| Streptoalloteichus tenebrarius | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Actinomycetota |
| Class: | Actinomycetia |
| Order: | Pseudonocardiales |
| Family: | Pseudonocardiaceae |
| Genus: | Streptoalloteichus |
| Species: | S. tenebrarius |
| Binomial name | |
| Streptoalloteichus tenebrarius (ex Higgins and Kastner, 1967) Tamura et al., 2008 | |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
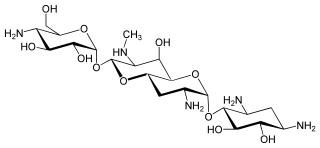
Streptoalloteichus tenebrarius is a bacterium that biosynthesizes the aminoglycoside antibiotics tobramycin and apramycin.