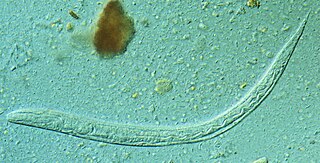
Strongyloides stercoralis is a human pathogenic parasitic roundworm causing the disease strongyloidiasis. Its common name in the US is threadworm. In the UK and Australia, however, the term threadworm can also refer to nematodes of the genus Enterobius, otherwise known as pinworms.
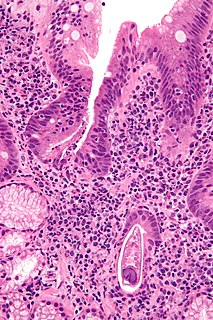
Strongyloidiasis is a human parasitic disease caused by the nematode called Strongyloides stercoralis, or sometimes the closely related S. fülleborni. These helminths belong to a group of nematodes called roundworms. These intestinal worms can cause a number of symptoms in people, principally skin symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea and weight loss, but also many other specific and vague symptoms in disseminated disease, and severe life-threatening conditions through hyperinfection. In some people, particularly those who require corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medication, Strongyloides can cause a hyperinfection syndrome that can lead to death if untreated. The diagnosis is made by blood and stool tests. The medication ivermectin is widely used to treat strongyloidiasis.
Cylicocyclus nassatus is a very common species of cyathostomin, which are important intestinal parasites of horses. Cyathostomins, including C. nassatus, are nematodes.

The pinworm, also known as threadworm or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. The medical condition associated with pinworm infestation is known as pinworm infection (enterobiasis) or less precisely as oxyuriasis in reference to the family Oxyuridae.
Angiostoma is a genus of parasitic nematodes in the family Angiostomatidae.

Mabel Josephine (Jo) Mackerras was an Australian zoologist, entomologist and parasitologist. Her research and life’s work contributed to entomology, veterinary medicine and medical science. Throughout her life she held a wide range of positions and duties that included Army medical officer, entomologist, medical scientist, and parasitologist. Mackerras was a major during WWII and served in the Army Malaria Research Unit. In an application for King’s Birthday Honours her work earned the citation,: "few women can have made a greater contribution to the Allied war effort".

Huffmanela is a genus of parasitic nematodes, belonging to the family Trichosomoididae.
Paratrichodorus is a genus of terrestrial root feeding (stubby-root) nematodes in the Trichodoridae family (trichorids), being one of five genera. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors. The females are didelphic, and are distributed worldwide.
Trichodoridae is a family of terrestrial root feeding nematodes, being one of two that constitute suborder Triplonchida. They are economically important plant parasites and virus vectors.
Strongyloides lutrae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the otter, Lutra canadensis. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides dasypodis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the large intestine of the armadillo, Dasypus novemcinctus. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides ardeae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of yellow-crowned night heron, Nyctanassa violacea, and eastern green heron, Butorides virescens. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides physali is a parasitic roundworm infecting the large intestine of the Gulf Coast toad. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides gulae is a parasitic roundworm infecting the esophagus of the green water snake, as well as eight other species of snakes. It was first described from Louisiana.
Strongyloides procyonis is a parasitic roundworm infecting the small intestine of the raccoon, Procyon lotor, hence its name. It was first described from Louisiana. It is morphologically similar to S. stercoralis, and as such infections of S. procyonis in humans, dogs, and other animals might be mistaken for the former.
Pterygodermatites peromysci is an intestinal parasitic nematode in the genus Pterygodermatites of the family Rictulariidae.

František Moravec is a Czech parasitologist who specialised on the Nematodes, especially the nematodes parasites of fishes. His research was mainly in the field of taxonomy of the Nematoda.

Hysterothylacium is a genus of parasitic roundworms in the family Raphidascarididae. As of 2020 it consists of over 70 species and is considered one of the largest of the ascaridoid genera parasitising fish.
Cryptosporidium serpentis is a protozoal parasite that infects the gastrointestinal tract of snakes. Sporated oocysts of C. serpentis are intermittently shed in the feces, and transmission is primarily via fecal-oral route. C. serpentis is a gastric parasite, primarily colonizing the stomach. Unlike mammalian Cryptosporidium - that is usually self-limiting - C. serpentis remains chronic and in most cases, eventually lethal in snakes. Cryptosporidiosis infection has been documented in a variety of snake species worldwide, such as North American Corn snakes and Australian Taipans, both free-living and captive. Necropsy examinations of expired captive snakes infected with C. serpentis note characteristic gastric mucosal hypertrophy that, in time, narrows the gastric lumen, resulting in classic symptoms of repetitive regurgitation and anorexia. Due to the enlargement of the stomach lining, a noticeable midbody bulge can be palpable and commonly visible. Frequent mucoid stools have been reported. However, some snakes will display no external symptoms at all throughout their lifetime, yet still remain infectious to counterparts.






