
The black-lyre leafroller moth is a tortrix moth species of the family Tortricidae.

Declana floccosa, the forest semilooper or manuka moth is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It was first described by Francis Walker in 1863 using specimens obtained from Colonel Bolton.

Archips semiferanus is a species of moth in the family Tortricidae, and one of several species of moth commonly known as oak leafroller or oak leaf roller. The larvae feed on the leaves of oak trees in the eastern United States and southeastern Canada and are a major defoliator of oak trees, which can lead to tree mortality. In Pennsylvania in the late 1960s and early 1970s, oak leafrollers defoliated over 1,045,000 acres (423,000 ha).

Stictea is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Olethreutinae of the family Tortricidae.

Planotortrix is a genus of moths belonging to the subfamily Tortricinae of the family Tortricidae.

The omnivorous leafroller is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Mexico and the United States.

Planotortrix excessana, the greenheaded leafroller, is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is native to New Zealand and is an introduced species in Hawaii. It is extremely variable in appearance and feeds on many native and introduced species. It is regarded as a pest of some agricultural and forestry crops.

Trigonospila brevifacies is a species of true fly in the family Tachinidae native to eastern Australia. This species is also found in New Zealand. Like the vast majority of tachinid flies, T. brevifacies is a parasitoid of other insects, specifically late larval stages of a number of species of Lepidoptera. It is also known as the Australian Leaf-Roller Fly or Leafroller Fly.

Stictea infensa is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is known from Australia, including Queensland and New South Wales. It is also found in New Zealand.

Planotortrix octo is a moth of the family Tortricidae. It is endemic to New Zealand, where it is found in both the North and South islands.
Archips asiaticus, the groundnut leafroller, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Russia (Siberia), Korea, Japan and China.
Archips fuscocupreanus, the exotic leafroller moth or apple tortrix, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in China, South Korea, Japan and Russia. It is an introduced species in the north-eastern United States, where it has been recorded from Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Jersey, New York and Rhode Island. It has also been recorded from Washington.
Choristoneura adumbratanus is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Japan, Korea and China.
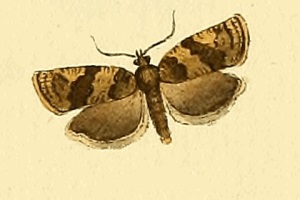
Choristoneura diversana is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Great Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, Austria, Switzerland, Italy, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Slovenia, Poland, Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Norway, Sweden, Finland, the Baltic region, Russia and the Near East. In the east, the range extends to China (Heilongjiang), Korea and Japan. The habitat consists of gardens, scrub and fens.

Choristoneura lafauryana, the strawberry leafroller, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in Spain, Great Britain, the Netherlands, Belgium, France, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Romania and Russia. In the east, the range extends to China, Korea and Japan.

Ctenopseustis fraterna, the brownheaded leafroller or the rusty ponga leaf-tyer, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in New Zealand, where it has been recorded from the North Island only. The common name is also used for the related species Ctenopseustis herana and Ctenopseustis obliquana.
Planotortrix puffini is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. Specimens have been collected from Lee Bay in Stewart Island.

Planotortrix notophaea, the blacklegged leafroller, is a species of moth in the family Tortricidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. It was also present near Sydney in Australia, but this population is thought to be extinct.

Epichorista emphanes, the beech leafroller, is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in New Zealand.
Stictea coriariae is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in China, Russia and Japan.
















