Related Research Articles

Entomology is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was vaguer, and historically the definition of entomology included the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. This wider meaning may still be encountered in informal use.

Mites are small arachnids.
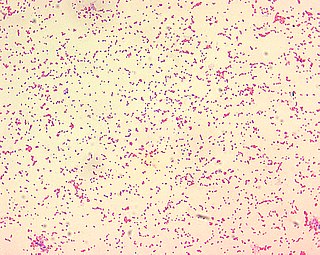
Brucellosis is a highly contagious zoonosis caused by ingestion of unpasteurized milk or undercooked meat from infected animals, or close contact with their secretions. It is also known as undulant fever, Malta fever, and Mediterranean fever.

Halictidae is the second-largest family of Anthophila bees. Halictid species occur all over the world and are usually dark-colored and often metallic in appearance. Several species are all or partly green and a few are red; a number of them have yellow markings, especially the males, which commonly have yellow faces, a pattern widespread among the various families of bees. The family is distinguished by the arcuate basal vein found on the wing.

The Arctiinae are a large and diverse subfamily of moths, with around 11,000 species found all over the world, including 6,000 neotropical species. This group includes the groups commonly known as tiger moths, which usually have bright colours, footmen, which are usually much drabber, lichen moths, and wasp moths. Many species have "hairy" caterpillars that are popularly known as woolly bears or woolly worms. The scientific name of this subfamily refers to this hairiness. Some species within the Arctiinae have the word tussock in their common name due to people misidentifying them as members of the Lymantriinae based on the characteristics of the larvae.

A leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family Cicadellidae. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and are covered with hairs that facilitate the spreading of a secretion over their bodies that acts as a water repellent and carrier of pheromones. They undergo a partial metamorphosis, and have various host associations, varying from very generalized to very specific. Some species have a cosmopolitan distribution, or occur throughout the temperate and tropical regions. Some are pests or vectors of plant viruses and phytoplasmas. The family is distributed all over the world, and constitutes the second-largest hemipteran family, with at least 20,000 described species.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Exhibition' is a selection made by the Patmore Nurseries from seeds of a tree at Brandon, Manitoba. Released in 1952, 'Exhibition' was propagated by grafting.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Lake City' was first described by Wyman in Trees Magazine 3 (4): 13, 1940.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Littleford' was cloned from a tree in Hinsdale, Illinois, circa 1915 and first released in 1927.
The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Ascendens' is a relatively old clone.

The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Aurea' was cloned from a tree discovered by F. L. Temple in Vermont at the end of the 19th century.
The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Beaverlodge' was selected as a seedling in 1925 at the Beaverlodge Experimental Farm, Morden, part of the Lacombe Research Centre, Alberta, for its hardiness and vigour, and released in 1954.

The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Columnaris' was propagated from a tree found by Mr John Dunbar at Conesus Lake, New York, before 1920. The tree should not be confused with U. americana var. columnarisRehder,J. Arnold Arbor. 3: 42, 1922.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Fiorei' was raised by the Charles Fiore Nurseries, Prairie View, Illinois, before 1956, but is no longer listed by the company.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Morden' was cloned from a selection made by the Dominion Experimental Farm, Morden, Manitoba, in 1939 on account of its ability to withstand severe ice storms without breakage.

The Phytoseiidae are a family of mites which feed on thrips and other mite species. They are often used as a biological control agent for managing mite pests. Because of their usefulness as biological control agents, interest in phytoseiids has steadily increased over the past century. In 1950, there were 34 known species. Today, there are 2,731 documented species.

Cavognathidae is a family of beetles, in the suborder Polyphaga. It contains a single genus, Taphropiestes Reitter 1875, with around a dozen species known from South America, Australia and New Zealand.

The Erebinae are a subfamily of moths in the family Erebidae erected by William Elford Leach in 1815. Erebine moths are found on all continents except Antarctica, but reach their greatest diversity in the tropics. While the exact number of species belonging to the Erebinae is not known, the subfamily is estimated to include around 10,000 species. Some well-known Erebinae include underwing moths (Catocala) and witch moths (Thermesiini). Many of the species in the subfamily have medium to large wingspans, up to nearly 30 cm in the white witch moth, which has the widest wingspan of all Lepidoptera. Erebine caterpillars feed on a broad range of plants; many species feed on grasses and legumes, and a few are pests of castor bean, sugarcane, rice, as well as pistachios and blackberries.
BugGuide is a website and online community of naturalists, both amateur and professional, who share observations of insects, spiders, and other related creatures. The website consists of informational guide pages and many thousands of photographs of arthropods from the United States and Canada which are used for identification and research. The non-commercial site is hosted by the Iowa State University Department of Entomology. BugGuide was conceived by photographer Troy Bartlett in 2003 and since 2006 has been maintained by Dr. John VanDyk, Adjunct Assistant Professor of Entomology and Senior Systems Analyst at Iowa State University. The website has been recognized for helping change public perception of insects.

Bactra bactrana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found on the Canary Islands, Sicily and Malta and in southern Spain, Portugal, southern Italy, France, Greece, Morocco, Algeria, Egypt, Asia Minor, Arabia, Iraq, Iran, the Caucasus, Afghanistan, the Caspian area, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Pakistan, India, the Republic of Congo, Madagascar, Sudan and Gambia.
References
- ↑ "New species featured in entomological journal". Times Of Malta. 2010-01-24. Retrieved 2010-01-24.
| | This article relating to the superfamily Tineoidea is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |