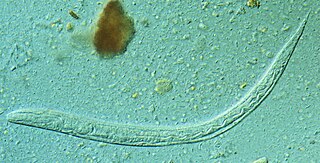
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.
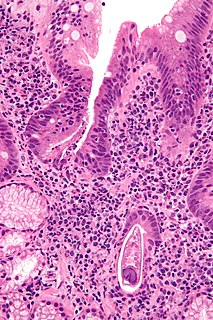
Strongyloidiasis is a human parasitic disease caused by the nematode called Strongyloides stercoralis, or sometimes S. fülleborni which is a type of helminth. It belongs to a group of nematodes called roundworms. This intestinal worm can cause a number of symptoms in people, principally skin symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea and weight loss, among many other specific and vague symptoms in disseminated disease, and severe life-threatening conditions through hyperinfection. In some people, particularly those who require corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medication, Strongyloides can cause a hyperinfection syndrome that can lead to death if untreated. The diagnosis is made by blood and stool tests. The medication ivermectin is widely used to treat strongyloidiasis.
Acanthocheilonema is a genus within the family Onchocercidae which comprises mainly tropical parasitic worms. Cobbold created the genus Acanthocheilonema with only one species, Acanthocheilonema dracunculoides, which was collected from aardwolf in the region of South Africa in the nineteenth century. These parasites have a wide range of mammalian species as hosts, including members of Carnivora, Macroscelidea, Rodentia, Pholidota, Edentata, and Marsupialia. Many species among several genera of filarioids exhibit a high degree of endemicity in studies done on mammalian species in Japan. However, no concrete evidence has confirmed any endemic species in the genus Acanthocheilonema.
The soil-transmitted helminths are a group of intestinal parasites belonging to the phylum Nematoda that are transmitted primarily through contaminated soil. They are so called because they have a direct life cycle which requires no intermediate hosts or vectors, and the parasitic infection occurs through faecal contamination of soil, foodstuffs and water supplies. The adult forms are essentially parasites of humans, causing soil-transmitted helminthiasis (STH), but also infect domesticated mammals. The juveniles are the infective forms and they undergo tissue-migratory stages during which they invade vital organs such as lungs and liver. Thus the disease manifestations can be both local and systemic. The geohelminths together present an enormous infection burden on humanity, amounting to 135,000 deaths every year, and persistent infection of more than two billion people.

The pinworm, also known as threadworm or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. The medical condition associated with pinworm infestation is known as pinworm infection (enterobiasis) or less precisely as oxyuriasis in reference to the family Oxyuridae.
Angiostoma is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the family Angiostomatidae.
Aelurostrongylus abstrusus is a species of nematode from the family Metastrongylidae.

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.
Trichinella papuae is a nematode parasite responsible for a zoonotic disease called trichinellosis, predominantly in Thailand. Currently, eight species of Trichinella are known.
Strongyloides lutrae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the otter, Lutra canadensis. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides dasypodis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the large intestine of the armadillo, Dasypus novemcinctus. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides ardeae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of yellow-crowned night heron, Nyctanassa violacea, and eastern green heron, Butorides virescens. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides serpentis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the intestine of the green water snake, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides gulae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the esophagus of the green water snake, as well as eight other species of snakes. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides procyonis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the raccoon, Procyon lotor, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana. It is morphologically similar to S. stercoralis, and as such infections of S. procyonis in humans, dogs, and other animals might be mistaken for the former.
Carcinogenic parasite is a parasitic organism which depends on other organisms for their survival, and cause cancer in such hosts. Medically-proven carcinogenic parasites are three species of flukes (trematodes), namely the urinary blood fluke, the Southeast Asian liver fluke and the Chinese liver fluke. S. haematobium is prevalent in Africa and the Middle East, and is the leading cause of bladder cancer. O. viverrini and C. sinensis are both found in eastern and southeastern Asia, and are responsible for cholangiocarcinoma. The International Agency for Research on Cancer declared them in 2009 as a Group 1 biological carcinogens in humans.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialised on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.

Jean-Lou Justine, French parasitologist and zoologist, is a professor at the National Museum of Natural History in Paris, France, and a specialist of fish parasites and invasive land planarians.

Hysterothylacium is a genus of parasitic roundworms in the family Raphidascarididae. As of 2020 it consists of over 70 species and is considered one of the largest of the ascaridoid genera parasitising fish.






