
Streptomyces is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of Streptomyces bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin.

Natamycin, also known as pimaricin, is an antifungal medication used to treat fungal infections around the eye. This includes infections of the eyelids, conjunctiva, and cornea. It is used as eyedrops. Natamycin is also used in the food industry as a preservative.
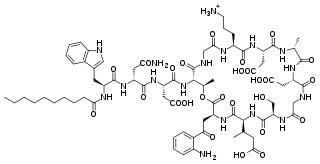
Daptomycin, sold under the brand name Cubicin among others, is a lipopeptide antibiotic used in the treatment of systemic and life-threatening infections caused by Gram-positive organisms.
An antimetabolite is a chemical that inhibits the use of a metabolite, which is another chemical that is part of normal metabolism. Such substances are often similar in structure to the metabolite that they interfere with, such as the antifolates that interfere with the use of folic acid; thus, competitive inhibition can occur, and the presence of antimetabolites can have toxic effects on cells, such as halting cell growth and cell division, so these compounds are used as chemotherapy for cancer.

The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus or Streptomyces lavendulae. They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usually refers to mitomycin C, its international nonproprietary name. Mitomycin C is used as a medicine for treating various disorders associated with the growth and spread of cells.

Mitomycin C is a mitomycin that is used as a chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity.

The Streptomycetaceae are a family of Actinomycetota, making up the monotypic order Streptomycetales. It includes the important genus Streptomyces. This was the original source of many antibiotics, namely streptomycin, the first antibiotic against tuberculosis.

Streptomyces hygroscopicus is a bacterial species in the genus Streptomyces. It was first described by Hans Laurits Jensen in 1931.
Streptomyces isolates have yielded the majority of human, animal, and agricultural antibiotics, as well as a number of fundamental chemotherapy medicines. Streptomyces is the largest antibiotic-producing genus of Actinomycetota, producing chemotherapy, antibacterial, antifungal, antiparasitic drugs, and immunosuppressants. Streptomyces isolates are typically initiated with the aerial hyphal formation from the mycelium.
Streptomyces albidoflavus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from Poland. Streptomyces albidoflavus produces dibutyl phthalate and streptothricins.
Streptomyces lavendulae is a species of bacteria from the genus Streptomyces. It is isolated from soils globally and is known for its production of medically useful biologically active metabolites. To see a photo of this organism click here.
The mitosenes are a class of organic chemicals based on a quinone-containing three-ring structure related to the two-ring core of the indolequinones. They are derived from the mitomycins by reduction and are the active alkylating agents responsible for the antitumor activity of the mitomycins.
Streptomyces michiganensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in the United States. Streptomyces michiganensis produces actinomycin X, antipain and mitomycin.
Streptomyces narbonensis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in France. Streptomyces narbonensis produces narbomycin and josamycin.
Cytochrome P450 family 107 subfamily G member 1 is an actinobacterial Cytochrome P450 enzyme originally from Streptomyces rapamycinicus, which catalyzes the oxidation reaction of C27 of pre-rapamycin in the biosynthesis pathway of the macrolide antibiotic rapamycin.
Cytochrome P450, family 105, also known as CYP105, is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family in bacteria, predominantly found in the phylum Actinomycetota and the order Actinomycetales. The first three genes and subfamilys identified in this family is the herbicide-inducible P-450SU1 and P-450SU2 from Streptomyces griseolus and choP from Streptomyces sp's cholesterol oxidase promoter region.
Cytochrome P450, family 107, also known as CYP107, is a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase family in bacteria, found to be conserved and highly populated in Streptomyces and Bacillus species. The first gene identified in this family is Cytochrome P450 eryF (CYP107A1) from Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Many enzymes of this family are involved in the synthesis of macrolide antibiotics. The members of this family are widely distributed in Alphaproteobacteria, cyanobacterial, Mycobacterium, Bacillota, and Streptomyces species, which may be due to horizontal gene transfer driven by selection pressure.
Vitamin D3 dihydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme purified from the actinobacterium Streptomyces griseolus, with EC number EC 1.14.15.22 and CYP Symbol CYP105A1, catalyses oxidation of cholecalciferol(vitamin D3) to calcitriol.
Cytochrome P450 family 154 subfamily C member 3 is an actinobacterial Cytochrome P450 enzyme originally from Streptomyces, which catalyzes the 16α-hydroxylation of various steroids.




