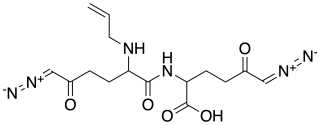
Alazopeptin is an antibiotic, with moderate anti-trypanosomal and antitumor activity. It was originally isolated from Streptacidiphilus griseoplanus, sourced from soil near Williamsburg, Iowa. It is also isolated from Kitasatospora azatica. It is still largely produced via fermentation broths of that organism. Structurally, alazopeptin is a tripeptide and contains 2 molecules of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine and one molecule of L-alanine. In 2021 the biosynthetic pathway of alazopeptin was elucidated.
Actinoalloteichus is a genus in the phylum Actinomycetota (Bacteria).
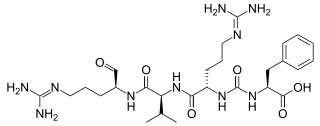
Antipain is an oligopeptide that is isolated from actinomycetes and used in biochemical research as a protease inhibitor of trypsin and papain. It was discovered in 1972 and was the first natural peptide found that contained an ureylene group. Antipain can aid in prevention of coagulation in blood. It is an inhibitor of serine and cysteine proteases.
Streptomyces albospinus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil from the Akita City in Japan. Streptomyces albospinus produces spinamycine, phenamide, phenelfamycin G and phenelfamycin H.
Streptomyces lavendulae is a species of bacteria from the genus Streptomyces. It is isolated from soils globally and is known for its production of medically useful biologically active metabolites. To see a photo of this organism click here.
Streptomyces flavotricini is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from mountain forest soil. Streptomyces flavotricini produces bafilomycin K and aminoacylase.
Streptomyces griseoaurantiacus is a thermotolerant bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which was isolated from marine sediment. Streptomyces griseoaurantiacus produces the antibiotics manumycin, diperamycin and chinikomycin, and griseolic acid.
Streptomyces griseoviridis is a filamentous bacterium species from the genus Streptomyces, which was isolated from soil in Texas, United States. Streptomyces griseoviridis produces etamycin, griseoviridin, bactobolin, prodigiosin R1, actinobolin, and rosophilin. Streptomyces griseoviridis can be used to protect plants since it inhibits the growth of fungal pathogens.
Streptomyces lydicus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil in the United States. Streptomyces lydicus produces actithiazic acid, natamycin, lydimycin, streptolydigin, and 1-deoxygalactonojirimycin. Streptomyces lydicus can be used as an agent against fungal plant pathogens like Fusarium, Pythium, Phytophthora, Rhizoctonia and Verticillum.
Nocardiopsis nikkonensis is a bacterium from the genus of Nocardiopsis which has been isolated from compost soil in Nikko in Japan.
Nocardioides iriomotensis is a Gram-positive, aerobic, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus Nocardioides which has been isolated from forest soil from Okinawa, Japan.
Streptomyces hyaluromycini is a Gram-positive bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from the tunicate Molgula manhattensis from the Tokyo Bay on Japan.
Streptomyces oryzae is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from the stem of a rice plant Oryza sativa.
Sphaerisporangium is a Gram-positive genus of bacteria from the family of Streptosporangiaceae.
Butyrolactol A is an organic chemical compound of interest for its potential use as an antifungal antibiotic.
Demequina mangrovi is a Gram-positive bacterium from the genus Demequina which has been isolated from rhizospheric soil of the mangrove plant Bruguiera gymnorhiza.
Angustibacter luteus is a bacterium from the genus of Angustibacter which has been isolated from subarctic forest soil.
Angustibacter is a genus of bacteria from the family Kineosporiaceae.
Streptomyces abyssomicinicus is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from rock soil. Streptomyces abyssomicinicus produces abyssomicin.
Lydicamycin is an organic compound with the molecular formula C47H74N4O10. Lydicamycin is an antibiotic with activity against Gram-positive bacteria. The bacteria Streptomyces lydicamycinicus and Streptomyces platensis produces lydicamycin.

