xers are also often the parents of Millennials and Generation Z.

Millennials, also known as Generation Y, are the demographic cohort following Generation X and preceding Generation Z. Researchers and popular media use the early 1980s as starting birth years and the mid-1990s to early 2000s as ending birth years, with the generation typically being defined as people born from 1981 to 1996. Most Millennials are the children of Baby Boomers and older Generation X. In turn Millennials are often the parents of Generation Alpha.

Youth culture refers to the societal norms of children, adolescents, and young adults. Specifically, it comprises the processes and symbolic systems that are shared by the youth and are distinct from those of adults in the community.

The Elachistidae are a family of small moths in the superfamily Gelechioidea. Some authors lump about 3,300 species in eight subfamilies here, but this arrangement almost certainly results in a massively paraphyletic and completely unnatural assemblage, united merely by symplesiomorphies retained from the first gelechioid moths.
In Western culture the Boomerang Generation refers to the generation of young adults graduating high school and college in the 21st century. They are so named for the percentage of whom choose to share a home with their parents after previously living on their own—thus boomeranging back to their parents' residence. This arrangement can take many forms, ranging from situations that mirror the high dependency of pre-adulthood to highly independent, separate-household arrangements.

Generation Z, colloquially known as Zoomers, is the demographic cohort succeeding Millennials and preceding Generation Alpha. Researchers and popular media use the mid-to-late 1990s as starting birth years and the early 2010s as ending birth years. Most members of Generation Z are the children of Generation X or older Millennials.

Cunila origanoides, with the common names stone mint, frost mint, dittany, and American dittany, is a perennial late-summer-flowering subshrub with small purple flowers that is native to the central and eastern United States. It belongs to the Lamiaceae (mint) family and is the only species in the Cunila genus native to the United States. It grows in habitats such as dry forests and the thin soil around rock outcrops. This species has historically been cultivated for use as a medicinal herb, tea, and ornamental plant.
Intergenerationality is interaction between members of different generations. Sociologists study many intergenerational issues, including equity, conflict, and mobility.
The Strauss–Howe generational theory, devised by William Strauss and Neil Howe, describes a theorized recurring generation cycle in American history and Western history. According to the theory, historical events are associated with recurring generational personas (archetypes). Each generational persona unleashes a new era lasting around 21 years, in which a new social, political, and economic climate (mood) exists. They are part of a larger cyclical "saeculum". The theory states that a crisis recurs in American history after every saeculum, which is followed by a recovery (high). During this recovery, institutions and communitarian values are strong. Ultimately, succeeding generational archetypes attack and weaken institutions in the name of autonomy and individualism, which eventually creates a tumultuous political environment that ripens conditions for another crisis.

Stephensia is a genus of the small and very small moths of the family Elachistidae.
Stephensia armata is a Central American moth of the family Elachistidae and Gelechioidea superfamily, discovered in 1998 at Las Cuevas Research Station, in Belize's Chiquibul Forest Reserve.
Stephensia abbreviatella is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found in France, Germany, Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Austria, Romania and Turkey.

Stephensia brunnichella is a moth of the family Elachistidae found in Europe and east into the Palearctic.
Stephensia calpella is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found in Spain and North Africa.

Stephensia cedronellae is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found on the Canary Islands.
Stephensia staudingeri is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found on the island of Rhodes in Greece.
Stephensia unipunctella is a moth of the family Elachistidae. It is found in Spain.
Stephensia is the scientific name for two genera of organisms and may refer to:
Stephensia ussuriella is a moth in the family Elachistidae. It was described by Sinev in 1992. It is found in the Russian Far East.

mRNA-1283 is a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by Moderna.





