
The anus is an opening at the opposite end of an animal's digestive tract from the mouth. Its function is to control the expulsion of feces, unwanted semi-solid matter produced during digestion, which, depending on the type of animal, may include: matter which the animal cannot digest, such as bones; food material after all the nutrients have been extracted, for example cellulose or lignin; ingested matter which would be toxic if it remained in the digestive tract; and dead or excess gut bacteria and other endosymbionts.

Fellatio is an oral sex act involving the use of the mouth or throat, usually performed by a person on the penis of another person. If performed on oneself, the act is called autofellatio. Oral stimulation of the scrotum may also be termed fellatio, or colloquially as teabagging.

A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at various body openings such as the eyes, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lip, vagina, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated.

The palate is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separate. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior bony hard palate and the posterior fleshy soft palate.

Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is a common infection caused by a group of viruses. It typically begins with a fever and feeling generally unwell. This is followed a day or two later by flat discolored spots or bumps that may blister, on the hands, feet and mouth and occasionally buttocks and groin. Signs and symptoms normally appear 3–6 days after exposure to the virus. The rash generally resolves on its own in about a week. Fingernail and toenail loss may occur a few weeks later, but they will regrow with time.
The Mouth of Sauron is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He appears in The Lord of the Rings — specifically in the chapter "The Black Gate Opens" in the third volume, The Return of the King — as the chief emissary of Sauron.

A mouth ulcer is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause.

Smash Mouth is an American rock band from San Jose, California. The band was formed in 1994, and was originally composed of Steve Harwell, Kevin Coleman (drums), Greg Camp (guitar), and Paul De Lisle (bass). They are known for songs such as "Walkin' on the Sun" (1997), "All Star" (1999), "Then The Morning Comes" (1999), and a cover of The Monkees' "I'm a Believer" (2001).
Kuchisake-onna is a malevolent figure appearing in Japanese ghost stories, possibly dating back to the Edo period. She would ask people if she's pretty with a mask on. If they say yes, she would take the mask off and ask again. Whatever then you'll say, she'll slit your mouth with a If you say no, when she ask you if she's pretty, she'll kill you with a knife. But there are some ways to trick her; when she asks "am I pretty", say "so-so", "you're average" or throw candies.

"All Star" is a song by American rock band Smash Mouth. It was released on May 4, 1999, as the second single from their album Astro Lounge, and it is one of the group's most successful songs, peaking at No. 4 on the Billboard Hot 100.

A bit is a type of horse tack used in equestrian activities, usually made of metal, or a synthetic material. It is placed in the mouth of a horse and assists a rider in communicating with the animal. It extends from one side of the mouth across to the other and rests on the bars of the mouth, which are a region, between the incisors and the molars, where there are no teeth. It is held on a horse's head by means of a bridle and has reins attached for use by a rider.

Deuterostomes comprise a superphylum of animals. It is a sister clade of Protostomia, with which it forms the Nephrozoa clade.

Protostomia is a clade of animals. Together with the deuterostomes and xenacoelomorpha, its members make up the Bilateria, mostly comprising animals with bilateral symmetry and three germ layers. The major distinctions between deuterostomes and protostomes are found in embryonic development and is based on the embryological origins of the mouth and anus.

Foot-and-mouth disease or hoof-and-mouth disease is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever for between two and six days, followed by blisters inside the mouth and on the feet that may rupture and cause lameness.

A river mouth is the part of a river where the river debouches into another river, a lake, a reservoir, a sea, or an ocean.
Word-of-mouth marketing, also called word of mouth advertising, differs from naturally occurring word of mouth, in that it is actively influenced or encouraged by organizations. While it is difficult to truly control WOM, research has shown that there are three generic avenues to 'manage' WOM for the purpose of WOMM: 1.) Build a strong WOM foundation, 2.) Indirect WOMM management which implies that managers only have a moderate amount of control, 3.) Direct WOMM management, which has higher levels of control. Proconsumer WOM has been suggested as a counterweight to commercially motivated word of mouth.

In human anatomy, the mouth is the first portion of the alimentary canal that receives food and produces saliva. The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane epithelium lining the inside of the mouth.
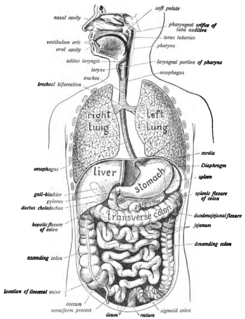
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion. Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has many stages. The first stage is the cephalic phase of digestion which begins with gastric secretions in response to the sight and smell of food. The next stage starts in the mouth.
Big Mouth is an American adult animated sitcom created by Nick Kroll, Andrew Goldberg, Mark Levin, and Jennifer Flackett featuring teens based on Kroll and Goldberg's upbringing in Westchester County, New York, with Kroll voicing his fictional self. The first season consisting of ten episodes premiered on Netflix on September 29, 2017, and the second season was released on October 5, 2018. In November 2018, Netflix announced that Big Mouth was renewed for a third season, which was preceded by a Valentine's Day special episode on February 8, 2019.














