
Armadillos are New World placental mammals in the order Cingulata. The Chlamyphoridae and Dasypodidae are the only surviving families in the order, which is part of the superorder Xenarthra, along with the anteaters and sloths. Nine extinct genera and 21 extant species of armadillo have been described, some of which are distinguished by the number of bands on their armor. All species are native to the Americas, where they inhabit a variety of different environments.

Xenarthra is a major clade of placental mammals unique to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and armadillos. Extinct xenarthrans are the glyptodonts, the ground sloths, and the aquatic sloths. Xenarthrans originated in South America during the Paleocene about 59 million years ago. They evolved and diversified extensively in South America during the continent's long period of isolation in the early to mid Cenozoic Era. They spread to the Antilles by the early Miocene and, starting about 3 Mya, spread to Central and North America as part of the Great American Interchange. Nearly all of the formerly abundant megafaunal xenarthrans became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene.
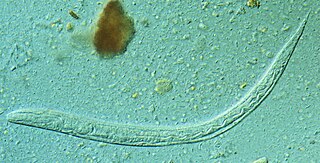
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.

Tunga penetrans is a parasitic insect found in most tropical and sub-tropical climates. Jiggers are often confused with chiggers - a type of mite. Jiggers are native to Central and South America, and have been inadvertently introduced by humans to sub-Saharan Africa.

The nine-banded armadillo, or the nine-banded, long-nosed armadillo, is a medium-sized mammal found in North, Central, and South America, making it the most widespread of the armadillos. Its ancestors originated in South America, and remained there until the formation of the Isthmus of Panama allowed them to enter North America as part of the Great American Interchange. The nine-banded armadillo is a solitary, mainly nocturnal animal, found in many kinds of habitats, from mature and secondary rainforests to grassland and dry scrub. It is an insectivore, feeding chiefly on ants, termites, and other small invertebrates. The armadillo can jump 3–4 ft (91–122 cm) straight in the air if sufficiently frightened, making it a particular danger on roads. It is the state small mammal of Texas.

Panstrogylus geniculatus is a blood-sucking sylvatic insect noted as a putative vector of minor importance in the transmission of Trypanosoma cruzi to humans; this is a parasite, which causes Chagas disease. The insect is described as sylvatic; subsisting primarily in humid forests, and is also known to inhabit vertebrate nesting places such as those of the armadillo, and is also involved in enzootic transmission of T. cruzi to those species. It has wide distribution throughout 16 Latin American countries.

Dasypus bellus, the beautiful armadillo, is an extinct armadillo species endemic to North America and South America from the Pleistocene, living from 1.8 mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 1.789 million years .

Dasypus is the only extant genus in the family Dasypodidae. Its species are known as long-nosed or naked-tailed armadillos. They are found in South, Central, and North America, as well as on the Caribbean islands of Grenada, Trinidad and Tobago. Members of Dasypus are solitary and primarily nocturnal to avoid temperature extremes and predation. They exist in numerous habitats ranging from brush to grassland areas and are mainly insectivorous.
Angiostoma is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the family Angiostomatidae.
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus is a species of nematode from the family Metastrongylidae.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.
Strongyloides lutrae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the otter, Lutra canadensis. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides ardeae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of yellow-crowned night heron, Nyctanassa violacea, and eastern green heron, Butorides virescens. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides physali is a parasitic roundworm infecting the large intestine of the Gulf Coast toad. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides serpentis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the intestine of the green water snake, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides gulae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the esophagus of the green water snake, as well as eight other species of snakes. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides procyonis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the raccoon, Procyon lotor, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana. It is morphologically similar to S. stercoralis, and as such infections of S. procyonis in humans, dogs, and other animals might be mistaken for the former.

Cucullanus is a genus of parasitic nematodes. The genus includes more than 100 species.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialised on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.










